Related Research Articles
Pelvic lipomatosis is a rare disease that is most often seen in older obese black men with hypertension. In pelvic lipomatosis, abnormally dense deposits of otherwise apparently normal fat may be observed in the spaces of the pelvic area. It is associated with cystitis glandularis, a precursor to adenocarcinoma of the urinary bladder. It is associated with deposition of mature unencapsulated fat in the retroperitoneal pelvic space producing the typical "pear-shaped" appearance of the bladder on CT scan. This condition also causes a straightening and tubular appearance of the rectum.

A lipoma is a benign tumor made of fat tissue. They are generally soft to the touch, movable, and painless. They usually occur just under the skin, but occasionally may be deeper. Most are less than 5 cm (2.0 in) in size. Common locations include upper back, shoulders, and abdomen. It is possible to have several lipomas.
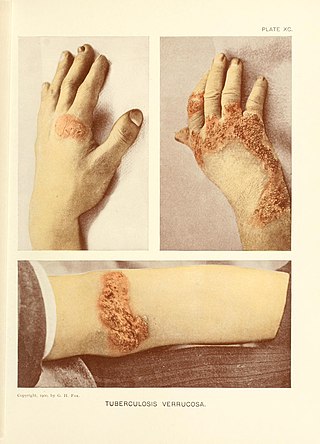
Tuberculosis verrucosa cutis is a rash of small, red papules and nodules in the skin that may appear two to four weeks after inoculation by Mycobacterium tuberculosis in a previously infected and immunocompetent individual.
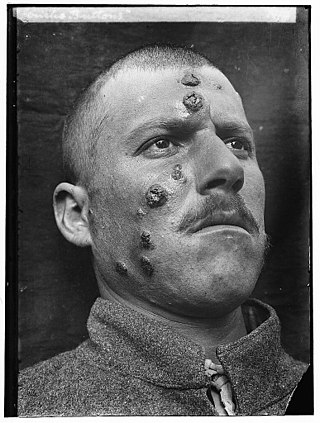
Cutaneous leishmaniasis is the most common form of leishmaniasis affecting humans. It is a skin infection caused by a single-celled parasite that is transmitted by the bite of a phlebotomine sand fly. There are about thirty species of Leishmania that may cause cutaneous leishmaniasis.

Lipomatosis is believed to be an autosomal dominant condition in which multiple lipomas are present on the body. Many discrete, encapsulated lipomas form on the trunk and extremities, with relatively few on the head and shoulders. In 1993, a genetic polymorphism within lipomas was localized to chromosome 12q15, where the HMGIC gene encodes the high-mobility-group protein isoform I-C. This is one of the most commonly found mutations in solitary lipomatous tumors but lipomas often have multiple mutations. Reciprocal translocations involving chromosomes 12q13 and 12q14 have also been observed within.

Bannayan–Riley–Ruvalcaba syndrome (BRRS) is a rare overgrowth syndrome and hamartomatous disorder with occurrence of multiple subcutaneous lipomas, macrocephaly and hemangiomas. The disease is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner. The disease belongs to a family of hamartomatous polyposis syndromes, which also includes Peutz–Jeghers syndrome, juvenile polyposis and Cowden syndrome. Mutation of the PTEN gene underlies this syndrome, as well as Cowden syndrome, Proteus syndrome, and Proteus-like syndrome, these four syndromes are referred to as PTEN Hamartoma-Tumor Syndromes.
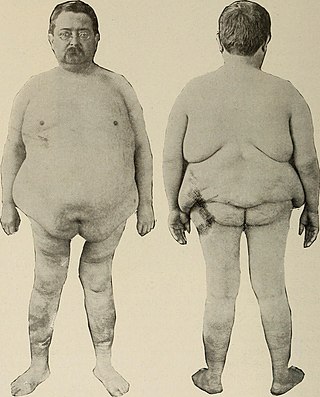
Adiposis dolorosa is an outdated term for many years used synonymously as Dercum's disease, lipedema or Anders disease. While there are numerous references to adiposis dolorosa, it is recommended that the term no longer be used. Dercum's is now recognized as a separate condition, as is lipedema.

