
Insurance is a means of protection from financial loss. It is a form of risk management, primarily used to hedge against the risk of a contingent or uncertain loss.

Workers' compensation or workers' comp is a form of insurance providing wage replacement and medical benefits to employees injured in the course of employment in exchange for mandatory relinquishment of the employee's right to sue his or her employer for the tort of negligence. The trade-off between assured, limited coverage and lack of recourse outside the worker compensation system is known as "the compensation bargain". One of the problems that the compensation bargain solved is the problem of employers becoming insolvent as a result of high damage awards. The system of collective liability was created to prevent that, and thus to ensure security of compensation to the workers.
Health insurance or medical insurance is a type of insurance that covers the whole or a part of the risk of a person incurring medical expenses. As with other types of insurance, risk is shared among many individuals. By estimating the overall risk of health risk and health system expenses over the risk pool, an insurer can develop a routine finance structure, such as a monthly premium or payroll tax, to provide the money to pay for the health care benefits specified in the insurance agreement. The benefit is administered by a central organization, such as a government agency, private business, or not-for-profit entity.
Universal health care is a health care system in which all residents of a particular country or region are assured access to health care. It is generally organized around providing either all residents or only those who cannot afford on their own, with either health services or the means to acquire them, with the end goal of improving health outcomes.

The U.S. Railroad Retirement Board (RRB) is an independent agency in the executive branch of the United States government created in 1935 to administer a social insurance program providing retirement benefits to the country's railroad workers.

Liberty Mutual Group is an American diversified global insurer and the sixth-largest property and casualty insurer in the United States. It ranks 71st on the Fortune 100 list of largest corporations in the United States based on 2020 revenue. Based in Boston, Massachusetts, and featuring the Statue of Liberty on its logo, it employs over 45,000 people in more than 900 locations throughout the world. As of December 31, 2021, Liberty Mutual Insurance had $156.043 billion in consolidated assets, $128.195 billion in consolidated liabilities and $48.2 billion in annual consolidated revenue.
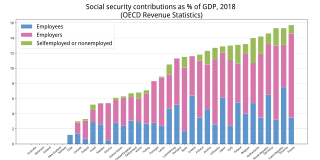
Social insurance is a form of social welfare that provides insurance against economic risks. The insurance may be provided publicly or through the subsidizing of private insurance. In contrast to other forms of social assistance, individuals' claims are partly dependent on their contributions, which can be considered insurance premiums to create a common fund out of which the individuals are then paid benefits in the future.
Liability insurance is a part of the general insurance system of risk financing to protect the purchaser from the risks of liabilities imposed by lawsuits and similar claims and protects the insured if the purchaser is sued for claims that come within the coverage of the insurance policy.

The Workplace Safety and Insurance Board is the workplace compensation board for provincially regulated workplaces in Ontario. As an agency of the Ontario government, the WSIB operates "at arm's length" from the Ministry of Labour, Training and Skills Development and is solely funded by employer premiums, administration fees, and investment revenue. The WSIB is one of the largest compensation boards in North America and is primarily responsible for administering and enforcing the Ontario Workplace Safety and Insurance Act (WSIA).

The State Compensation Insurance Fund is a workers' compensation insurer that was created as a "public enterprise fund" by the U.S. state of California, and today has partial autonomy from the rest of the state government. It is required by state law to maintain its headquarters in San Francisco, but has regional offices all over the state.
The New York Disability Benefits Law (DBL) is article 9 of the Workers' Compensation Law and creates a state disability insurance program designed to provide employees with some level of income replacement in case of disability caused off-the-job.
Disability Insurance, often called DI or disability income insurance, or income protection, is a form of insurance that insures the beneficiary's earned income against the risk that a disability creates a barrier for completion of core work functions. For example, the worker may be unable to maintain composure in the case of psychological disorders or sustain an injury, illness or condition that causes physical impairment or incapacity to work. DI encompasses paid sick leave, short-term disability benefits (STD), and long-term disability benefits (LTD). The same concept is instantiated in some countries as income protection insurance.
Australia's insurance market can be divided into roughly three components: life insurance, general insurance and health insurance. These markets are fairly distinct, with most larger insurers focusing on only one type, although in recent times several of these companies have broadened their scope into more general financial services, and have faced competition from banks and subsidiaries of foreign financial conglomerates. With services such as disability insurance, income protection and even funeral insurance, these insurance giants are stepping in to fill the gap where people may have otherwise been in need of a personal or signature loan from their financial institution.
The State Accident Insurance Fund Corporation (SAIF) is a not-for-profit, state-chartered workers’ compensation insurance company in the U.S. state of Oregon. It provides workers' compensation insurance and workplace safety services for Oregon employers, and claim management for injured workers. It is based in Salem, Oregon.
Health insurance in the United States is any program that helps pay for medical expenses, whether through privately purchased insurance, social insurance, or a social welfare program funded by the government. Synonyms for this usage include "health coverage", "health care coverage", and "health benefits". In a more technical sense, the term "health insurance" is used to describe any form of insurance providing protection against the costs of medical services. This usage includes both private insurance programs and social insurance programs such as Medicare, which pools resources and spreads the financial risk associated with major medical expenses across the entire population to protect everyone, as well as social welfare programs like Medicaid and the Children's Health Insurance Program, which both provide assistance to people who cannot afford health coverage.
The Defense Base Act (DBA) is an extension of the federal workers' compensation program that covers longshoremen and harbor workers, the Longshore and Harbor Workers' Compensation Act 33 U.S.C. §§ 901–950. The DBA covers persons employed at United States defense bases overseas. The DBA is designed to provide medical treatment and compensation to employees of defense contractors injured in the scope and course of employment. The DBA is administered by the United States Department of Labor.
The Ohio Bureau of Workers' Compensation provides medical and compensation benefits for work-related injuries, diseases and deaths. It was founded in 1912. With assets under management of more than $29 billion, it is the largest state-operated and second largest overall provider of workers’ compensation insurance in the United States.
The Virginia Workers' Compensation Commission (VWC) is an agency of the U.S. state of Virginia that oversees the resolution of workers' compensation claims brought in that state, in accordance with the Virginia Workers' Compensation Act. The Commission has exclusive jurisdiction to adjudicate such claims. Its decisions may be appealed to the Virginia Court of Appeals. The Commission is led by a Senior Leadership team consisting of three Commissioners, an Executive Director and a Chief Deputy Commissioner. The Commissioners are appointed by the Virginia General Assembly and serve staggered six-year terms. Honorable Robert A. Rapaport, Honorable Wesley G. Marshall and Honorable R. Ferrell Newman currently serve as Commissioners. The Commissioners elect a Chairman for a term of three years. Commissioner Rapaport currently serves as Chairman. Ms. Evelyn McGill is the Commission’s Executive Director and Honorable James J. Szablewicz is the Commission’s Chief Deputy Commissioner. The Commission is headquartered in Richmond, Virginia, and has offices and hearing locations at various places around the state.
Berkshire Hathaway GUARD Insurance Companies currently insure over 250,000 businesses in the US.
Workers' compensation in the United States is a primarily state-based system of workers' compensation.







