Related Research Articles

A geographic coordinate system (GCS) is a coordinate system associated with positions on Earth. A GCS can give positions:

A grid reference system, also known as grid reference or grid system, is a geographic coordinate system that defines locations in maps using Cartesian coordinates based on a particular map projection. Grid lines on maps illustrate the underlying coordinate system. Such coordinate lines are numbered to provide a unique reference to each location on the map. Grid coordinates are normally eastings and northings.

The Ordnance Survey National Grid reference system is a system of geographic grid references used in Great Britain, distinct from latitude and longitude.
In geodesy, conversion among different geographic coordinate systems is made necessary by the different geographic coordinate systems in use across the world and over time. Coordinate conversion is composed of a number of different types of conversion: format change of geographic coordinates, conversion of coordinate systems, or transformation to different geodetic datums. Geographic coordinate conversion has applications in cartography, surveying, navigation and geographic information systems.
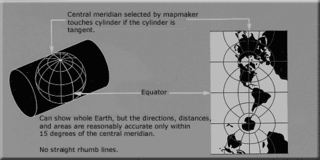
The transverse Mercator map projection is an adaptation of the standard Mercator projection. The transverse version is widely used in national and international mapping systems around the world, including the Universal Transverse Mercator. When paired with a suitable geodetic datum, the transverse Mercator delivers high accuracy in zones less than a few degrees in east-west extent.

The Irish grid reference system is a system of geographic grid references used for paper mapping in Ireland. The Irish grid partially overlaps the British grid, and uses a similar co-ordinate system but with a meridian more suited to its westerly location.

ED50 is a geodetic datum which was defined after World War II for the international connection of geodetic networks.

The oblique Mercator map projection is an adaptation of the standard Mercator projection. The oblique version is sometimes used in national mapping systems. When paired with a suitable geodetic datum, the oblique Mercator delivers high accuracy in zones less than a few degrees in arbitrary directional extent.

The Universal Transverse Mercator (UTM) is a system for assigning coordinates to locations on the surface of the Earth. Like the traditional method of latitude and longitude, it is a horizontal position representation, which means it ignores altitude and treats the earth as a perfect ellipsoid. However, it differs from global latitude/longitude in that it divides earth into 60 zones and projects each to the plane as a basis for its coordinates. Specifying a location means specifying the zone and the x, y coordinate in that plane. The projection from spheroid to a UTM zone is some parameterization of the transverse Mercator projection. The parameters vary by nation or region or mapping system.

The universal polar stereographic (UPS) coordinate system is used in conjunction with the universal transverse Mercator (UTM) coordinate system to locate positions on the surface of the earth. Like the UTM coordinate system, the UPS coordinate system uses a metric-based cartesian grid laid out on a conformally projected surface. UPS covers the Earth's polar regions, specifically the areas north of 84°N and south of 80°S, which are not covered by the UTM grids, plus an additional 30 minutes of latitude extending into UTM grid to provide some overlap between the two systems.

A Lambert conformal conic projection (LCC) is a conic map projection used for aeronautical charts, portions of the State Plane Coordinate System, and many national and regional mapping systems. It is one of seven projections introduced by Johann Heinrich Lambert in his 1772 publication Anmerkungen und Zusätze zur Entwerfung der Land- und Himmelscharten.

A spatial reference system (SRS) or coordinate reference system (CRS) is a coordinate-based local, regional or global system used to locate geographical entities. A spatial reference system defines a specific map projection, as well as transformations between different spatial reference systems. Spatial reference systems are defined by the OGC's Simple Feature Access using well-known text representation of coordinate reference systems, and support has been implemented by several standards-based geographic information systems. Spatial reference systems can be referred to using a SRID integer, including EPSG codes defined by the International Association of Oil and Gas Producers. It is specified in ISO 19111:2007 Geographic information—Spatial referencing by coordinates, prepared by ISO/TC 211, also published as OGC Abstract Specification, Topic 2: Spatial referencing by coordinate.
The State Plane Coordinate System (SPCS) is a set of 124 geographic zones or coordinate systems designed for specific regions of the United States. Each state contains one or more state plane zones, the boundaries of which usually follow county lines. There are 110 zones in the contiguous US, with 10 more in Alaska, 5 in Hawaii, and one for Puerto Rico and US Virgin Islands. The system is widely used for geographic data by state and local governments. Its popularity is due to at least two factors. First, it uses a simple Cartesian coordinate system to specify locations rather than a more complex spherical coordinate system. By using the Cartesian coordinate system's simple XY coordinates, "plane surveying" methods can be used, speeding up and simplifying calculations. Second, the system is highly accurate within each zone. Outside a specific state plane zone accuracy rapidly declines, thus the system is not useful for regional or national mapping.

Irish Transverse Mercator (ITM) is the geographic coordinate system for Ireland. It was implemented jointly by the Ordnance Survey Ireland (OSi) and the Ordnance Survey of Northern Ireland (OSNI) in 2001. The name is derived from the Transverse Mercator projection it uses and the fact that it is optimised for the island of Ireland.

The Hellenic Geodetic Reference System 1987 or HGRS87 is a geodetic system commonly used in Greece (SRID=2100). The system specifies a local geodetic datum and a projection system. In some documents it is called Greek Geodetic Reference System 1987 or GGRS87.
The Gauss–Boaga projection is a map projection used in Italy that uses a Hayford ellipsoid.

The British Mandate Palestine grid was the geographic coordinate system used by the Survey Department of Palestine.
The Geocentric Datum of Australia 1994 (GDA94) is a geodetic datum covering the Australian continent. Details of this datum are provided by the GDA94 Technical Manual.

The Cartography of New Zealand is the history of surveying and creation of maps of New Zealand. Surveying in New Zealand began with the arrival of Abel Tasman in the mid 17th century. Cartography and surveying have developed in incremental steps since that time till the integration of New Zealand into a global system based on GPS and the New Zealand Geodetic Datum 2000.
References
- ↑ "New Zealand Map Grid (NZMG) | Land Information New Zealand". LINZ. Retrieved 2015-07-31.
- ↑ "New Zealand Transverse Mercator 2000 (NZTM2000) | Land Information New Zealand". LINZ. Retrieved 2015-07-31.