
Peñuelas is a town and municipality in Puerto Rico located in the Peñuelas Valley on the southern coast of the island, south of Adjuntas, east of Guayanilla, west of Ponce and north of the Caribbean Sea. Peñuelas is spread over 12 barrios and Peñuelas Pueblo. It is part of the Yauco Metropolitan Statistical Area. Peñuelas is known as "La Capital del Güiro" and "El Valle de los Flamboyanes". In 2020, Peñuelas had a population of 20,399.
The Cerro Maravilla murders, also known as the Cerro Maravilla massacre, occurred on July 25, 1978, at Cerro Maravilla, a mountain in Ponce, Puerto Rico, wherein two young Puerto Rican pro-independence activists, Carlos Enrique Soto-Arriví (1959–1978) and Arnaldo Darío Rosado-Torres (1953–1978), were murdered in a Puerto Rico Police ambush. The event sparked a series of political controversies where, in the end, the police officers were found guilty of murder and several high-ranking local government officials were accused of planning and/or covering up the incident.

The Nationalist Party of Puerto Rico is a Puerto Rican political party founded on September 17, 1922, in San Juan, Puerto Rico. Its primary goal is to work for Puerto Rico's independence. The Party's selection in 1930 of Pedro Albizu Campos as its president brought a radical change to the organization and its tactics.

The Senate of Puerto Rico is the upper house of the Legislative Assembly of Puerto Rico, the territorial legislature of Puerto Rico. The Senate, together with the House of Representatives of Puerto Rico, control the legislative branch of the government of Puerto Rico.

Blanca Canales was an educator and a Puerto Rican Nationalist. Canales joined the Puerto Rican Nationalist Party in 1931 and helped organize the Daughters of Freedom, the women's branch of the Puerto Rican Nationalist Party.

The Jayuya Uprising, also known as Jayuya Revolt or Cry of Jayuya, was a Nationalist insurrection that took place on October 30, 1950, in the town of Jayuya, Puerto Rico. The insurrection, led by Blanca Canales, was one of the multiple insurrections that occurred throughout Puerto Rico on that day against the Puerto Rican government supported by the United States. The insurrectionists were opposed to US sovereignty over Puerto Rico.

The Río Piedras massacre occurred on October 24, 1935, at the University of Puerto Rico in Río Piedras. Puerto Rico Police officers confronted and opened fire on supporters of the Puerto Rican Nationalist Party. Four Nationalist Party members were killed, and one police officer was wounded during the shooting.

The Rafael Cordero Santiago Port of the Americas —Spanish: Puerto de las Américas Rafael Cordero Santiago (PLA)— is a megaport currently under construction in Ponce, Puerto Rico. The project aims to convert the current Port of Ponce into a value-added tax-free customs-free international shipping hub similar to, though not as large as, the megaports located in Singapore and Rotterdam. The Port of the Americas is Puerto Rico's main Caribbean port, and, at a depth of 50 feet, it is also the deepest port in the Caribbean.

The Puerto Rico Police, officially the Puerto Rico Police Bureau, is a law enforcement agency with jurisdiction over the entire Commonwealth of Puerto Rico. It is a division of the Puerto Rico Department of Public Safety, alongside the Puerto Rico Special Investigations Bureau and the Puerto Rico Municipal Police and handles both traffic and criminal law enforcement in the commonwealth. As of 2020, the Puerto Rico Police force had 11,532 members. It is organized into thirteen regions within the island for operational purposes. Its headquarters are located at 601 Franklin D. Roosevelt Avenue in San Juan.

The Utuado uprising, also known as the Utuado revolt or El Grito de Utuado, refers to the revolt against the United States government in Puerto Rico which occurred on October 30, 1950, in the town of Utuado. There were simultaneous revolts in various other towns in Puerto Rico, including the capital of San Juan and the cities of Mayaguez and Arecibo, plus major confrontations in the city of Ponce and the towns of Peñuelas and Jayuya.

The San Juan Nationalist revolt was one of many uprisings against United States Government rule which occurred in Puerto Rico on October 30, 1950 during the Puerto Rican Nationalist Party revolts. Amongst the uprising's main objectives were an attack on La Fortaleza, and the U.S. Federal Court House Building in Old San Juan.

