
Niacinamide or nicotinamide is a form of vitamin B3 found in food and used as a dietary supplement and medication. As a supplement, it is used by mouth to prevent and treat pellagra (niacin deficiency). While nicotinic acid (niacin) may be used for this purpose, niacinamide has the benefit of not causing skin flushing. As a cream, it is used to treat acne. It is a water-soluble vitamin. Niacinamide is the supplement name while nicotinamide is the scientific name.

Acne, also known as acne vulgaris, is a long-term skin condition that occurs when dead skin cells and oil from the skin clog hair follicles. Typical features of the condition include blackheads or whiteheads, pimples, oily skin, and possible scarring. It primarily affects skin with a relatively high number of oil glands, including the face, upper part of the chest, and back. The resulting appearance can lead to lack of confidence, anxiety, reduced self-esteem, and, in extreme cases, depression or thoughts of suicide.

Seborrhoeic dermatitis, sometimes inaccurately referred to as seborrhoea, is a long-term skin disorder. Symptoms include red, scaly, greasy, itchy, and inflamed skin. Areas of the skin rich in oil-producing glands are often affected including the scalp, face, and chest. It can result in social or self-esteem problems. In babies, when the scalp is primarily involved, it is called cradle cap. Dandruff is a milder form of the condition without inflammation.
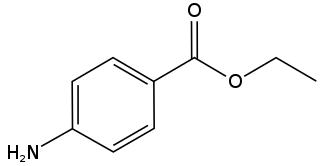
Benzocaine, sold under the brand name Orajel amongst others, is a local anesthetic, belonging to the amino ester drug class, commonly used as a topical painkiller or in cough drops. It is the active ingredient in many over-the-counter anesthetic ointments such as products for oral ulcers. It is combined with antipyrine to form A/B ear drops. In the US, products containing benzocaine for oral application are contraindicated in children younger than two years old. In the European Union, the contraindication applies to children under 12 years of age.
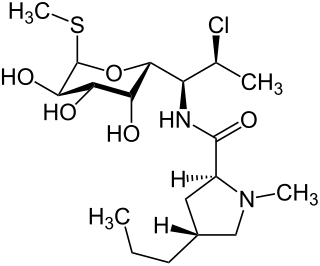
Clindamycin is an antibiotic medication used for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections, including osteomyelitis (bone) or joint infections, pelvic inflammatory disease, strep throat, pneumonia, acute otitis media, and endocarditis. It can also be used to treat acne, and some cases of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). In combination with quinine, it can be used to treat malaria. It is available by mouth, by injection into a vein, and as a cream or a gel to be applied to the skin or in the vagina.

Tretinoin, also known as all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA), is a medication used for the treatment of acne and acute promyelocytic leukemia. For acne, it is applied to the skin as a cream, gel or ointment. For leukemia, it is taken by mouth for up to three months. Topical tretinoin is also the most extensively investigated retinoid therapy for photoaging.

Benzoyl peroxide is a chemical compound (specifically, an organic peroxide) with structural formula (C6H5−C(=O)O−)2, often abbreviated as (BzO)2. In terms of its structure, the molecule can be described as two benzoyl (C6H5−C(=O)−, Bz) groups connected by a peroxide (−O−O−). It is a white granular solid with a faint odour of benzaldehyde, poorly soluble in water but soluble in acetone, ethanol, and many other organic solvents. Benzoyl peroxide is an oxidizer, but it is principally used as in the production of polymers.
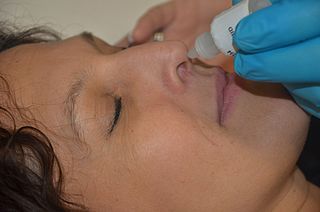
A topical medication is a medication that is applied to a particular place on or in the body. Most often topical medication means application to body surfaces such as the skin or mucous membranes to treat ailments via a large range of classes including creams, foams, gels, lotions, and ointments. Many topical medications are epicutaneous, meaning that they are applied directly to the skin. Topical medications may also be inhalational, such as asthma medications, or applied to the surface of tissues other than the skin, such as eye drops applied to the conjunctiva, or ear drops placed in the ear, or medications applied to the surface of a tooth. The word topical derives from Greek τοπικόςtopikos, "of a place".

Adapalene is a third-generation topical retinoid primarily used in the treatment of mild-moderate acne, and is also used off-label to treat keratosis pilaris as well as other skin conditions. Studies have found adapalene is as effective as other retinoids, while causing less irritation. It also has several advantages over other retinoids. The adapalene molecule is more stable compared to tretinoin and tazarotene, which leads to less concern for photodegradation. It is also chemically more stable compared to the other two retinoids, allowing it to be used in combination with benzoyl peroxide. Due to its effects on keratinocyte proliferation and differentiation, adapalene is superior to tretinoin for the treatment of comedonal acne and is often used as a first-line agent. The Swiss company Galderma sells adapalene under the brand-name product Differin.

