Nickel oxide may refer to:
- Nickel(II) oxide, NiO, green, well-characterised oxide
- Nickel(III) oxide, Ni2O3, black, not well-characterised oxide
- Nickel(IV) oxide
- Oxonickelates
- Nickel oxide hydroxide
Nickel oxide may refer to:

Nickel is a chemical element; it has symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive, but large pieces are slow to react with air under standard conditions because a passivation layer of nickel oxide forms on the surface that prevents further corrosion. Even so, pure native nickel is found in Earth's crust only in tiny amounts, usually in ultramafic rocks, and in the interiors of larger nickel–iron meteorites that were not exposed to oxygen when outside Earth's atmosphere.

Group 10, numbered by current IUPAC style, is the group of chemical elements in the periodic table that consists of nickel (Ni), palladium (Pd), platinum (Pt), and darmstadtium (Ds). All are d-block transition metals. All known isotopes of darmstadtium are radioactive with short half-lives, and are not known to occur in nature; only minute quantities have been synthesized in laboratories.

Thorium dioxide (ThO2), also called thorium(IV) oxide, is a crystalline solid, often white or yellow in colour. Also known as thoria, it is mainly a by-product of lanthanide and uranium production. Thorianite is the name of the mineralogical form of thorium dioxide. It is moderately rare and crystallizes in an isometric system. The melting point of thorium oxide is 3300 °C – the highest of all known oxides. Only a few elements (including tungsten and carbon) and a few compounds (including tantalum carbide) have higher melting points. All thorium compounds, including the dioxide, are radioactive because there are no stable isotopes of thorium.
Nio or NIO may refer to:
Plating is a finishing process in which a metal is deposited on a surface. Plating has been done for hundreds of years; it is also critical for modern technology. Plating is used to decorate objects, for corrosion inhibition, to improve solderability, to harden, to improve wearability, to reduce friction, to improve paint adhesion, to alter conductivity, to improve IR reflectivity, for radiation shielding, and for other purposes. Jewelry typically uses plating to give a silver or gold finish.

Chrysoprase, chrysophrase or chrysoprasus is a gemstone variety of chalcedony that contains small quantities of nickel. Its color is normally apple-green, but varies from turquoise-like cyan to deep green. The darker varieties of chrysoprase are also referred to as prase.
Metal fume fever, also known as brass founders' ague, brass shakes, zinc shakes, galvie flu, galvo poisoning, metal dust fever, welding shivers, or Monday morning fever, is an illness primarily caused by exposure to chemicals such as zinc oxide (ZnO), aluminium oxide (Al2O3), or magnesium oxide (MgO) which are produced as byproducts in the fumes that result when certain metals are heated. Other common sources are fuming silver, gold, platinum, and chromium.

Nickel(II) fluoride is the chemical compound with the formula NiF2. It is an ionic compound of nickel and fluorine and forms yellowish to green tetragonal crystals. Unlike many fluorides, NiF2 is stable in air.
N10 may refer to:

Nickel (III) oxide is the inorganic compound with the formula Ni2O3. It is not well characterized, and is sometimes referred to as black nickel oxide. Traces of Ni2O3 on nickel surfaces have been mentioned.

Electroless nickel-phosphorus plating, also referred to as E-nickel, is a chemical process that deposits an even layer of nickel-phosphorus alloy on the surface of a solid substrate, like metal or plastic. The process involves dipping the substrate in a water solution containing nickel salt and a phosphorus-containing reducing agent, usually a hypophosphite salt. It is the most common version of electroless nickel plating and is often referred by that name. A similar process uses a borohydride reducing agent, yielding a nickel-boron coating instead.

Nickel(II) oxide is the chemical compound with the formula NiO. It is the principal oxide of nickel. It is classified as a basic metal oxide. Several million kilograms are produced annually of varying quality, mainly as an intermediate in the production of nickel alloys. The mineralogical form of NiO, bunsenite, is very rare. Other nickel(III) oxides have been claimed, for example: Ni
2O
3 and NiO
2, but remain unproven.
Germanium oxide may refer to:
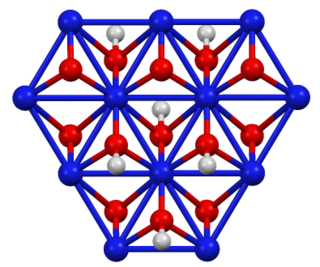
Nickel oxide hydroxide is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula NiO(OH). It is a black solid that is insoluble in all solvents but attacked by base and acid. It is a component of the nickel–metal hydride battery and of the nickel–iron battery.

Glass-to-metal seals are a type of mechanical seal which joins glass and metal surfaces. They are very important elements in the construction of vacuum tubes, electric discharge tubes, incandescent light bulbs, glass-encapsulated semiconductor diodes, reed switches, glass windows in metal cases, and metal or ceramic packages of electronic components.

Nickel–Strunz classification is a scheme for categorizing minerals based upon their chemical composition, introduced by German mineralogist Karl Hugo Strunz in his Mineralogische Tabellen (1941). The 4th and the 5th edition was also edited by Christel Tennyson (1966). It was followed by A.S. Povarennykh with a modified classification.
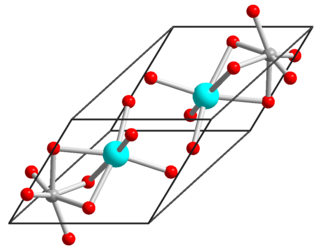
Nickel(II) titanate, also known as nickel titanium oxide, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula NiTiO3. It is a coordination compound between nickel(II), titanium(IV) and oxide ions. It has the appearance of a yellow powder. Nickel(II) titanate has been used as a catalyst for toluene oxidation.
Nickel battery may refer to:
The lithium nickel cobalt aluminium oxides (abbreviated as Li-NCA, LNCA, or NCA) are a group of mixed metal oxides. Some of them are important due to their application in lithium-ion batteries. NCAs are used as active material in the positive electrode (which is the cathode when the battery is discharged). NCAs are composed of the cations of the chemical elements lithium, nickel, cobalt and aluminium. The compounds of this class have a general formula LiNixCoyAlzO2 with x + y + z = 1. In case of the NCA comprising batteries currently available on the market, which are also used in electric cars and electric appliances, x ≈ 0.84, and the voltage of those batteries is between 3.6 V and 4.0 V, at a nominal voltage of 3.6 V or 3.7 V. A version of the oxides currently in use in 2019 is LiNi0.84Co0.12Al0.04O2.
Lithium battery may refer to: