The 6th millennium BC spanned the years 6000 BC to 5001 BC. It is impossible to precisely date events that happened around the time of this millennium and all dates mentioned here are estimates mostly based on geological and anthropological analysis. The only exceptions are the felling dates for some construction timbers from Neolithic wells in Central Europe.

Neolithic architecture refers to structures encompassing housing and shelter from approximately 10,000 to 2,000 BC, the Neolithic period. In southwest Asia, Neolithic cultures appear soon after 10,000 BC, initially in the Levant and from there into the east and west. Early Neolithic structures and buildings can be found in southeast Anatolia, Syria, and Iraq by 8,000 BC with agriculture societies first appearing in southeast Europe by 6,500 BC, and central Europe by ca. 5,500 BC (of which the earliest cultural complexes include the Starčevo-Koros, Linearbandkeramic, and Vinča.

The European Neolithic is the period from the arrival of Neolithic technology and the associated population of Early European Farmers in Europe, c. 7000 BC until c. 2000–1700 BC. The Neolithic overlaps the Mesolithic and Bronze Age periods in Europe as cultural changes moved from the southeast to northwest at about 1 km/year – this is called the Neolithic Expansion.

Stara Zagora, formerly known as the Stara Zagora okrug, is a province of south-central Bulgaria. It is named after its administrative and industrial centre—the city of Stara Zagora—the sixth-biggest town in the country. The province embraces a territory of 5,151.1 km2 (1,988.9 sq mi) that is divided into 11 municipalities with a total population, as of December 2009, of 350,925 inhabitants.

Stara Zagora is a city in Bulgaria, and the administrative capital of the homonymous Stara Zagora Province and municipality. Its located in the Upper Thracian Plain, being near the cities of Kazanlak, Plovdiv, Sliven. Its population is around 121,582 making it the sixth largest city, just below Ruse and above Pleven.

Prehistoric Europe refers to Europe before the start of written records, beginning in the Lower Paleolithic. As history progresses, considerable regional unevenness in cultural development emerges and grows. The region of the eastern Mediterranean is, due to its geographic proximity, greatly influenced and inspired by the classical Middle Eastern civilizations, and adopts and develops the earliest systems of communal organization and writing. The Histories of Herodotus is the oldest known European text that seeks to systematically record traditions, public affairs and notable events.
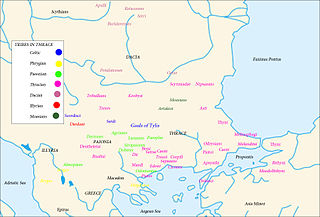
Tylis or Tyle was a capital of a short-lived Balkan state mentioned by Polybius that was founded by Celts led by Comontorius in the 3rd century BC. Following their invasion of Thrace and Greece in 279 BC, the Gauls were defeated by the Macedonian king Antigonus II Gonatas in the Battle of Lysimachia in 277 BC, after which they turned inland to Thrace and founded their kingdom at Tylis. It was located near the eastern edge of the Haemus (Balkan) Mountains in what is now eastern Bulgaria. Some bands of Celts, namely the Tectosages, Tolistobogii and Trocmi, did not settle in Thrace, but crossed into Asia Minor to become known as the Galatians. The last king of Tylis was Cavarus who maintained good relations with the city of Byzantium. His capital was destroyed by the Thracians in 212 BC and this was also the end of his kingdom. The modern Bulgarian village of Tulovo in Stara Zagora Province now occupies the site.

The Varna Necropolis, or Varna Cemetery, is a burial site in the western industrial zone of Varna, internationally considered one of the key archaeological sites in world prehistory. The oldest gold treasure and jewelry in the world, dating from 4,600 BC to 4,200 BC, was discovered at the site. Several prehistoric Bulgarian finds are considered no less old – the golden treasures of Hotnitsa, Durankulak, artifacts from the Kurgan settlement of Yunatsite near Pazardzhik, the golden treasure Sakar, as well as beads and gold jewelry found in the Kurgan settlement of Provadia – Solnitsata. However, Varna gold is most often called the oldest since this treasure is the largest and most diverse.

