
The neutron is a subatomic particle, symbol
n
or
n0
, which has no electric charge, and a mass slightly greater than that of a proton. Protons and neutrons constitute the nuclei of atoms. Since protons and neutrons behave similarly within the nucleus, they are both referred to as nucleons. Nucleons have a mass of approximately one atomic mass unit, or dalton. Their properties and interactions are described by nuclear physics. Protons and neutrons are not elementary particles; each is composed of three quarks.

In nuclear physics, a nuclear chain reaction occurs when one single nuclear reaction causes an average of one or more subsequent nuclear reactions, thus leading to the possibility of a self-propagating series or "positive feedback loop" of these reactions. The specific nuclear reaction may be the fission of heavy isotopes. A nuclear chain reaction releases several million times more energy per reaction than any chemical reaction.

In physics, radiation is the emission or transmission of energy in the form of waves or particles through space or a material medium. This includes:
In nuclear engineering, fissile material is material that can undergo nuclear fission when struck by a neutron of low energy. A self-sustaining thermal chain reaction can only be achieved with fissile material. The predominant neutron energy in a system may be typified by either slow neutrons or fast neutrons. Fissile material can be used to fuel thermal-neutron reactors, fast-neutron reactors and nuclear explosives.

In nuclear engineering, a critical mass is the smallest amount of fissile material needed for a sustained nuclear chain reaction. The critical mass of a fissionable material depends upon its nuclear properties, density, shape, enrichment, purity, temperature, and surroundings. The concept is important in nuclear weapon design.

In nuclear engineering, a neutron moderator is a medium that reduces the speed of fast neutrons, ideally without capturing any, leaving them as thermal neutrons with only minimal (thermal) kinetic energy. These thermal neutrons are immensely more susceptible than fast neutrons to propagate a nuclear chain reaction of uranium-235 or other fissile isotope by colliding with their atomic nucleus.

Neutron diffraction or elastic neutron scattering is the application of neutron scattering to the determination of the atomic and/or magnetic structure of a material. A sample to be examined is placed in a beam of thermal or cold neutrons to obtain a diffraction pattern that provides information of the structure of the material. The technique is similar to X-ray diffraction but due to their different scattering properties, neutrons and X-rays provide complementary information: X-Rays are suited for superficial analysis, strong x-rays from synchrotron radiation are suited for shallow depths or thin specimens, while neutrons having high penetration depth are suited for bulk samples.

Neutron radiation is a form of ionizing radiation that presents as free neutrons. Typical phenomena are nuclear fission or nuclear fusion causing the release of free neutrons, which then react with nuclei of other atoms to form new nuclides—which, in turn, may trigger further neutron radiation. Free neutrons are unstable, decaying into a proton, an electron, plus an electron antineutrino. Free neutrons have a mean lifetime of 887 seconds.

Control rods are used in nuclear reactors to control the rate of fission of the nuclear fuel – uranium or plutonium. Their compositions include chemical elements such as boron, cadmium, silver, hafnium, or indium, that are capable of absorbing many neutrons without themselves decaying. These elements have different neutron capture cross sections for neutrons of various energies. Boiling water reactors (BWR), pressurized water reactors (PWR), and heavy-water reactors (HWR) operate with thermal neutrons, while breeder reactors operate with fast neutrons. Each reactor design can use different control rod materials based on the energy spectrum of its neutrons. Control rods have been used in nuclear aircraft engines like Project Pluto as a method of control.
A neutron reflector is any material that reflects neutrons. This refers to elastic scattering rather than to a specular reflection. The material may be graphite, beryllium, steel, tungsten carbide, gold, or other materials. A neutron reflector can make an otherwise subcritical mass of fissile material critical, or increase the amount of nuclear fission that a critical or supercritical mass will undergo. Such an effect was exhibited twice in accidents involving the Demon Core, a subcritical plutonium pit that went critical in two separate fatal incidents when the pit's surface was momentarily surrounded by too much neutron reflective material.

Neutron activation is the process in which neutron radiation induces radioactivity in materials, and occurs when atomic nuclei capture free neutrons, becoming heavier and entering excited states. The excited nucleus decays immediately by emitting gamma rays, or particles such as beta particles, alpha particles, fission products, and neutrons. Thus, the process of neutron capture, even after any intermediate decay, often results in the formation of an unstable activation product. Such radioactive nuclei can exhibit half-lives ranging from small fractions of a second to many years.
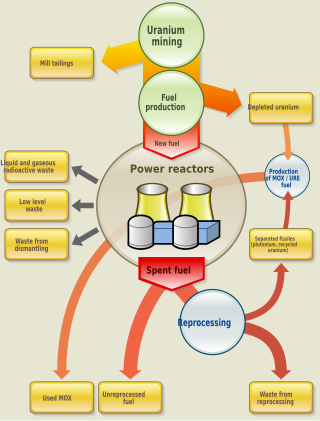
Nuclear fuel refers to any substance, typically fissile material, which is used by nuclear power stations or other nuclear devices to generate energy.

Fertile material is a material that, although not fissile itself, can be converted into a fissile material by neutron absorption.

Research reactors are nuclear fission-based nuclear reactors that serve primarily as a neutron source. They are also called non-power reactors, in contrast to power reactors that are used for electricity production, heat generation, or maritime propulsion.

Nuclear graphite is any grade of graphite, usually synthetic graphite, manufactured for use as a moderator or reflector within a nuclear reactor. Graphite is an important material for the construction of both historical and modern nuclear reactors because of its extreme purity and ability to withstand extremely high temperatures.
Radiation damage is the effect of ionizing radiation on physical objects including non-living structural materials. It can be either detrimental or beneficial for materials.
Radiation materials science is a subfield of materials science which studies the interaction of radiation with matter: a broad subject covering many forms of irradiation and of matter.
The index of physics articles is split into multiple pages due to its size.
Neutron embrittlement, sometimes more broadly radiation embrittlement, is the embrittlement of various materials due to the action of neutrons. This is primarily seen in nuclear reactors, where the release of high-energy neutrons causes the long-term degradation of the reactor materials. The embrittlement is caused by the microscopic movement of atoms that are hit by the neutrons; this same action also gives rise to neutron-induced swelling causing materials to grow in size, and the Wigner effect causing energy buildup in certain materials that can lead to sudden releases of energy.








