Related Research Articles

Coronary artery disease (CAD), also called coronary heart disease (CHD), ischemic heart disease (IHD), myocardial ischemia, or simply heart disease, involves the reduction of blood flow to the heart muscle due to build-up of atherosclerotic plaque in the arteries of the heart. It is the most common of the cardiovascular diseases. Types include stable angina, unstable angina, myocardial infarction, and sudden cardiac death. A common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which may travel into the shoulder, arm, back, neck, or jaw. Occasionally it may feel like heartburn. Usually symptoms occur with exercise or emotional stress, last less than a few minutes, and improve with rest. Shortness of breath may also occur and sometimes no symptoms are present. In many cases, the first sign is a heart attack. Other complications include heart failure or an abnormal heartbeat.

Angina, also known as angina pectoris, is chest pain or pressure, usually caused by insufficient blood flow to the heart muscle (myocardium). It is most commonly a symptom of coronary artery disease.

Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome, a group of signs and symptoms, caused by an impairment of the heart's blood pumping function. Symptoms typically include shortness of breath, excessive fatigue, and leg swelling. The shortness of breath may occur with exertion or while lying down, and may wake people up during the night. Chest pain, including angina, is not usually caused by heart failure, but may occur if the heart failure was caused by a heart attack. The severity of the heart failure is mainly decided based on ejection fraction and also measured by the severity of symptoms. Other conditions that may have symptoms similar to heart failure include obesity, kidney failure, liver disease, anemia, and thyroid disease.

A cardiac stress test is a cardiological test that measures the heart's ability to respond to external stress in a controlled clinical environment. The stress response is induced by exercise or by intravenous pharmacological stimulation.

Valvular heart disease is any cardiovascular disease process involving one or more of the four valves of the heart. These conditions occur largely as a consequence of aging, but may also be the result of congenital (inborn) abnormalities or specific disease or physiologic processes including rheumatic heart disease and pregnancy.

Variant angina, also known as Prinzmetal angina,vasospastic angina, angina inversa, coronary vessel spasm, or coronary artery vasospasm, is a syndrome typically consisting of angina. Variant angina differs from stable angina in that it commonly occurs in individuals who are at rest or even asleep, whereas stable angina is generally triggered by exertion or intense exercise. Variant angina is caused by vasospasm, a narrowing of the coronary arteries due to contraction of the heart's smooth muscle tissue in the vessel walls. In comparison, stable angina is caused by the permanent occlusion of these vessels by atherosclerosis, which is the buildup of fatty plaque and hardening of the arteries.

Unstable angina is a type of angina pectoris that is irregular or more easily provoked. It is classified as a type of acute coronary syndrome (ACS).
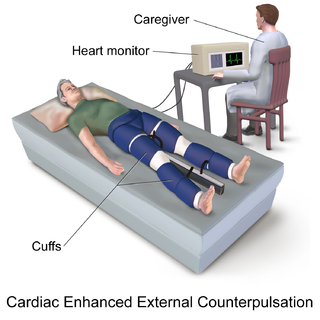
External counterpulsation therapy (ECP) is a procedure that may be performed on individuals with angina, heart failure, or cardiomyopathy.
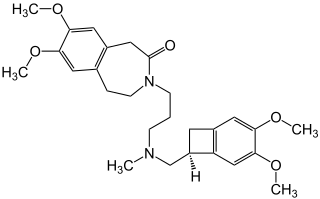
Ivabradine, sold under the brand name Procoralan among others, is a medication, which is a pacemaker current (If) inhibitor, used for the symptomatic management of heart-related chest pain and heart failure. Patients who qualify for use of Ivabradine for coronary heart failure are patients who have symptomatic heart failure, with reduced ejection volume, and heart rate at least 70 bpm, and the condition not able to be fully managed by beta blockers.
Coronary vasospasm refers to when a coronary artery suddenly undergoes either complete or sub-total temporary occlusion.

Ranolazine, sold under the brand name Ranexa among others, is a medication used to treat heart related chest pain. Typically it is used together with other medications when those are insufficient. Benefits appear smaller in women than men. It is taken by mouth.
The Canadian Cardiovascular Society (CCS) is the national voice for cardiovascular physicians and scientists in Canada. The CCS is a membership organization that represents more than 1,800 professionals in the cardiovascular field. Its mission is to promote cardiovascular health and care through knowledge translation, professional development and leadership in health policy.

