
The Federal Housing Administration (FHA), also known as the Office of Housing within the Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD), is a United States government agency founded by President Franklin Delano Roosevelt, established in part by the National Housing Act of 1934. Its primary function is to provide insurance for mortgages originated by private lenders for various types of properties, including single-family homes, multifamily rental properties, hospitals, and residential care facilities. FHA mortgage insurance serves to safeguard these private lenders from financial losses. In the event that a property owner defaults on their mortgage, FHA steps in to compensate the lender for the outstanding principal balance.

The Government National Mortgage Association (GNMA), or Ginnie Mae, is a government-owned corporation of the United States Federal Government within the Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD). It was founded in 1968 and works to expand affordable housing by guaranteeing housing loans (mortgages) thereby lowering financing costs such as interest rates for those loans. It does that through guaranteeing to investors the on-time payment of mortgage-backed securities (MBS) even if homeowners default on the underlying mortgages and the homes are foreclosed upon.

An FHA insured loan is a US Federal Housing Administration mortgage insurance backed mortgage loan that is provided by an FHA-approved lender. FHA mortgage insurance protects lenders against losses. They have historically allowed lower-income Americans to borrow money to purchase a home that they would not otherwise be able to afford. Because this type of loan is more geared towards new house owners than real estate investors, FHA loans are different from conventional loans in the sense that the house must be owner-occupant for at least a year. Since loans with lower down-payments usually involve more risk to the lender, the home-buyer must pay a two-part mortgage insurance that involves a one-time bulk payment and a monthly payment to compensate for the increased risk. Frequently, individuals "refinance" or replace their FHA loan to remove their monthly mortgage insurance premium. Removing mortgage insurance premium by paying down the loan has become more difficult with FHA loans as of 2013.

Canada Mortgage and Housing Corporation is Canada's federal crown corporation responsible for administering the National Housing Act, with the mandate to improve housing by living conditions in the country.

In the United States, 80/20 housing is multifamily housing program that meets federal guidelines for tax-exempt financing. 80/20 housing developments reserve 20 percent of units as affordable housing, only to be rented by low-income residents, leaving the remaining 80 percent of units to be rented at the typical market rate. Housing projects that meet these the 80/20 rule receive tax-exempt financing from State Housing Finance Agencies (HFAs). The 80/20 program uses the Low-Income Housing Tax Credit (LIHTC) along with bond sales to finance housing projects.

The Mitchell–Lama Housing Program is a non-subsidy governmental housing guarantee in the state of New York. It was sponsored by New York State Senator MacNeil Mitchell and Assemblyman Alfred A. Lama and signed into law in 1955.
The New York State Housing Finance Agency (HFA) is a New York State public-benefit corporation created in 1960 to increase the supply of rental housing for low-income people by issuing bonds and providing low-interest mortgage loans to regulated housing companies.
The State of New York Mortgage Agency is a New York State public-benefit corporation created in 1970 by the state government of New York to provide affordable homeownership to low- and moderate-income New Yorkers. It offers affordably priced fixed-rate mortgages through several mortgage programs for eligible homebuyers. Each program offers competitive interest rates, low down payments, down payment assistance and no prepayment penalties. SONYMA offers its programs through a network of participating lenders throughout New York state who contract with the agency to offer SONYMA's programs to their customers. The mortgage loans are purchased from the lenders by SONYMA, which funds the purchases by issuing tax-exempt bonds. In 2017, it had operating expenses of $62.57 million, an outstanding debt of $2.533 billion, and a staff level of 275 people.

The Texas Department of Housing and Community Affairs (TDHCA) is the state's lead agency responsible for homeownership, affordable rental housing, community and energy assistance programs, and colonia activities serving primarily low income Texans. The Manufactured Housing Division of TDHCA regulates the manufactured housing industry in Texas. The Department annually administers more than $400 million through for-profit, nonprofit, and local government partnerships to deliver local housing and community-based opportunities and assistance to Texans in need. The department is headquartered at 221 East 11th Street in Austin.