A blue nevus is a type of coloured mole, typically a single well-defined blue-black bump.

Nevus lipomatosus superficialis is characterized by soft, yellowish papules or cerebriform plaques, usually of the buttock or thigh, less often of the ear or scalp, with a wrinkled rather than warty surface. It is usually congenital in origin or appears within the first three decades.
Neural fibrolipoma is an overgrowth of fibro-fatty tissue along a nerve trunk that often leads to nerve compression. These only occur in the extremities, and often affect the median nerve. They are rare, very slow-growing, and their origin is unknown. It is believed that they may begin growth in response to trauma. They are not encapsulated by any sort of covering or sheath around the growth itself, as opposed to other cysts beneath the skin that often are. This means there are loosely defined margins of this lipoma. Despite this, they are known to be benign. Neural fibrolipomas are often more firm and tough to the touch than other lipomas. They are slightly mobile under the skin, and compress with pressure.
Paraneoplastic acrokeratosis, or Bazex syndrome is a cutaneous condition characterized by psoriasiform changes of hands, feet, ears, and nose, with involvement of the nails and periungual tissues being characteristic and indistinguishable from psoriatic nails. The condition is associated with carcinomas of the upper aerodigestive tract.
Benign symmetric lipomatosis, also known as Madelung's disease, is an adult-onset skin condition characterized by extensive symmetric fat deposits in the head, neck, and shoulder girdle area. The symmetrical fat deposits are made of unencapsulated lipomas, which distinguishes it from typical lipomatosis which has encapsulated lipomas that are not usually symmetrical. Benjamin Brodie described the condition in 1846. The German surgeon Otto Wilhelm Madelung was the first to give a detailed description of the disorder in 1888, followed by Launois and Bensaude in 1898.

A myxoid cyst is a cutaneous condition often characterized by nail plate depression and grooves.

Laryngo-onycho-cutaneous syndrome is a rare epithelial disorder inherited in an autosomal recessive fashion. It is characterized by abnormalities in the larynx, nails, and skin ("cutaneous"). The disorder is only found in Punjabi Muslims and only a few cases have been reported.
Oculocerebrocutaneous syndrome is a condition characterized by orbital cysts, microphthalmia, porencephaly, agenesis of the corpus callosum, and facial skin tags.
Hemihyperplasia–multiple lipomatosis syndrome is a cutaneous condition characterized by multiple lipomas in association with asymmetric overgrowth, cutaneous capillary malformations, and thickened plantar skin with prominent creases.
Encephalocraniocutaneous lipomatosis (ECCL), is a rare condition primarily affecting the brain, eyes, and skin of the head and face. It is characterized by unilateral subcutaneous and intracranial lipomas, alopecia, unilateral porencephalic cysts, epibulbar choristoma and other ophthalmic abnormalities. This condition is described as sporadic because it occurs in people without a history of the disorder in their family.

Facial infiltrating lipomatosis (FIL), also referred to as congenital infiltrating lipomatosis of the face or facial infused lipomatosis, is an ultra-rare craniofacial overgrowth condition caused by a genetic mutation of the PIK3CA gene. The condition is a part of the PIK3CA related overgrowth spectrum (PROS). The disease is congenital and non-hereditary. First described by Slavin and colleagues in 1983.

Familial multiple lipomatosis is a hereditary adipose tissue disorder that is characterized by the formation of multiple lipomas that occur in a particular distribution. The lipomas are well-encapsulated, slow-growing, benign fatty tumors. The distribution is defined as being focused in the trunk of the body and extremities. Familial Multiple Lipomatosis can be identified when multiple lipomas occur in multiple family members that span different generations. Some people may have hundreds of lipomas present.
References
- ↑ Rapini, Ronald P.; Bolognia, Jean L.; Jorizzo, Joseph L. (2007). Dermatology: 2-Volume Set. St. Louis: Mosby. ISBN 978-1-4160-2999-1.
- ↑ Encephalocraniocutaneous Lipomatosis and Didymosis Aplasticopsilolipara