Related Research Articles
Wireless sensor networks (WSNs) refer to networks of spatially dispersed and dedicated sensors that monitor and record the physical conditions of the environment and forward the collected data to a central location. WSNs can measure environmental conditions such as temperature, sound, pollution levels, humidity and wind.

Ian F. Akyildiz is a Turkish-American electrical engineer. He received his BS, MS, and PhD degrees in Electrical and Computer Engineering from the University of Erlangen-Nürnberg, Germany, in 1978, 1981 and 1984, respectively. Currently, he is the President and CTO of the Truva Inc. since March 1989. He retired from the School of Electrical and Computer Engineering (ECE) at Georgia Tech in 2021 after almost 35 years service as Ken Byers Chair Professor in Telecommunications and Chair of the Telecom group.
Extremely Opportunistic Routing (ExOR) is a combination of routing protocol and media access control for a wireless ad hoc network, invented by Sanjit Biswas and Robert Morris of the MIT Artificial Intelligence Laboratory, and described in a 2005 paper. A very similar opportunistic routing scheme was also independently proposed by Zhenzhen Ye and Yingbo Hua from University of California, Riverside and presented in a paper in 2005. Previously open source, ExOR was available in 2005 but is no longer obtainable. The broadcast and retransmission strategies used by the algorithm were already described in the literature. ExOR is valuable because it can operate available digital radios to use some previously impractical algorithmic optimizations.
Cross-layer optimization is an escape from the pure waterfall-like concept of the OSI communications model with virtually strict boundaries between layers. The cross layer approach transports feedback dynamically via the layer boundaries to enable the compensation for overload, latency or other mismatch of requirements and resources by any control input to another layer, but that layer directly affected by the detected deficiency.
In communication networks, cognitive network (CN) is a new type of data network that makes use of cutting edge technology from several research areas to solve some problems current networks are faced with. Cognitive network is different from cognitive radio (CR) as it covers all the layers of the OSI model.

Adam Wierman is Professor of Computer Science in the Department of Computing and Mathematical Sciences at the California Institute of Technology. He is known for his work on scheduling (computing), heavy tails, green computing, queueing theory, and algorithmic game theory.
Devavrat Shah is a professor in the Electrical Engineering and Computer Science department at MIT. He is director of the Statistics and Data Science Center at MIT. He received a B.Tech. degree in computer science from IIT Bombay in 1999 and a Ph.D. in computer science from Stanford University in 2004, where his thesis was completed under the supervision of Balaji Prabhakar.
In mathematics and telecommunications, stochastic geometry models of wireless networks refer to mathematical models based on stochastic geometry that are designed to represent aspects of wireless networks. The related research consists of analyzing these models with the aim of better understanding wireless communication networks in order to predict and control various network performance metrics. The models require using techniques from stochastic geometry and related fields including point processes, spatial statistics, geometric probability, percolation theory, as well as methods from more general mathematical disciplines such as geometry, probability theory, stochastic processes, queueing theory, information theory, and Fourier analysis.

Victor Bahl is an American Technical Fellow and CTO of Azure for Operators at Microsoft. He started networking research at Microsoft. He is known for his research contributions to white space radio data networks, radio signal-strength based indoor positioning systems, multi-radio wireless systems, wireless network virtualization, edge computing, and for bringing wireless links into the datacenter. He is also known for his leadership of the mobile computing community as the co-founder of the ACM Special Interest Group on Mobility of Systems, Users, Data, and Computing (SIGMOBILE). He is the founder of international conference on Mobile Systems, Applications, and Services Conference (MobiSys), and the founder of ACM Mobile Computing and Communications Review, a quarterly scientific journal that publishes peer-reviewed technical papers, opinion columns, and news stories related to wireless communications and mobility. Bahl has received important awards; delivered dozens of keynotes and plenary talks at conferences and workshops; delivered over six dozen distinguished seminars at universities; written over hundred papers with more than 65,000 citations and awarded over 100 US and international patents. He is a Fellow of the Association for Computing Machinery, IEEE, and American Association for the Advancement of Science.

Bruce Edward Hajek is a Professor in the Coordinated Science Laboratory, the head of the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, and the Leonard C. and Mary Lou Hoeft Chair in Engineering at the University of Illinois Urbana–Champaign. He does research in communication networking, auction theory, stochastic analysis, combinatorial optimization, machine learning, information theory, and bioinformatics.
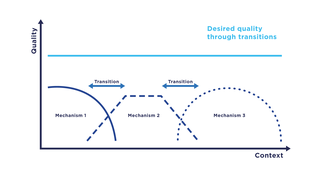
Transition refers to a computer science paradigm in the context of communication systems which describes the change of communication mechanisms, i.e., functions of a communication system, in particular, service and protocol components. In a transition, communication mechanisms within a system are replaced by functionally comparable mechanisms with the aim to ensure the highest possible quality, e.g., as captured by the quality of service.
Yunhao Liu is a Chinese computer scientist. He is the Dean of Global Innovation Exchange (GIX) at Tsinghua University.
Sunghyun Choi is an electrical engineer and academic.

Xi Zhang is a Full Professor and the Founding Director of the Networking and Information Systems Laboratory, Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Texas A&M University. He is a Fellow of the IEEE for contributions to quality of service (QoS) in mobile wireless networks. His research interests include statistical delay-bounded QoS provisioning for multimedia mobile wireless networks, edge computing, finite blocklength coding theory, in-network caching, and offloading over 5G mobile wireless networks.