Clobetasol propionate is a corticosteroid used to treat skin conditions such as eczema, contact dermatitis, seborrheic dermatitis, and psoriasis. It is applied to the skin as a cream, ointment, or shampoo. Use should be short term and only if other weaker corticosteroids are not effective. Use is not recommended in rosacea or perioral dermatitis.

Betamethasone is a steroid medication. It is used for a number of diseases including rheumatic disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus, skin diseases such as dermatitis and psoriasis, allergic conditions such as asthma and angioedema, preterm labor to speed the development of the baby's lungs, Crohn's disease, cancers such as leukemia, and along with fludrocortisone for adrenocortical insufficiency, among others. It can be taken by mouth, injected into a muscle, or applied to the skin, typically in cream, lotion, or liquid forms.

Azelaic acid (AzA) is an organic compound with the formula HOOC(CH2)7COOH. This saturated dicarboxylic acid exists as a white powder. It is found in wheat, rye, and barley. It is a precursor to diverse industrial products including polymers and plasticizers, as well as being a component of a number of hair and skin conditioners. AzA inhibits tyrosinase.

Perioral dermatitis, also known as periorificial dermatitis, is a common type of skin rash. Symptoms include multiple small (1–2 mm) bumps and blisters sometimes with background redness and scale, localized to the skin around the mouth and nostrils. Less commonly the eyes and genitalia may be involved. It can be persistent or recurring and resembles particularly rosacea and to some extent acne and allergic dermatitis. The term "dermatitis" is a misnomer because this is not an eczematous process.

Clindamycin/benzoyl peroxide is a topical gel used for the treatment of acne. It is a fixed-dose combination of clindamycin, as the phosphate, an antibiotic, and benzoyl peroxide, an antiseptic.

Lotion is a low-viscosity topical preparation intended for application to the skin. By contrast, creams and gels have higher viscosity, typically due to lower water content. Lotions are applied to external skin with bare hands, a brush, a clean cloth, or cotton wool.

Amcinonide is a topical glucocorticoid used to treat itching, redness and swelling associated with several dermatologic conditions such as atopic dermatitis and allergic contact dermatitis. Amcinonide can also be classified as a multi-functional small molecule corticosteroid, which has been approved by the FDA and is currently marketed as an ointment, lotion, or cream. It acts as both a transcription factor for responses to glucocorticoids and modulator for other transcription factors while also regulating phospholipase A2 activity.

Nadifloxacin is a topical fluoroquinolone antibiotic for the treatment of acne vulgaris. It is also used to treat bacterial skin infections.

A pimple or zit is a kind of comedo that results from excess sebum and dead skin cells getting trapped in the pores of the skin. In its aggravated state, it may evolve into a pustule or papules. Pimples can be treated by acne medications, antibiotics, and anti-inflammatories prescribed by a physician, or various over the counter remedies purchased at a pharmacy.
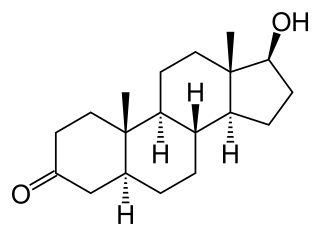
Androstanolone, or stanolone, also known as dihydrotestosterone (DHT) and sold under the brand name Andractim among others, is an androgen and anabolic steroid (AAS) medication and hormone which is used mainly in the treatment of low testosterone levels in men. It is also used to treat breast development and small penis in males. It is typically given as a gel for application to the skin, but can also be used as an ester by injection into muscle.

Topical cream formulation is an emulsion semisolid dosage form that is used for skin external application. Most of the topical cream formulations contain more than 20 per cent of water and volatiles and/or less than 50 per cent of hydrocarbons, waxes, or polyethylene glycols as the vehicle for external skin application. In a topical cream formulation, ingredients are dissolved or dispersed in either a water-in-oil (W/O) emulsion or an oil-in-water (O/W) emulsion. The topical cream formulation has a higher content of oily substance than gel, but a lower content of oily ingredient than ointment. Therefore, the viscosity of topical cream formulation lies between gel and ointment. The pharmacological effect of the topical cream formulation is confined to the skin surface or within the skin. Topical cream formulation penetrates through the skin by transcellular route, intercellular route, or trans-appendageal route. Topical cream formulation is used for a wide range of diseases and conditions, including atopic dermatitis (eczema), psoriasis, skin infection, acne, and wart. Excipients found in a topical cream formulation include thickeners, emulsifying agents, preservatives, antioxidants, and buffer agents. Steps required to manufacture a topical cream formulation include excipient dissolution, phase mixing, introduction of active substances, and homogenization of the product mixture.


















