
Metro-North Railroad, trading as MTA Metro-North Railroad, is a suburban commuter rail service operated by the Metropolitan Transportation Authority (MTA), a public authority of the U.S. state of New York. Metro-North serves the New York Metropolitan Area, running service between New York City and its northern suburbs in New York and Connecticut, including Port Jervis, Spring Valley, Poughkeepsie, Yonkers, New Rochelle, Mount Vernon, White Plains, Southeast and Wassaic in New York and Stamford, New Canaan, Danbury, Bridgeport, Waterbury, and New Haven in Connecticut. Service in Connecticut is operated under contract with the Connecticut Department of Transportation. Metro-North also provides local rail service within the New York City boroughs of Manhattan and the Bronx.

New Haven Union Station is the main railroad passenger station in New Haven, Connecticut. It is the third such station in the city of New Haven, preceded by both an 1848 built station in a different location, and an 1879 built station near the current station's location. Designed by noted American architect Cass Gilbert, the present beaux-arts Union Station was completed and opened in 1920 after the previous Union Station was destroyed by fire. It served the New York, New Haven and Hartford Railroad for the next five decades, but fell into decline following World War II along with the United States railroad industry as a whole.

The Vermonter is a passenger train operated by Amtrak between St. Albans, Vermont, and Washington, D.C., via New York City. It replaced the overnight Montrealer, which terminated in Montreal until 1995. Amtrak receives funding from the states of Connecticut, Massachusetts, and Vermont for Vermonter operations north of New Haven.

Shore Line East (SLE) is a commuter rail service which operates along the Northeast Corridor through southern Connecticut, United States. The rail service is a fully owned subsidiary of the Connecticut Department of Transportation (CTDOT) and is operated under the CT Rail brand. SLE provides service seven days a week along the Northeast Corridor between New London and New Haven; limited through service west of New Haven to Bridgeport and Stamford has been suspended since 2020. Cross-platform transfers to Metro-North Railroad New Haven Line trains are available at New Haven for service to southwestern Connecticut and New York City. Pre-COVID, around 2,200 riders used the service on weekdays.

The New Haven Line is a 72.7 mi (117.0 km) commuter rail line operated by the Metro-North Railroad in the U.S. states of New York and Connecticut. Running from New Haven, Connecticut, to New York City, the New Haven Line joins the Harlem Line in Mount Vernon, New York, and continues south to Grand Central Terminal in Manhattan. The New Haven Line carries 125,000 passengers every weekday and 39 million passengers a year. The busiest intermediate station is Stamford, with 8.4 million passengers, or 21% of the line's ridership.

The New Canaan Branch is an 8.2-mile (13 km) long branch line of the Metro-North Railroad New Haven Line that begins from a junction east of downtown Stamford, Connecticut, north to New Canaan. It opened in 1868 as the New Canaan Railroad.

The Danbury Branch is a diesel branch of the Metro-North Railroad's New Haven Line in the U.S. state of Connecticut, running from downtown Norwalk north to Danbury. It opened in 1852 as the Danbury and Norwalk Railroad. Until the early 1970s, passenger service continued north from Danbury to Canaan, Connecticut, and Pittsfield, Massachusetts. Metro-North took over operation of the line from Conrail in 1983, and the modern-day branch is mostly single-tracked.

The New Haven–Springfield Line is a railroad line owned by Amtrak from New Haven, Connecticut, north to Springfield, Massachusetts, serving the Knowledge Corridor. As a branch of the Northeast Corridor just north of New Haven State Street station, it is served by approximately seven daily Northeast Regional round trips, some continuing from New Haven to Washington, D.C., along the Corridor and others terminating at New Haven as shuttles. On weekends, there is one train daily to Roanoke, Virginia. It is also served by the daily Vermonter, which starts in Washington, D.C., and continues north from Springfield, finally terminating in St. Albans, Vermont. The line is part of the Inland Route connecting Boston and New York via Hartford, Springfield, and Worcester, in contrast to the "Shore Line" along the Connecticut Shore and through Rhode Island.

The Connecticut Southern Railroad is a 90-mile (140 km) long short-line railroad operating in Connecticut and Massachusetts. The company was formed in 1996 as a spinoff of Conrail by shortline holding company RailTex and subsequently acquired in 2000 by RailAmerica. Since 2012, it has been a subsidiary of Genesee & Wyoming. CSO is headquartered in Hartford, Connecticut, site of its Hartford Yard. The company also operates East Hartford Yard.

