Investment is traditionally defined as the "commitment of resources to achieve later benefits". If an investment involves money, then it can be defined as a "commitment of money to receive more money later". From a broader viewpoint, an investment can be defined as "to tailor the pattern of expenditure and receipt of resources to optimise the desirable patterns of these flows". When expenditures and receipts are defined in terms of money, then the net monetary receipt in a time period is termed cash flow, while money received in a series of several time periods is termed cash flow stream.

In accounting, revenue is the total amount of income generated by the sale of goods and services related to the primary operations of the business. Commercial revenue may also be referred to as sales or as turnover. Some companies receive revenue from interest, royalties, or other fees. "Revenue" may refer to income in general, or it may refer to the amount, in a monetary unit, earned during a period of time, as in "Last year, Company X had revenue of $42 million". Profits or net income generally imply total revenue minus total expenses in a given period. In accounting, revenue is a subsection of the Equity section of the balance statement, since it increases equity. It is often referred to as the "top line" due to its position at the very top of the income statement. This is to be contrasted with the "bottom line" which denotes net income.

The break-even point (BEP) in economics, business—and specifically cost accounting—is the point at which total cost and total revenue are equal, i.e. "even". There is no net loss or gain, and one has "broken even", though opportunity costs have been paid and capital has received the risk-adjusted, expected return. In short, all costs that must be paid are paid, and there is neither profit nor loss. The break-even analysis was developed by Karl Bücher and Johann Friedrich Schär.

A company's earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization is a measure of a company's profitability of the operating business only, thus before any effects of indebtedness, state-mandated payments, and costs required to maintain its asset base. It is derived by subtracting from revenues all costs of the operating business but not decline in asset value, cost of borrowing, lease expenses, and obligations to governments.
An investment trust is a form of investment fund found mostly in the United Kingdom and Japan. Investment trusts are constituted as public limited companies and are therefore closed ended since the fund managers cannot redeem or create shares.

Throughput accounting (TA) is a principle-based and simplified management accounting approach that provides managers with decision support information for enterprise profitability improvement. TA is relatively new in management accounting. It is an approach that identifies factors that limit an organization from reaching its goal, and then focuses on simple measures that drive behavior in key areas towards reaching organizational goals. TA was proposed by Eliyahu M. Goldratt as an alternative to traditional cost accounting. As such, Throughput Accounting is neither cost accounting nor costing because it is cash focused and does not allocate all costs to products and services sold or provided by an enterprise. Considering the laws of variation, only costs that vary totally with units of output e.g. raw materials, are allocated to products and services which are deducted from sales to determine Throughput. Throughput Accounting is a management accounting technique used as the performance measure in the Theory of Constraints (TOC). It is the business intelligence used for maximizing profits, however, unlike cost accounting that primarily focuses on 'cutting costs' and reducing expenses to make a profit, Throughput Accounting primarily focuses on generating more throughput. Conceptually, Throughput Accounting seeks to increase the speed or rate at which throughput is generated by products and services with respect to an organization's constraint, whether the constraint is internal or external to the organization. Throughput Accounting is the only management accounting methodology that considers constraints as factors limiting the performance of organizations.

In business and accounting, net income is an entity's income minus cost of goods sold, expenses, depreciation and amortization, interest, and taxes for an accounting period.

DuPont analysis is a tool used in financial analysis, where return on equity (ROE) is separated into its component parts.
In business, operating margin—also known as operating income margin, operating profit margin, EBIT margin and return on sales (ROS)—is the ratio of operating income to net sales, usually expressed in percent.
The return on equity (ROE) is a measure of the profitability of a business in relation to its equity; where:

Contribution margin (CM), or dollar contribution per unit, is the selling price per unit minus the variable cost per unit. "Contribution" represents the portion of sales revenue that is not consumed by variable costs and so contributes to the coverage of fixed costs. This concept is one of the key building blocks of break-even analysis.
Price–sales ratio, P/S ratio, or PSR, is a valuation metric for stocks. It is calculated by dividing the company's market capitalization by the revenue in the most recent year; or, equivalently, divide the per-share stock price by the per-share revenue.

Taxation in Ireland in 2017 came from Personal Income taxes, and Consumption taxes, being VAT and Excise and Customs duties. Corporation taxes represents most of the balance, but Ireland's Corporate Tax System (CT) is a central part of Ireland's economic model. Ireland summarises its taxation policy using the OECD's Hierarchy of Taxes pyramid, which emphasises high corporate tax rates as the most harmful types of taxes where economic growth is the objective. The balance of Ireland's taxes are Property taxes and Capital taxes.

In financial accounting, reserve always has a credit balance and can refer to a part of shareholders' equity, a liability for estimated claims, or contra-asset for uncollectible accounts.
In bookkeeping, accounting, and financial accounting, net sales are operating revenues earned by a company for selling its products or rendering its services. Also referred to as revenue, they are reported directly on the income statement as Sales or Net sales.
Return on investment (ROI) or return on costs (ROC) is a ratio between net income and investment. A high ROI means the investment's gains compare favourably to its cost. As a performance measure, ROI is used to evaluate the efficiency of an investment or to compare the efficiencies of several different investments. In economic terms, it is one way of relating profits to capital invested.
Human Resource (HR) metrics are measurements used to determine the value and effectiveness of HR initiatives, typically including such areas as turnover, training, return on human capital, costs of labor, and expenses per employee.

A financial ratio or accounting ratio states the relative magnitude of two selected numerical values taken from an enterprise's financial statements. Often used in accounting, there are many standard ratios used to try to evaluate the overall financial condition of a corporation or other organization. Financial ratios may be used by managers within a firm, by current and potential shareholders (owners) of a firm, and by a firm's creditors. Financial analysts use financial ratios to compare the strengths and weaknesses in various companies. If shares in a company are traded in a financial market, the market price of the shares is used in certain financial ratios.
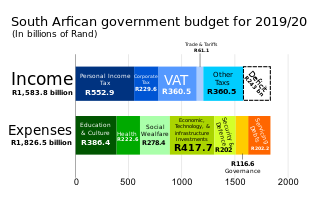
Taxation may involve payments to a minimum of two different levels of government: central government through SARS or to local government. Prior to 2001 the South African tax system was "source-based", where in income is taxed in the country where it originates. Since January 2001, the tax system was changed to "residence-based" wherein taxpayers residing in South Africa are taxed on their income irrespective of its source. Non residents are only subject to domestic taxes.
Top-line growth is the increase in revenue or gross sales by a company over a defined period and is used to indicate the financial strength of a business and its potential for growth in the future. It is usually measured over periods of one-half or full years and is often reported as a percentage growth compared to the previous year or period. Top-line growth does not accrue across periods, instead it is recalculated based on the performance of the business in a specified reporting period. It is a gross figure that represents economic inflows to the company, prior to the deduction of expenses or changes in equity contributed by the business owners or the investors. Top-line growth is often used as a metric for business growth potential and overall operating performance. In most businesses, it forms an integral part of their strategic planning and a means of assessments for such strategies.