The Puerto Rican Nationalist Party insurgency was a series of coordinated insurrections for the secession of Puerto Rico led by the president of the Puerto Rican Nationalist Party, Don Pedro Albizu Campos, against the United States government's rule over the islands of Puerto Rico. The party repudiated the "Free Associated State" status that had been enacted in 1950 and which the Nationalists considered a continuation of colonialism.

Puerto Rico Highway 132 (PR-132) is a secondary highway that connects the town of Guayanilla to the city of Ponce, Puerto Rico. The road runs through the town of Peñuelas before reaching Ponce. In Ponce, PR-132 starts where Calle Villa ends.
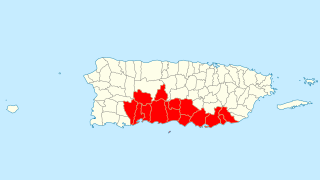
Porta Caribe is a tourism region in southern Puerto Rico. It was established in 2003 by the Puerto Rico Tourism Company, an agency of the Government of Puerto Rico. When created in 2003 it consisted of 14 municipalities in the south central zone. With the creation of the neighboring Porta Cordillera zone in July 2012, the municipalities of Adjuntas and Jayuya were transferred to the newly created Porta Cordillera zone and Porta Caribe became a 12-municipality tourism region. The name Porta Caribe translates to "Doorway to the Caribbean." Its executive director is Maritza W. Ruiz Cabán.

Isolina Rondón was a political activist. She was one of the few witnesses of the killing of four Nationalists committed by local police officers in Puerto Rico during a confrontation with the supporters of the Nationalist Party that occurred on October 24, 1935, and which is known as the Río Piedras massacre. Rondón joined the political movement and became the Treasurer of the Puerto Rican Nationalist Party which staged various uprisings in Puerto Rico against the colonial Government of the United States in 1950.
Angel "Chayanne" Martínez Santiago is a Puerto Rican politician and Senator. He has been a member of the Senate of Puerto Rico since 2008.

Isabel Rosado, also known as Doña Isabelita, was an educator, social worker, activist and member of the Puerto Rican Nationalist Party. Influenced by the events of the Ponce massacre, Rosado became a believer of the Puerto Rican independence movement and was imprisoned because of her commitment to the cause.

Vidal Santiago Díaz was a member of the Puerto Rican Nationalist Party and served as president of the Santurce Municipal Board of officers of the party. He was also the personal barber of Nationalist leader Pedro Albizu Campos. Though not involved in the Puerto Rican Nationalist Party Revolts of the 1950s, Santiago Díaz's barbershop was attacked by forty armed police officers and U.S. National Guardsmen. The attack was historic in Puerto Rico—the first time an event of that magnitude had ever been transmitted live via radio and heard all over the island.

The President of the House of Representatives of Puerto Rico —commonly called the Speaker of the House — is the highest-ranking officer and the presiding officer of the House of Representatives of Puerto Rico. The Speaker has voting powers as it is elected amongst the own members of the House as established by Article III of the Constitution of Puerto Rico. The Constitution, however, does not establish its functions and since the House is the only body authorized by the Constitution to regulate its own internal affairs, the functions of the Speaker vary from session to session—save being called "Speaker" as the Constitution establishes. The Speaker is typically elected during the House inaugural session.

Law 53 of 1948 better known as the Gag Law, was an act enacted by the Puerto Rico legislature of 1948, with the purpose of suppressing the independence movement in Puerto Rico. The act made it a crime to own or display a Puerto Rican flag, to sing a patriotic tune, to speak or write of independence, or to meet with anyone or hold any assembly in favor of Puerto Rican independence. It was passed by a legislature that was overwhelmingly dominated by members of the Popular Democratic Party (PPD), which supported developing an alternative political status for the island. The bill was signed into law on June 10, 1948 by Jesús T. Piñero, the United States-appointed governor. Opponents tried but failed to have the law declared unconstitutional by the United States Supreme Court.










