The New Zealand Dermatological Society is a not-for-profit incorporated society for dermatologists in New Zealand. Its website for public education, DermNet, was started in 1996. [1]
The New Zealand Dermatological Society is a not-for-profit incorporated society for dermatologists in New Zealand. Its website for public education, DermNet, was started in 1996. [1]

Dermatitis is inflammation of the skin, typically characterized by itchiness, redness and a rash. In cases of short duration, there may be small blisters, while in long-term cases the skin may become thickened. The area of skin involved can vary from small to covering the entire body. Dermatitis is often called eczema, and the difference between those terms is not standardized.
Dermatology is the branch of medicine dealing with the skin. It is a speciality with both medical and surgical aspects. A dermatologist is a specialist medical doctor who manages diseases related to skin, hair, nails, and some cosmetic problems.

Indoor tanning involves using a device that emits ultraviolet radiation to produce a cosmetic tan. Typically found in tanning salons, gyms, spas, hotels, and sporting facilities, and less often in private residences, the most common device is a horizontal tanning bed, also known as a sunbed or solarium. Vertical devices are known as tanning booths or stand-up sunbeds.

Podiatry, or podiatric medicine, also known as chiropody, is a branch of medicine devoted to the study, diagnosis, and treatment of disorders of the foot, and ankle. The healthcare professional is known as a podiatrist. The US podiatric medical school curriculum includes lower extremity anatomy, general human anatomy, physiology, general medicine, physical assessment, biochemistry, neurobiology, pathophysiology, genetics and embryology, microbiology, histology, pharmacology, women's health, physical rehabilitation, sports medicine, research, ethics and jurisprudence, biomechanics, general principles of orthopedic surgery, and foot and ankle surgery.
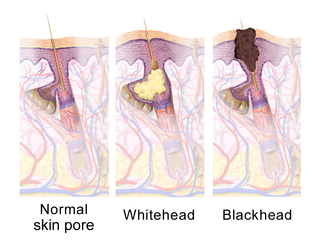
A comedo is a clogged hair follicle (pore) in the skin. Keratin combines with oil to block the follicle. A comedo can be open (blackhead) or closed by skin (whitehead) and occur with or without acne. The word "comedo" comes from the Latin comedere, meaning "to eat up", and was historically used to describe parasitic worms; in modern medical terminology, it is used to suggest the worm-like appearance of the expressed material.
Selenium disulfide, also known as selenium sulfide, is a chemical compound and medication used to treat seborrheic dermatitis, dandruff, and pityriasis versicolor. It is applied to the affected area as a lotion or shampoo. Symptoms frequently return if treatment is stopped.
The International League of Dermatological Societies (ILDS) is a non-governmental organization that works closely with the World Health Organization. It was founded in 1935, but because of World War II no congresses were held until 1952. It is governed by the International Committee of Dermatology.
The Royal Australasian College of Physicians (RACP) is a not-for-profit professional organisation responsible for training and educating physicians and paediatricians across Australia and New Zealand.

A squamous cell papilloma is a generally benign papilloma that arises from the stratified squamous epithelium of the skin, lip, oral cavity, tongue, pharynx, larynx, esophagus, cervix, vagina or anal canal. Squamous cell papillomas are typically associated with human papillomavirus (HPV) while sometimes the cause is unknown.
Teledermatology is a subspecialty in the medical field of dermatology and probably one of the most common applications of telemedicine and e-health. In teledermatology, telecommunication technologies are used to exchange medical information over a distance using audio, visual, and data communication. Applications comprise health care management such as diagnoses, consultation, and treatment as well as (continuous) education.
Readily visible alterations of the skin surface have been recognized since the dawn of history, with some being treated, and some not. One of the earliest known sources documenting skin ailments is the Ebers Papyrus, a medical document from ancient Egypt dating to around 1500 BC. It describes various skin diseases, including ulcers, rashes, and tumors, and prescribes surgery and ointments to treat the ailments.
Phlebology is a medical speciality that is concerned with venous issues including the diagnosis and treatment of disorders of the veins. A medical specialist in this field is known as a phlebologist. The specialty of phlebology has developed to enable physicians sharing an interest in venous disease and health to share knowledge and experience despite being trained in a variety of backgrounds such as dermatology, vascular surgery, haematology, interventional radiology or general medicine. Diagnostic techniques used include the patient's history and physical examination, venous imaging techniques in particular vascular ultrasound and laboratory evaluation related to venous thromboembolism. The American Medical Association and the American Osteopathic Association have added phlebology to their list of self-designated practice specialties.
Alan Menter is an English-born dermatologist, and former flyhalf rugby union player for the Springboks.
The American College of Mohs Surgery is a membership-based organization of surgeons who are fellowship-trained (FACMS) in Mohs surgery, a technique that removes skin cancer in stages, one tissue layer at a time. The ACMS is the oldest and largest professional membership organization for Mohs surgeons.
Indira Gandhi Institute of Child Health is a premier organization promoting tertiary level Child Health Care services. It is government-run referral centre for children in Karnataka state, India and it is an autonomous body, registered under the Karnataka Societies Registration Act 1960 and functioning under the control of the Ministry of Medical Education, Government of Karnataka. It is located in Jayanagar 1st Block, Bangalore.

Daisy Maude Orleman Robinson was an American medical doctor, a dermatologist, decorated for her work in France during World War I.
DermNet is a New Zealand-based clinical resource website about dermatology and skin conditions. Its founder and former editor-in-chief is dermatologist and Adjunct Associate Professor Amanda Oakley. The website was launched in 1996 under the umbrella of the New Zealand Dermatological Society, and as of 2017, around 2 million people access the website monthly.

Carl Emanuel Flemming Rasch was a Danish dermatologist and venereologist who in 1900 coined the term "polymorphic light eruption", following his studies of the effect of sunlight on the skin.

Amanda Margaret Meredith Oakley is a New Zealand-based dermatologist, specialising in melanoma research and teledermatology. She is a founder and former editor-in-chief of DermNet.