Salman A. Avestimehr is a Dean's professor at the Electrical & Computer Engineering and Computer Science Departments of University of Southern California, where he is the inaugural director of the USC-Amazon Center for Secure and Trusted Machine Learning and the director of the Information Theory and Machine Learning (vITAL) research lab. He is also the CEO and Co-Founder of FedML. Avestimehr's contributions in research and publications are in the areas of information theory, machine learning, large-scale distributed computing, and secure/private computing and learning. In particular, he is best known for deterministic approximation approaches to network information theory and coded computing. He was a general co-chair of the 2020 International Symposium on Information Theory (ISIT), and is a Fellow of IEEE. He is also co-authors of four books titled “An Approximation Approach to Network Information Theory”, “Multihop Wireless Networks: A Unified Approach to Relaying and Interference Management”, “Coded Computing”, and “Problem Solving Strategies for Elementary-School Math.”
Wonjun Lee (Korean: 이원준) is a professor of Department of Cyber Defense, School of Cybersecurity at Korea University in Seoul, South Korea. His research interests include communication and network protocols, wireless communication and networking optimization techniques, security and privacy in mobile computing, and RF-powered computing and networking. He has authored 15 international patents, over 250 papers in refereed international journals and conferences, and a book “Optimal Coverage in Wireless Sensor Networks,” Springer, 2020.
Danijela Branislav Cabric is a Serbian-American electrical engineer. She is a professor in the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering at the University of California, Los Angeles. In 2021, Cabric was elected a Fellow of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) for her "contributions to theory and practice of spectrum sensing and cognitive radio systems."
Can Emre Koksal is an electrical engineer, computer scientist, academic, and entrepreneur. He is the Founder and CEO of Datanchor, and a professor of Electrical and Computer Engineering at Ohio State University.
George N. Rouskas is a computer scientist, academic, and author. He is an Alumni Distinguished Graduate Professor and Director of Graduate Programs in the Department of Computer Science at North Carolina State University.

Moshe Sidi is a professor emeritus in the Faculty of Electrical and Computer Engineering at the Technion - Israel Institute of Technology.
References
- ↑ "Ness B. Shroff". Ohio State University. Retrieved 7 October 2022.
- ↑ X. Liu and E. K. P. Chong, and N. B. Shroff, “Opportunistic Transmission Scheduling With Resource-Sharing Constraints in Wireless Networks,” IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, vol. 19, no. 10, pp. 2053–2065.
- ↑ X. Liu, E. K. P. Chong, and N. B. Shroff, “A Framework for Opportunistic Scheduling in Wireless Networks,” Computer Networks, vol. 41, no. 4, pp. 451–474, March 2003.
- ↑ X. Lin and N. B. Shroff, “The Impact of Imperfect Scheduling on Cross-Layer Rate Control in Multihop Wireless Networks,” IEEE INFOCOM’05, Miami, Florida, Mar. 2005
- ↑ Xiaojun Lin and Ness B. Shroff. "Joint rate control and scheduling in multihop wireless networks." 43rd IEEE Conference on Decision and Control (CDC), Vol. 2. 2004.
- ↑ Lin, Xiaojun, and Ness B. Shroff. "The impact of imperfect scheduling on cross-layer rate control in wireless networks." Proceedings of the 24th Annual Joint Conference of the IEEE Computer and Communications Societies (INFOCOM).,Vol. 3. IEEE, 2005. (Extended version in IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 2006).
- ↑ X. Lin, N. B. Shroff, R. Srikant, “A Tutorial on Cross-Layer Optimization in Wireless Networks,” IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications on “ Non-Linear Optimization of Communication Systems”, vol. 24, Issue 8, June 2006, pp. 1452- 1463.
- ↑ "New strategy may protect computer networks from most virulent computer worms". Oneindia. Retrieved 7 October 2022.
- ↑ "A new way to protect computer networks from Internet worms". Phys.org. Retrieved 7 October 2022.
- ↑ "Boffins tackle random scanning worms". iTnews.
- ↑ Yin Sun, E. Uysal-Biyikoglu, R. D. Yates, C. E. Koksal, and N. B. Shroff, “Update or Wait: How to Keep Your Data Fresh,” IEEE Trans. on Information Theory, vol. 63, no. 11, pp. 7492-7508, Nov. 2017.
- ↑ "NSF funds 2 Ohio State-based institutes to expand artificial intelligence research". Osu.edu.
- ↑ "IEEE INFOCOM 2016 Best Paper Award". IEEE.
- ↑ "Most highly cited researchers". Thomas Reuters.
- ↑ "IEEE INFOCOM 2014 Achievement Awards". IEEE.
- ↑ "Professor Ness Shroff receives IEEE INFOCOM award". Electrical & Computer Engineering. 8 May 2014.
- ↑ "The world's most influential scientific mind: 2014". Thomas Reuters.
- ↑ "IEEE WiOPT 2012". IEEE .
- ↑ "IEEE Fellows 2007". IEEE Communications Society.
- 1 2 "Best Paper Awards". Computer Science and Engineering. 17 September 2013.
- ↑ "NSF Award Search: Award # 9624525 – CAREER: ATM and Wireless Networks: Theory, Experiments, and Applications". Nsf.gov.
- ↑ "NSF awards fund seven young faculty members". Purdue.edu.