The M2, M4 and M6 were three similar series of electric multiple unit rail cars produced by the Budd Company (M2), Tokyu Car Corporation (M4), and Morrison-Knudsen (M6) for the Metropolitan Transportation Authority (MTA) and the Connecticut Department of Transportation (ConnDOT). Initially branded as the Cosmopolitans, the cars were later more popularly known under their model names, M2, M4, M6. They ran on the New Haven Line for most of their service life.

The Hartford Line is a commuter rail service between New Haven, Connecticut, and Springfield, Massachusetts, using the Amtrak-owned New Haven–Springfield Line. The project is a joint venture between the states of Connecticut and Massachusetts, with support from the federal government as well. CT Rail-branded trains provide service along the corridor, and riders can use Hartford Line tickets to travel on board most Amtrak trains along the corridor at the same prices. The service launched on June 16, 2018.

The M8 is an electric multiple unit railroad car built by Kawasaki for use on the Metro-North Railroad New Haven Line and the CTrail Shore Line East. The fleet of 471 cars first entered service in 2011, replacing the M2, M4 and M6 cars, which entered service in 1973, 1987 and 1994, respectively. An additional 60-car order is currently finishing delivery in response to increased ridership and usage on Shore Line East.

New Canaan station is a commuter rail station on the New Canaan Branch of the Metro-North Railroad's New Haven Line in New Canaan, Connecticut.

The Fairfield/Bridgeport train crash occurred on May 17, 2013, when a Metro-North Railroad passenger train derailed between the Fairfield Metro and Bridgeport stations in Fairfield, Connecticut, in the United States. The derailed train fouled the adjacent line and a train heading in the opposite direction then collided with it. There were at least 65 injured among the approximately 250 people on board each of the two trains. Metro-North reported damages at $18.5 million.
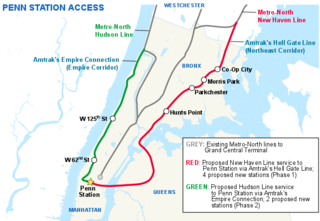
Penn Station Access (PSA) is a public works project underway by the Metropolitan Transportation Authority in New York City. The goal of the project is to allow Metro-North Railroad commuter trains to access Penn Station on Manhattan's West Side, using existing trackage owned by Amtrak. Metro-North trains currently terminate exclusively at Grand Central in Midtown Manhattan.

County Yard is a rail yard complex comprising Adams Yard, Delco Lead, and the eponymous County Yard along the Northeast Corridor (NEC). The complex straddles the New Brunswick and North Brunswick border in Central New Jersey.
The Metro-North Railroad is a commuter railroad serving northern suburbs of New York City. It principally uses a fleet of electric railcars for its services; diesel locomotives and push-pull coaches are in use as well for non-electrified portions of the system.

Barnum station is a planned regional rail station to be located on the Metro-North Railroad's New Haven Line in East Bridgeport, Connecticut. The station will be named after the circus showman and former Bridgeport mayor P. T. Barnum, and will be located on the south side of Barnum Avenue between Seaview Avenue and Pembroke Street. A feasibility study was released in July 2013, followed by preliminary planning funding in July 2014 and an application for planning funding in June 2015. By January 2017, the station was planned to open in 2021. However, the project was indefinitely postponed in January 2019.

CT Rail, stylized as CTrail, is the brand for commuter rail services overseen by the Connecticut Department of Transportation (CTDOT), in the U.S. state of Connecticut, with some service extending into Massachusetts. CTDOT oversees two lines: Shore Line East, between New Haven and New London, Connecticut, and the Hartford Line, from New Haven, through Hartford, to Springfield, Massachusetts.

Cedar Hill Yard is a classification yard located in New Haven, North Haven and Hamden, Connecticut, United States. It was built by the New York, New Haven and Hartford Railroad in the early 1890s in and around New Haven's Cedar Hill neighborhood, which gave the yard its name. Electrical catenary for electric locomotives was added to the yard in 1915. To handle increasing traffic as a result of World War I, the yard was greatly expanded between 1917 and 1920 with additional construction along both sides of the Quinnipiac River. The construction project added two humps where railroad cars were sorted into trains by gravity. The yard was further modernized in the 1920s, becoming one of the busiest railroad yards in the United States, and the most important yard in the entire New Haven Railroad system.




















