Neva Dell Hunter (died January 27, 1978) pioneered the practice of aura balancing, a form of spiritual therapy in which the practitioner works directly with the energy fields surrounding and penetrating the physical body.
Hunter claimed to have served as a channel (or medium) for a being who was purported to be in touch with Phineas Parkhurst Quimby, an American transcendentalist who developed a form of spiritual healing in the mid-19th century that he called the "Science of the Christ." [1]
Hunter was the founder of the Quimby Memorial Library in Alamogordo, New Mexico. Work on the library began in 1940s during her research and travels, and the library was dedicated in 1963. Its collection included copies of Quimby's manuscripts. [2] The library moved to Santa Fe, New Mexico and later became known as the Quimby Center. In 1976, the center was rededicated as Quimby College, with Hunter as the guest of honor. Quimby College later became Southwestern College.
Her students included Dr. Robert D. Waterman, developer of Noetic Field Balancing and founder and former president of Southwestern College; and Dr. Ron Hulnick, President of the University of Santa Monica, and co-author of "Loyalty to Your Soul" and "Remembering the Light Within." [3] Elavivian Power, author of "The Auric Mirror"; [4] Kirby Benson; [5] Billy Whelan, founder of Hawaii International School Family Peace Group; [6] UFOlogist George Hunt Williamson [7] and many others.
Hunter performed Karmic readings for many individuals over the years, including the daughter of Beat Generation hero Neal Cassady. [8] She was a speaker at dozens of events over her lifetime, including the first national convention of the Amalgamated Flying Saucer Clubs of America on July 11 and 12, 1959 at the Statler-Hilton Hotel in Los Angeles, California. [9] She was the author of the book "Numerology: The Key to Self Understanding" (published in 1978 by the Quimby Metaphysical Libraries).

Hunter College is a public university in New York City, United States. It is one of the constituent colleges of the City University of New York and offers studies in more than one hundred undergraduate and postgraduate fields across five schools. It also administers Hunter College High School and Hunter College Elementary School.
Magnetic therapy is a pseudoscientific alternative medicine practice involving the weak static magnetic field produced by a permanent magnet which is placed on the body. It is similar to the alternative medicine practice of electromagnetic therapy, which uses a magnetic field generated by an electrically powered device. Magnet therapy products may include wristbands, jewelry, blankets, and wraps that have magnets incorporated into them.

Huna is the word adopted by the New Age author Max Freedom Long (1890–1971) in 1936 to describe his theory of metaphysics. Long cited what he believed to be the spiritual practices of the ancient Hawaiian kahunas (priests) as inspiration; however, contemporary scholars consider the system to be his invention designed through a mixture of a variety of spiritual practices from various cultures, with roots in New Thought and Theosophy, rather than in traditional Hawaiian beliefs.
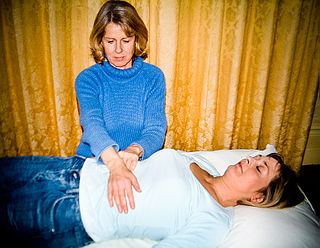
Reiki is a pseudoscientific form of energy healing, a type of alternative medicine originating in Japan. Reiki practitioners use a technique called palm healing or hands-on healing through which, according to practitioners, a "universal energy" is transferred through the palms of the practitioner to the client, to encourage emotional or physical healing. It is based on qi ("chi"), which practitioners say is a universal life force, although there is no empirical evidence that such a life force exists.

Neal Leon Cassady was a major figure of the Beat Generation of the 1950s and the psychedelic and counterculture movements of the 1960s.

Chromotherapy, sometimes called color therapy, colorology or cromatherapy, is an alternative medicine that is considered pseudoscience and quackery. Chromotherapists claim to be able to use light in the form of color to balance "energy" lacking from a person's body, whether it be on physical, emotional, spiritual, or mental levels. For example, they thought that shining a colored light on a person would cure constipation. Historically, chromotherapy has been associated with mysticism and occultism.

The Last Time I Committed Suicide is a 1997 American drama film directed by Stephen T. Kay. Based on a 1950 letter written by Neal Cassady to Jack Kerouac, it stars Thomas Jane as Cassady. The cast also includes Keanu Reeves, Adrien Brody, Gretchen Mol and Claire Forlani. It received a limited release on June 20, 1997.
The New Thought movement is a new religious movement that coalesced in the United States in the early 19th century. New Thought was seen by its adherents as succeeding "ancient thought", accumulated wisdom and philosophy from a variety of origins, such as Ancient Greek, Roman, Egyptian, Chinese, Taoist, Hindu, and Buddhist cultures and their related belief systems, primarily regarding the interaction among thought, belief, consciousness in the human mind, and the effects of these within and beyond the human mind. Though no direct line of transmission is traceable, many adherents to New Thought in the 19th and 20th centuries claimed to be direct descendants of those systems.

