This article may rely excessively on sources too closely associated with the subject , potentially preventing the article from being verifiable and neutral.(July 2022) |
| Neofetch | |
|---|---|
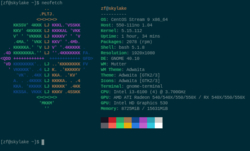 Neofetch running on CentOS | |
| Developer | Dylan Araps |
| Initial release | 31 December 2015 |
| Final release | |
| Repository | github |
| Written in | Bash 3.2 |
| Operating system | Linux, macOS, BSD, Windows, iOS, Android, GNU Hurd, Haiku, IRIX, MINIX, Solaris |
| Size | 277 KB |
| Available in | English |
| Type | Benchmark |
| License | MIT License |
Neofetch is a system information tool written in the Bash shell scripting language. [2] It displays a logo of the distribution, rendered in ASCII art, [3] [4] and a static display of the computer's basic hardware and software configurations and their versions. The display includes the operating system, the host (namely the technical name of the machine), uptime, package managers, the shell, display resolution, desktop environment, window manager, themes and icons, the computer terminal, CPU, GPU, and RAM. Neofetch can also display images on the terminal with w3m-img or Sixel in place of the ASCII logo art.
Neofetch development was discontinued on 26 April 2024, nearly four years after it was last updated. [5] [6]