Coronary ischemia, myocardial ischemia, or cardiac ischemia, is a medical term for a reduced blood flow in the coronary circulation through the coronary arteries. Coronary ischemia is linked to heart disease, and heart attacks. Coronary arteries deliver oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscle. Reduced blood flow to the heart associated with coronary ischemia can result in inadequate oxygen supply to the heart muscle. When oxygen supply to the heart is unable to keep up with oxygen demand from the muscle, the result is the characteristic symptoms of coronary ischemia, the most common of which is chest pain. Chest pain due to coronary ischemia commonly radiates to the arm or neck. Certain individuals such as women, diabetics, and the elderly may present with more varied symptoms. If blood flow through the coronary arteries is stopped completely, cardiac muscle cells may die, known as a myocardial infarction, or heart attack.
Cardiorenal syndrome (CRS) is an umbrella term used in the medical field that defines disorders of the heart and kidneys whereby "acute or chronic dysfunction in one organ may induce acute or chronic dysfunction of the other". The kidney and the heart are compared to a marriage that has "bumps" in the road, some may even say it can come to an end. The heart and kidney play vital functions that contribute to the wellbeing of the body in a healthy person. When one of these organs fail, the other subsequently fails as well, like a domino affect. The heart and the kidneys are involved in maintaining hemodynamic stability and organ perfusion through an intricate network. Patients who have renal failure first may be hard to determine if heart failure is concurrent. These two organs communicate with one another through a variety of pathways in an interdependent relationship. In a 2004 report from National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute, CRS was defined as a condition where treatment of congestive heart failure is limited by decline in kidney function. This definition has since been challenged repeatedly but there still remains little consensus over a universally accepted definition for CRS. At a consensus conference of the Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative (ADQI), the CRS was classified into five subtypes primarily based upon the organ that initiated the insult as well as the acuity of disease.
A diagnosis of myocardial infarction is created by integrating the history of the presenting illness and physical examination with electrocardiogram findings and cardiac markers. A coronary angiogram allows visualization of narrowings or obstructions on the heart vessels, and therapeutic measures can follow immediately. At autopsy, a pathologist can diagnose a myocardial infarction based on anatomopathological findings.
The Canadian Cardiovascular Societygrading of angina pectoris is a classification system used to grade the severity of exertional angina.
The Q-Symbio study was an international multi-center clinical trial that was reported in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology: Heart Failure in September 2014.

Ischemic cardiomyopathy is a type of cardiomyopathy caused by a narrowing of the coronary arteries which supply blood to the heart. Typically, patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy have a history of acute myocardial infarction, however, it may occur in patients with coronary artery disease, but without a past history of acute myocardial infarction. This cardiomyopathy is one of the leading causes of sudden cardiac death. The adjective ischemic means characteristic of, or accompanied by, ischemia — local anemia due to mechanical obstruction of the blood supply.
The European Heart Rhythm Association score of atrial fibrillation is a classification system for the extent of atrial fibrillation. It places patients in one of four categories based on how much they are limited during physical activity; the limitations/symptoms are in regard to normal breathing and varying degrees in shortness of breath and/or angina.

Richard Gorlin was an American cardiologist known for his contributions to the fields of valvular heart disease, coronary artery disease and cardiac catheterization, digitalis and vasodilators in congestive heart failure, and thrombolysis in myocardial infarctions. Along with his father, developed the Gorlin formula used to calculate valve areas in aortic valve stenosis and mitral valve stenosis.
References
- ↑ "Classification of Functional Capacity and Objective Assessment". professional.heart.org. Retrieved 2021-03-20.
- ↑ Raphael C, Briscoe C, Davies J, Ian Whinnett Z, Manisty C, Sutton R, Mayet J, Francis DP (April 2007). "Limitations of the New York Heart Association functional classification system and self-reported walking distances in chronic heart failure". Heart. 93 (4): 476–82. doi:10.1136/hrt.2006.089656. PMC 1861501 . PMID 17005715.
- ↑ The Criteria Committee of the New York Heart Association. (1994). Nomenclature and Criteria for Diagnosis of Diseases of the Heart and Great Vessels (9th ed.). Boston: Little, Brown & Co. pp. 253–256.