Related Research Articles

Electronic mail is a method of transmitting and receiving messages using electronic devices. It was conceived in the late–20th century as the digital version of, or counterpart to, mail. Email is a ubiquitous and very widely used communication medium; in current use, an email address is often treated as a basic and necessary part of many processes in business, commerce, government, education, entertainment, and other spheres of daily life in most countries.
In computing, the Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP) is an Internet standard protocol used by email clients to retrieve email messages from a mail server over a TCP/IP connection. IMAP is defined by RFC 9051.
Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions (MIME) is an Internet standard that extends the format of email messages to support text in character sets other than ASCII, as well as attachments of audio, video, images, and application programs. Message bodies may consist of multiple parts, and header information may be specified in non-ASCII character sets. Email messages with MIME formatting are typically transmitted with standard protocols, such as the Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP), the Post Office Protocol (POP), and the Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP).
The Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) is an Internet standard communication protocol for electronic mail transmission. Mail servers and other message transfer agents use SMTP to send and receive mail messages. User-level email clients typically use SMTP only for sending messages to a mail server for relaying, and typically submit outgoing email to the mail server on port 587 or 465 per RFC 8314. For retrieving messages, IMAP is standard, but proprietary servers also often implement proprietary protocols, e.g., Exchange ActiveSync.
8-bit clean is an attribute of computer systems, communication channels, and other devices and software, that process 8-bit character encodings without treating any byte as an in-band control code.
An email address identifies an email box to which messages are delivered. While early messaging systems used a variety of formats for addressing, today, email addresses follow a set of specific rules originally standardized by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) in the 1980s, and updated by RFC 5322 and 6854. The term email address in this article refers to just the addr-spec in Section 3.4 of RFC 5322. The RFC defines address more broadly as either a mailbox or group. A mailbox value can be either a name-addr, which contains a display-name and addr-spec, or the more common addr-spec alone.
S/MIME is a standard for public-key encryption and signing of MIME data. S/MIME is on an IETF standards track and defined in a number of documents, most importantly RFC 8551. It was originally developed by RSA Data Security, and the original specification used the IETF MIME specification with the de facto industry standard PKCS #7 secure message format. Change control to S/MIME has since been vested in the IETF, and the specification is now layered on Cryptographic Message Syntax (CMS), an IETF specification that is identical in most respects with PKCS #7. S/MIME functionality is built into the majority of modern email software and interoperates between them. Since it is built on CMS, MIME can also hold an advanced digital signature.
Email authentication, or validation, is a collection of techniques aimed at providing verifiable information about the origin of email messages by validating the domain ownership of any message transfer agents (MTA) who participated in transferring and possibly modifying a message.
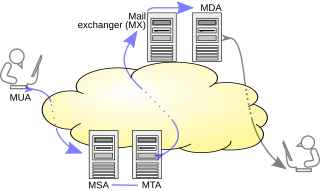
A message submission agent (MSA), or mail submission agent, is a computer program or software agent that receives electronic mail messages from a mail user agent (MUA) and cooperates with a mail transfer agent (MTA) for delivery of the mail. It uses ESMTP, a variant of the Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP), as specified in RFC 6409.
Many email clients now offer some support for Unicode. Some clients will automatically choose between a legacy encoding and Unicode depending on the mail's content, either automatically or when the user requests it.
Sieve is a programming language that can be used for email filtering. It owes its creation to the CMU Cyrus Project, creators of Cyrus IMAP server.
Nathaniel S. Borenstein is an American computer scientist. He is one of the original designers of the MIME protocol for formatting multimedia Internet electronic mail and sent the first e-mail attachment.
DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM) is an email authentication method designed to detect forged sender addresses in email, a technique often used in phishing and email spam.
A media type is a two-part identifier for file formats and format contents transmitted on the Internet. Their purpose is somewhat similar to file extensions in that they identify the intended data format. The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) is the official authority for the standardization and publication of these classifications. Media types were originally defined in Request for Comments RFC 2045 (MIME) Part One: Format of Internet Message Bodies in November 1996 as a part of the MIME specification, for denoting type of email message content and attachments; hence the original name, MIME type. Media types are also used by other internet protocols such as HTTP and document file formats such as HTML, for similar purposes.
Einar A. Stefferud (Stef) was a computer researcher and entrepreneur, who made many significant contributions to the development of the Internet, particularly in the areas of IETF RFCs and standards, secure online payment systems, DNS, and secure email. Stefferud was one of the original designers of the MIME protocol for sending multimedia Internet electronic mail.
International email arises from the combined provision of internationalized domain names (IDN) and email address internationalization (EAI). The result is email that contains international characters, encoded as UTF-8, in the email header and in supporting mail transfer protocols. The most significant aspect of this is the allowance of email addresses in most of the world's writing systems, at both interface and transport levels.
A mailbox is the destination to which electronic mail messages are delivered. It is the equivalent of a letter box in the postal system.

Barry Leiba is a computer scientist and software researcher. He retired from IBM's Thomas J. Watson Research Center in Hawthorne, New York in February 2009, and now works for FutureWei Technologies as a Director of Internet Standards. His work has focused for many years on electronic mail and anti-spam technology, on mobile computing and the Internet of things, and on Internet standards.
A mailbox provider, mail service provider or, somewhat improperly, email service provider is a provider of email hosting. It implements email servers to send, receive, accept, and store email for other organizations or end users, on their behalf.
The JSON Meta Application Protocol (JMAP) is a set of related open Internet Standard protocols for handling email. JMAP is implemented using JSON APIs over HTTP and has been developed as an alternative to IMAP/SMTP and proprietary email APIs such as Gmail and Outlook. Additional protocols and data models being built on top of the core of JMAP for handling contacts and calendar synchronization are meant to be potential replacements for CardDAV and CalDAV, and other support is currently in the works.
References
- ↑ "Networksorcery - Freed, Ned" . Retrieved 2009-09-14.
- ↑ Dave Crocker (24 May 2022). "Ned Freed". ietf-smtp (Mailing list). Retrieved 28 May 2022.
- ↑ "Profile for Ned Freed".