Newfoundland is an island in North America and part of the province of Newfoundland and Labrador.
Contents
Newfoundland may also refer to:
Newfoundland is an island in North America and part of the province of Newfoundland and Labrador.
Newfoundland may also refer to:

Newfoundland and Labrador is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region of Labrador, having a total size of 405,212 km2 (156,453 sq mi) As of January 1, 2024, the population of Newfoundland and Labrador was estimated to be 541,391. The island of Newfoundland is home to around 94 per cent of the province's population, with more than half residing in the Avalon Peninsula. Labrador shares a land border with both the province of Quebec and the territory of Nunavut on Killiniq Island. The French overseas collectivity of Saint Pierre and Miquelon lies about 20 km (12 mi) west of the Burin Peninsula.
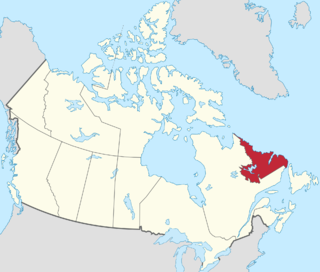
Labrador is a geographic and cultural region within the Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador. It is the primarily continental portion of the province and constitutes 71% of the province's area but is home to only 6% of its population. It is separated from the island of Newfoundland by the Strait of Belle Isle. It is the largest and northernmost geographical region in the four Atlantic provinces.
Canada has ten provinces and three territories that are sub-national administrative divisions under the jurisdiction of the Canadian Constitution. In the 1867 Canadian Confederation, three provinces of British North America—New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, and the Province of Canada —united to form a federation, becoming a fully independent country over the next century. Over its history, Canada's international borders have changed several times as it has added territories and provinces, making it the world's second-largest country by area.

The flag of Newfoundland and Labrador was introduced in 1980 and was designed by Newfoundland artist Christopher Pratt. The flag design was approved by the House of Assembly of the province of Newfoundland, Canada, on May 28, 1980. It was flown for the first time on Discovery Day, June 24, 1980. The name of the province was changed to Newfoundland and Labrador by an amendment to the constitution of Canada in December 2001 at the request of the provincial legislature.

British North America comprised the colonial territories of the British Empire in North America from 1783 onwards. English colonisation of North America began in the 16th century in Newfoundland, then further south at Roanoke and Jamestown, Virginia, and more substantially with the founding of the Thirteen Colonies along the Atlantic coast of North America.

Newfoundland was a British dominion in eastern North America, today the modern Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador. It was confirmed by the Balfour Declaration of 1926 and the Statute of Westminster of 1931. It included the island of Newfoundland, and Labrador on the continental mainland. Newfoundland was one of the original dominions within the meaning of the Balfour Declaration, and accordingly enjoyed a constitutional status equivalent to the other dominions of the time.
Terra Nova may refer to:

British America comprised the colonial territories of the English Empire, and the successor British Empire, in the Americas from 1607 to 1783. These colonies were formally known as British America and the British West Indies immediately prior to thirteen of the colonies seceding in the American Revolutionary War (1775–1783) and forming the United States of America.

Starting with the 1763 Treaty of Paris, New France, of which the colony of Canada was a part, formally became a part of the British Empire. The Royal Proclamation of 1763 enlarged the colony of Canada under the name of the Province of Quebec, which with the Constitutional Act 1791 became known as the Canadas. With the Act of Union 1840, Upper and Lower Canada were joined to become the United Province of Canada.

The history of post-confederation Canada began on July 1, 1867, when the British North American colonies of Canada, New Brunswick, and Nova Scotia were united to form a single Dominion within the British Empire. Upon Confederation, the United Province of Canada was immediately split into the provinces of Ontario and Quebec. The colonies of Prince Edward Island and British Columbia joined shortly after, and Canada acquired the vast expanse of the continent controlled by the Hudson's Bay Company, which was eventually divided into new territories and provinces. Canada evolved into a fully sovereign state by 1982.

By the arrangements of the Canadian federation, the Canadian monarchy operates in Newfoundland and Labrador as the core of the province's Westminster-style parliamentary democracy. As such, the Crown within Newfoundland and Labrador's jurisdiction is referred to as the Crown in Right of Newfoundland and Labrador, His Majesty in Right of Newfoundland and Labrador, or the King in Right of Newfoundland and Labrador. The Constitution Act, 1867, however, leaves many royal duties in the province specifically assigned to the sovereign's viceroy, the lieutenant governor of Newfoundland and Labrador, whose direct participation in governance is limited by the conventional stipulations of constitutional monarchy.

The province of Newfoundland and Labrador covers the period from habitation by Archaic peoples thousands of years ago to the present day.

The Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador has a unicameral legislature, the General Assembly composed of the Lieutenant Governor and the House of Assembly, which operates on the Westminster system of government. The executive function of government is formed by the Lieutenant Governor, the premier and his or her cabinet.

The 1763 Treaty of Paris ended the major war known by Americans as the French and Indian War and by Canadians as the Seven Years' War / Guerre de Sept Ans, or by French-Canadians, La Guerre de la Conquête. It was signed by Great Britain, France and Spain, with Portugal in agreement. Preferring to keep Guadeloupe, France gave up Canada and all of its claims to territory east of the Mississippi River to Britain. With France out of North America this dramatically changed the European political scene on the continent.
A dominion was any of several largely self-governing countries of the British Empire. Progressing from colonies, their degrees of colonial self-governance increased unevenly over the late 19th century through the 1930s. Vestiges of empire lasted in some dominions well into the late 20th century. With the evolution of the British Empire into the Commonwealth of Nations, finalised in 1949, the dominions became independent states, either as Commonwealth republics or Commonwealth realms.

Newfoundland is a large island within the Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador. It is situated off the eastern coast of the North American mainland and the geographical region of Labrador.

Newfoundland was an English and, later, British colony established in 1610 on the island of Newfoundland, now the province of Newfoundland and Labrador. That followed decades of sporadic English settlement on the island, which was at first seasonal, rather than permanent. It was made a Crown colony in 1824 and a dominion in 1907. Its economy collapsed during the Great Depression and on 16 February 1934, the Newfoundland legislature agreed to the creation of a six-member Commission of Government to govern the country. In 1949, the country voted to join Canada as the province of Newfoundland.

The border between the province of Newfoundland and Labrador and the province of Quebec is the longest interprovincial border in Canada. It stretches for more than 3,500 kilometres (2,200 mi) on land, and, according to both provincial governments, also contains a maritime part. Starting from the north, the border follows the Laurentian Divide on the Labrador Peninsula for the majority of the border's length, then follows the divide between the Côte-Nord-Gaspé and Newfoundland-Labrador drainage basins as far as Brûlé Lake, after which it goes along the Romaine River downstream to the 52nd parallel, which it follows east to its southeastern terminus at Blanc-Sablon.