The California Housing Finance Agency (CalHFA), established in 1975, is an independent California state agency within the California Department of Housing and Community Development that makes low-rate housing loans through the sale of taxable and tax exempt bonds.
Deborah VanAmerongen joined Nixon Peabody as a strategic policy adviser in February 2010. She works closely with attorneys in the firm's Affordable Housing practice to provide advice to developers, owners, and managers of affordable housing, as well as their financing partners, in the preservation and production of affordable housing nationwide.
The Vermont Housing Finance Agency (VHFA) is chartered as a private non-profit agency to finance and promote affordable housing opportunities for low- and moderate- income Vermonters. They are located in Burlington, Vermont.

The New York State Executive Department of the New York state government serves as the administrative department of the Governor of New York. This department has no central operating structure; it consists of a number of divisions, offices, boards, commissions, councils, and other independent agencies that provide policy advice and assistance to the governor and conduct activities according to statute or executive order. Its regulations are compiled in title 9 of the New York Codes, Rules and Regulations.
Kentucky Housing Corporation (KHC), the Kentucky state housing agency, was created by the 1972 Kentucky General Assembly to provide affordable housing opportunities. KHC is a self-supporting, public corporation.
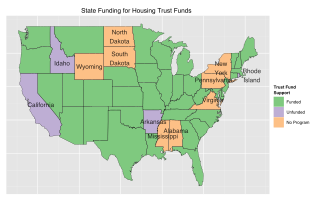
Housing trust funds are established sources of funding for affordable housing construction and other related purposes created by governments in the United States (U.S.). Housing Trust Funds (HTF) began as a way of funding affordable housing in the late 1970s. Since then, elected government officials from all levels of government in the U.S. have established housing trust funds to support the construction, acquisition, and preservation of affordable housing and related services to meet the housing needs of low-income households. Ideally, HTFs are funded through dedicated revenues like real estate transfer taxes or document recording fees to ensure a steady stream of funding rather than being dependent on regular budget processes. As of 2016, 400 state, local and county trust funds existed across the U.S.
Non-profit housing developers build affordable housing for individuals under-served by the private market. The non-profit housing sector is composed of community development corporations (CDC) and national and regional non-profit housing organizations whose mission is to provide for the needy, the elderly, working households, and others that the private housing market does not adequately serve. Of the total 4.6 million units in the social housing sector, non-profit developers have produced approximately 1.547 million units, or roughly one-third of the total stock. Since non-profit developers seldom have the financial resources or access to capital that for-profit entities do, they often use multiple layers of financing, usually from a variety of sources for both development and operation of these affordable housing units.
A USDA Home Loan from the USDA loan program, also known as the USDA Rural Development Guaranteed Housing Loan Program, is a mortgage loan offered to rural property owners by the United States Department of Agriculture, Rural Development.
The Texas State Affordable Housing Corporation (TSAHC) is a nonprofit affordable housing provider in Texas.
The Utah Housing Corporation or UHC is a public corporation that the Utah legislature created in 1975 to advocate for affordable housing for lower-income residents in the state of Utah. UHC is an independent government agency that raises funds in order to offer mortgage loans to lower-income people and to provide resources to developers and builders for creating affordable housing projects. It does not receive any funds from the State of Utah and is completely self-supporting via the issuing of tax-exempt bonds and the creation of and selling of mortgage-backed securities to investors.
The New York State Division of Housing and Community Renewal (DHCR) is an agency of the New York state government responsible for administering housing and community development programs to promote affordable housing, community revitalization, and economic growth. Its primary functions include supervising rent regulations through the State Office of Rent Administration (ORA), administering affordable housing programs, providing financial assistance for housing development and rehabilitation, supporting community development initiatives, ensuring compliance with fair housing laws, and managing the Weatherization Assistance Program. DHCR has been criticized by tenant rights groups for its failure to monitor their own programs and massive delays in investigating cases of the illegal deregulation due to an extensive backlog.