Sukyo Mahikari is an organization with centers in more than 100 countries. The stated aim of the organization is to help people improve the quality of their lives and attain happiness by practicing universal principles and a method of spiritual purification called the art of True Light. It was founded by Kōtama Okada in 1959 under the name L. H. Yokoshi no Tomo. Sukyo Mahikari was registered on June 23, 1978, by Keishu Okada as part of an amicable settlement following the passing of Kōtama Okada. In 2013, Sukyo Mahikari announced it had a membership of approximately one million practitioners.
Carolyn Elizabeth Robinson Cassady was an American writer and associated with the Beat Generation through her marriage to Neal Cassady and her friendships with Jack Kerouac, Allen Ginsberg, and other prominent Beat figures. She became a frequent character in the works of Jack Kerouac.
Proponents and practitioners of various esoteric forms of spirituality and alternative medicine refer to a variety of claimed experiences and phenomena as being due to "energy" or "force" that defy measurement or experimentation, and thus are distinct from uses of the term "energy" in science.

Energy medicine is a branch of alternative medicine based on a pseudo-scientific belief that healers can channel "healing energy" into patients and effect positive results. The field is defined by shared beliefs and practices relating to mysticism and esotericism in the wider alternative medicine sphere rather than any sort of unified terminology, leading to terms such as energy healing, vibrational medicine, and similar terms being used synonymously. In most cases, no empirically measurable "energy" is involved: the term refers instead to so-called subtle energy. Practitioners may classify their practice as hands-on, hands-off, or distant wherein the patient and healer are in different locations. Many approaches to energy healing exist: for example, “biofield energy healing”, “spiritual healing”, “contact healing”, “distant healing”, therapeutic touch, Reiki, and Qigong.

Although modern, scientific psychology is often dated from the 1879 opening of the first psychological clinic by Wilhelm Wundt, attempts to create methods for assessing and treating mental distress existed long before. The earliest recorded approaches were a combination of religious, magical and/or medical perspectives. Early examples of such psychological thinkers included Patañjali, Padmasambhava, Rhazes, Avicenna and Rumi.
Southwestern College is a private graduate school in Santa Fe, New Mexico, that specializes in counseling and art therapy. It is the only college or university in the state of New Mexico to offer a Master's Degree in Art Therapy.

New Harbinger Publications, Inc. is an employee-owned, Oakland-based American publisher of self-help books.
Philosophical consultancy, also sometimes called philosophical practice or philosophical counseling or clinical philosophy, is a contemporary movement in practical philosophy. Developing since the 1980s as a profession but since the 1950s as a practice, practitioners of philosophical counseling ordinarily have a doctorate or minimally a master's degree in philosophy and offer their philosophical counseling or consultation services to clients who look for a philosophical understanding of their lives, social problems, or even mental problems. In the last case, philosophical counseling might be in lieu of, or in conjunction with, psychotherapy. The movement has often been said to be rooted in the Socratic tradition, which viewed philosophy as a search for the Good and the good life. A life without philosophy was not worth living for Socrates. This led to the philosophy of Stoicism, for example, resulting in Stoic therapy.
William Robert Quimby was an American author, columnist, editor and publisher who specialized in subjects related to big game hunting for more than four decades.

Warren Felt Evans was an American author of the New Thought movement.
The history of New Thought started in the 1830s, with roots in the United States and England. As a spiritual movement with roots in metaphysical beliefs, New Thought has helped guide a variety of social changes throughout the 19th, 20th, and into the 21st centuries. Psychologist and philosopher William James labelled New Thought "the religion of healthy-mindedness" in his study on religion and science, The Varieties of Religious Experience.
Zero balancing is a type of manual therapy devised by American osteopathic doctor Frederick "Fritz" Smith in the 1970s. Drawing from principles of osteopathy, Chinese medicine and Structural Integration, Smith proposed that the energy field within the human body could be affected by manual manipulations, thus bringing health benefits. The practice teaches that currents of energy are stored within the human skeleton, and that these affect both physical and mental wellbeing.










