
The philosophy of perception is concerned with the nature of perceptual experience and the status of perceptual data, in particular how they relate to beliefs about, or knowledge of, the world. Any explicit account of perception requires a commitment to one of a variety of ontological or metaphysical views. Philosophers distinguish internalist accounts, which assume that perceptions of objects, and knowledge or beliefs about them, are aspects of an individual's mind, and externalist accounts, which state that they constitute real aspects of the world external to the individual. The position of naïve realism—the 'everyday' impression of physical objects constituting what is perceived—is to some extent contradicted by the occurrence of perceptual illusions and hallucinations and the relativity of perceptual experience as well as certain insights in science. Realist conceptions include phenomenalism and direct and indirect realism. Anti-realist conceptions include idealism and skepticism. Recent philosophical work have expanded on the philosophical features of perception by going beyond the single paradigm of vision.

In visual perception, an optical illusion is an illusion caused by the visual system and characterized by a visual percept that arguably appears to differ from reality. Illusions come in a wide variety; their categorization is difficult because the underlying cause is often not clear but a classification proposed by Richard Gregory is useful as an orientation. According to that, there are three main classes: physical, physiological, and cognitive illusions, and in each class there are four kinds: Ambiguities, distortions, paradoxes, and fictions. A classical example for a physical distortion would be the apparent bending of a stick half immersed in water; an example for a physiological paradox is the motion aftereffect. An example for a physiological fiction is an afterimage. Three typical cognitive distortions are the Ponzo, Poggendorff, and Müller-Lyer illusion. Physical illusions are caused by the physical environment, e.g. by the optical properties of water. Physiological illusions arise in the eye or the visual pathway, e.g. from the effects of excessive stimulation of a specific receptor type. Cognitive visual illusions are the result of unconscious inferences and are perhaps those most widely known.
Gestalt psychology, gestaltism, or configurationism is a school of psychology and a theory of perception that emphasises the processing of entire patterns and configurations, and not merely individual components. It emerged in the early twentieth century in Austria and Germany as a rejection of basic principles of Wilhelm Wundt's and Edward Titchener's elementalist and structuralist psychology.

The Müller-Lyer illusion is an optical illusion consisting of three stylized arrows. When viewers are asked to place a mark on the figure at the midpoint, they tend to place it more towards the "tail" end. The illusion was devised by Franz Carl Müller-Lyer (1857–1916), a German sociologist, in 1889.

Depth perception is the ability to perceive distance to objects in the world using the visual system and visual perception. It is a major factor in perceiving the world in three dimensions

The Cornsweet illusion, also known as the Craik–O'Brien–Cornsweet illusion or the Craik–Cornsweet illusion, is an optical illusion that was described in detail by Tom Cornsweet in the late 1960s. Kenneth Craik and Vivian O'Brien had made earlier observations in a similar vein.

The Moon illusion is the optical illusion of the Moon appearing larger near the horizon than it does higher up in the sky. It has been known since ancient times and recorded by various cultures. The explanation of this illusion is still debated.
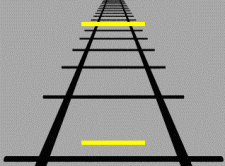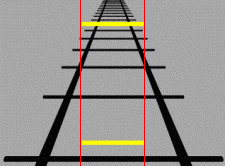
The Ponzo illusion is a geometrical-optical illusion that takes its name from the Italian psychologist Mario Ponzo (1882–1960). Ponzo never claimed to have discovered it, and it is indeed present in earlier work. Much confusion is present about this including many references to a paper that Ponzo published in 1911 on the Aristotle illusion. This is a tactile effect and it has nothing at all to do with what we now call the Ponzo illusion. The illusion can be demonstrated by drawing two identical lines across a pair of converging lines, similar to railway tracks, but the effect works also at different orientations.
Depiction is reference conveyed through pictures. A picture refers to its object through a non-linguistic two-dimensional scheme, and is distinct from writing or notation. A depictive two-dimensional scheme is called a picture plane and may be constructed according to descriptive geometry, where they are usually divided between projections and perspectives.

The motion aftereffect (MAE) is a visual illusion experienced after viewing a moving visual stimulus for a time with stationary eyes, and then fixating a stationary stimulus. The stationary stimulus appears to move in the opposite direction to the original stimulus. The motion aftereffect is believed to be the result of motion adaptation.

Richard Langton Gregory, was a British psychologist and Professor of Neuropsychology at the University of Bristol.

The lilac chaser is a visual illusion, also known as the Pac-Man illusion. It consists of 12 lilac, blurred discs arranged in a circle, around a small black, central cross on a grey background. One of the discs disappears briefly, then the next, and the next, and so on, in a clockwise direction. When one stares at the cross for at least 30 seconds, one sees three illusions
- A gap running around the circle of lilac discs;
- A green disc running around the circle of lilac discs in place of the gap; and
- The green disc running around on the grey background, with the lilac discs having disappeared in sequence.

David Tacey is an Australian public intellectual, writer and interdisciplinary scholar. He is Emeritus Professor of Literature at La Trobe University in Melbourne and Research Professor at the Australian Centre for Christianity and Culture in Canberra.

Richard Sakwa is a British political scientist and a former professor of Russian and European politics at the University of Kent, a senior research fellow at the National Research University-Higher School of Economics in Moscow, and an honorary professor in the Faculty of Political Science at Moscow State University. He has written books about Russian, Central and Eastern European communist and post-communist politics.
In human visual perception, the visual angle, denoted θ, subtended by a viewed object sometimes looks larger or smaller than its actual value. One approach to this phenomenon posits a subjective correlate to the visual angle: the perceived visual angle or perceived angular size. An optical illusion where the physical and subjective angles differ is then called a visual angle illusion or angular size illusion.
Mark Addis FRSA is a British philosopher who is known for his work on Ludwig Wittgenstein
Geometrical–optical are visual illusions, also optical illusions, in which the geometrical properties of what is seen differ from those of the corresponding objects in the visual field.
Philip Kellman is Distinguished Professor of Psychology and the current Cognitive Area Chair in the Department of Psychology at the University of California, Los Angeles. He is also Adjunct Professor of Surgery in the David Geffen UCLA School of Medicine, and the founder of Insight Learning Technology, Inc, a company that applies perceptual learning, adaptive learning technology, and principles from cognitive science research to improve education and training. His research interests involve perception and visual cognition, specifically visual perception of objects, shape, space, and motion, and perceptual development. He is also an expert in perceptual learning, adaptive learning, and their applications to skill acquisition and educational technology.

Keith James Topping is a researcher in education. He designs intervention programs for teachers, parents and others to help children, then researches whether and how they work.
Interocular transfer (IOT) is a phenomenon of visual perception in which information available to one eye will produce an effect in the other eye. For example, the state of adaptation of one eye can have a small effect on the state of light adaptation of the other. Aftereffects induced through one eye can be measured through the other.











