Earned value management (EVM), earned value project management, or earned value performance management (EVPM) is a project management technique for measuring project performance and progress in an objective manner.
Project management is the process of leading the work of a team to achieve goals and meet success criteria at a specified time. The primary challenge of project management is to achieve all of the project goals within the given constraints. This information is usually described in project documentation, created at the beginning of the development process. The primary constraints are scope, time, budget. The secondary challenge is to optimize the allocation of necessary inputs and apply them to meet pre-defined objectives.
Critical chain project management (CCPM) is a method of planning and managing projects that emphasizes the resources required to execute project tasks. It was developed by Eliyahu M. Goldratt. It differs from more traditional methods that derive from critical path and PERT algorithms, which emphasize task order and rigid scheduling. A critical chain project network strives to keep resources levelled, and requires that they be flexible in start times.

The Project Management Body of Knowledge is a set of standard terminology and guidelines for project management. The body of knowledge evolves over time and is presented in A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge, a book whose sixth edition was released in 2017. The Guide is a document resulting from work overseen by the Project Management Institute (PMI), which offers the CAPM and PMP certifications.

The critical path method (CPM), or critical path analysis (CPA), is an algorithm for scheduling a set of project activities. It is commonly used in conjunction with the program evaluation and review technique (PERT). A critical path is determined by identifying the longest stretch of dependent activities and measuring the time required to complete them from start to finish.
Project management software (PMS) has the capacity to help plan, organize, and manage resource tools and develop resource estimates. Depending on the sophistication of the software, it can manage estimation and planning, scheduling, cost control and budget management, resource allocation, collaboration software, communication, decision-making, quality management, time management and documentation or administration systems. Today, numerous PC and browser-based project management software and contract management software solutions exist, and are finding applications in almost every type of business.

The program (or project) evaluation and review technique (PERT) is a statistical tool used in project management, which was designed to analyze and represent the tasks involved in completing a given project.
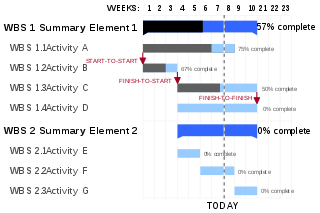
A Gantt chart is a type of bar chart that illustrates a project schedule, named after its inventor, Henry Gantt (1861–1919), who designed such a chart around the years 1910–1915. Modern Gantt charts also show the dependency relationships between activities and the current schedule status.
Rapid-application development (RAD), also called rapid-application building (RAB), is both a general term for adaptive software development approaches, and the name for James Martin's method of rapid development. In general, RAD approaches to software development put less emphasis on planning and more emphasis on an adaptive process. Prototypes are often used in addition to or sometimes even instead of design specifications.
In project management, a schedule is a listing of a project's milestones, activities, and deliverables, usually with intended start and finish dates. Those items are often estimated by other information included in the project schedule of resource allocation, budget, task duration, and linkages of dependencies and scheduled events. A schedule is commonly used in the project planning and project portfolio management parts of project management. Elements on a schedule may be closely related to the work breakdown structure (WBS) terminal elements, the Statement of work, or a Contract Data Requirements List.

Microsoft Project is a project management software product, developed and sold by Microsoft. It is designed to assist a project manager in developing a schedule, assigning resources to tasks, tracking progress, managing the budget, and analyzing workloads.

MacProject was a project management and scheduling business application released along with the first Apple Macintosh systems in 1984. MacProject was one of the first major business tools for the Macintosh which enabled users to calculate the "critical path" to completion and estimate costs in money and time. If a project deadline was missed or if available resources changed, MacProject recalculated everything automatically.
Construction management (CM) is a professional service that uses specialized, project management techniques to oversee the planning, design, and construction of a project, from its beginning to its end. The purpose of Construction management is to control a project's time / delivery, cost and quality—sometimes referred to as a project management triangle or "triple constraints." CM is compatible with all project delivery systems, including design-bid-build, design-build, CM At-Risk and Public Private Partnerships. Professional construction managers may be reserved for lengthy, large-scale, high budget undertakings, called capital projects.
Takt time, or simply Takt, is a manufacturing term to describe the required product assembly duration that is needed to match the demand. Often confused with cycle time, takt time is a tool used to design work and it measures the average time interval between the start of production of one unit and the start of production of the next unit when items are produced sequentially. For calculations, it is the time to produce parts divided by the number of parts demanded in that time interval. The takt time is based on customer demand; if a process or a production line are unable to produce at takt time, either demand leveling, additional resources, or process re-engineering is needed to ensure on-time delivery.
Linear scheduling method (LSM) is a graphical scheduling method focusing on continuous resource utilization in repetitive activities.
A glossary of terms relating to project management and consulting.
The Graphical Path Method (GPM) is a mathematically based algorithm used in project management for planning, scheduling and resource control. GPM represents logical relationships of dated objects – such as activities, milestones, and benchmarks – in a time-scaled network diagram.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to project management:

Spider Project is a project management software, developed by a Russian company, Spider Project Team.
Project production management (PPM) is the application of operations management to the delivery of capital projects. The PPM framework is based on a project as a production system view, in which a project transforms inputs into outputs.