Sredna Gora is a mountain range in central Bulgaria, situated south of and parallel to the Balkan Mountains and extending from the river Iskar to the west and the elbow of river Tundzha north of the city of Yambol to the east. Sredna Gora is 285 km long, reaching 50 km at its greatest width. Its highest peak is Golyam Bogdan at 1,604 m (5,262 ft). It is part of the Srednogorie mountain chain system, which extends longitudinally across the most country from west to east, between the Balkan Mountains and the Sub-Balkan valleys to the north and the Kraishte, Rila and the Upper Thracian Plain to the south.

The Monument to the Unknown Soldier is a monument in the centre of Sofia, the capital of Bulgaria, located just next to the 6th-century Church of St Sophia, on 2 Paris Street. The monument commemorates the hundreds of thousands of Bulgarian soldiers who died in wars defending their homeland. Ceremonies involving the President of Bulgaria and foreign state leaders are often performed here.

Starosel is a village in central Bulgaria, Hisarya Municipality, Plovdiv Province. It lies at the foothills of the Sredna Gora mountain range along the shores of Pyasachnik river.

The Varna culture was a Chalcolithic culture of northeastern Bulgaria, dated c. 4500 BC, contemporary and closely related with the Gumelnița culture. The oldest golden artifacts in the world were found in the Necropolis of Varna. These artefacts are on display in the Varna Archaeological Museum
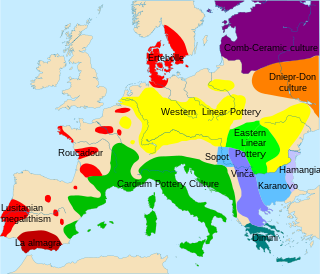
The Karanovo culture is a Neolithic culture named after the Bulgarian village of Karanovo. The culture, which is part of the Danube civilization, is considered the largest and most important of the Azmak River Valley agrarian settlements.

Pfahlbaumuseum Unteruhldingen is an archaeological open-air museum on Lake Constance (Bodensee) in Unteruhldingen, Germany, consisting of reconstructions of stilt houses or lake dwellings from the Neolithic and Bronze Age.

The prehistory of Southeastern Europe, defined roughly as the territory of the wider Southeast Europe covers the period from the Upper Paleolithic, beginning with the presence of Homo sapiens in the area some 44,000 years ago, until the appearance of the first written records in Classical Antiquity, in Greece. First Greek language is Linear A and follows Linear B, which is a syllabic script that was used for writing in Mycenaean Greek, the earliest attested form of the Greek language. The script predates the Greek alphabet by several centuries. The oldest Mycenaean writing dates to about 1400 BC. It is descended from the older Linear A, an undeciphered earlier script used for writing the Minoan language, as is the later Cypriot syllabary, which also recorded Greek. Linear B, found mainly in the palace archives at Knossos, Kydonia, Pylos, Thebes and Mycenae, disappeared with the fall of Mycenaean civilization during the Late Bronze Age collapse.

This timeline of prehistoric Scotland is a chronologically ordered list of important archaeological sites in Scotland and of major events affecting Scotland's human inhabitants and culture during the prehistoric period. The period of prehistory prior to occupation by the genus Homo is part of the geology of Scotland. Prehistory in Scotland ends with the arrival of the Romans in southern Scotland in the 1st century AD and the beginning of written records. The archaeological sites and events listed are the earliest examples or among the most notable of their type.
The Granit oak is an pedunculate oak tree that grows within the boundaries of Granit village, Bulgaria.

Starozagorski bani is a village and a mineral spring spa resort in central Bulgaria. It is located 15 km (9 mi) north-west of Stara Zagora, in the Sredna Gora mountain.

Tell Yunatsite, also known as Ploskata mogila, is situated in the Pazardzhik Province of southern Bulgaria, some 8 kilometres (5 mi) to the west of the district capital Pazardzhik. The tell stands 12 metres (39 ft) above modern ground level and has a diameter of 110 m (360 ft). It is situated on a low terrace at the right bank of the former Topolnitsa riverbed near to its confluence with the Maritsa River. Medieval, Roman, Iron Age, Early Bronze Age, and Copper Age periods have all been attested at the site. The Copper Age tell is associated with the Karanovo culture.

Durankulak is a prehistoric archaeological site on the Golemija ostrov in Durankulak lake, Bulgaria. Prehistoric settlement commenced on the small island approximately 7000 BP and lasted for thousands of years.



















