Related Research Articles

Ascorbic acid is an organic compound with formula C
6H
8O
6, originally called hexuronic acid. It is a white solid, but impure samples can appear yellowish. It dissolves freely in water to give mildly acidic solutions. It is a mild reducing agent.

A carcinogen is any agent that promotes the development of cancer. Carcinogens can include synthetic chemicals, naturally occurring substances, physical agents such as ionizing and non-ionizing radiation, and biologic agents such as viruses and bacteria. Most carcinogens act by creating mutations in DNA that disrupt a cell's normal processes for regulating growth, leading to uncontrolled cellular proliferation. This occurs when the cell's DNA repair processes fail to identify DNA damage allowing the defect to be passed down to daughter cells. The damage accumulates over time. This is typically a multi-step process during which the regulatory mechanisms within the cell are gradually dismantled allowing for unchecked cellular division.

Ham is pork from a leg cut that has been preserved by wet or dry curing, with or without smoking. As a processed meat, the term ham includes both whole cuts of meat and ones that have been mechanically formed.

In genetics, a mutagen is a physical or chemical agent that permanently changes genetic material, usually DNA, in an organism and thus increases the frequency of mutations above the natural background level. As many mutations can cause cancer in animals, such mutagens can therefore be carcinogens, although not all necessarily are. All mutagens have characteristic mutational signatures with some chemicals becoming mutagenic through cellular processes.

Nitrate is a polyatomic ion with the chemical formula NO−
3. Salts containing this ion are called nitrates. Nitrates are common components of fertilizers and explosives. Almost all inorganic nitrates are soluble in water. An example of an insoluble nitrate is bismuth oxynitrate.
A preservative is a substance or a chemical that is added to products such as food products, beverages, pharmaceutical drugs, paints, biological samples, cosmetics, wood, and many other products to prevent decomposition by microbial growth or by undesirable chemical changes. In general, preservation is implemented in two modes, chemical and physical. Chemical preservation entails adding chemical compounds to the product. Physical preservation entails processes such as refrigeration or drying. Preservative food additives reduce the risk of foodborne infections, decrease microbial spoilage, and preserve fresh attributes and nutritional quality. Some physical techniques for food preservation include dehydration, UV-C radiation, freeze-drying, and refrigeration. Chemical preservation and physical preservation techniques are sometimes combined.

Sodium nitrate is the chemical compound with the formula NaNO
3. This alkali metal nitrate salt is also known as Chile saltpeter to distinguish it from ordinary saltpeter, potassium nitrate. The mineral form is also known as nitratine, nitratite or soda niter.
The nitrite ion has the chemical formula NO−
2. Nitrite is widely used throughout chemical and pharmaceutical industries. The nitrite anion is a pervasive intermediate in the nitrogen cycle in nature. The name nitrite also refers to organic compounds having the –ONO group, which are esters of nitrous acid.

Sodium nitrite is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula NaNO2. It is a white to slightly yellowish crystalline powder that is very soluble in water and is hygroscopic. From an industrial perspective, it is the most important nitrite salt. It is a precursor to a variety of organic compounds, such as pharmaceuticals, dyes, and pesticides, but it is probably best known as a food additive used in processed meats and in fish products.
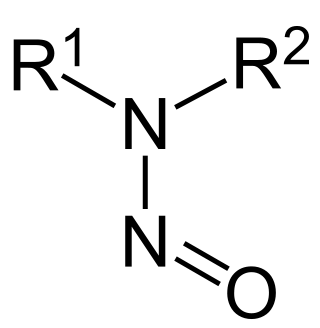
Nitrosamines are organic compounds produced by industrial processes.

Erythorbic acid is a stereoisomer of ascorbic acid. It is synthesized by a reaction between methyl 2-keto-D-gluconate and sodium methoxide. It can also be synthesized from sucrose or by strains of Penicillium that have been selected for this feature. It is denoted by E number E315, and is widely used as an antioxidant in processed foods.

In gastronomy, red meat is commonly red when raw, in contrast to white meat, which is pale in color before cooking. In culinary terms, only flesh from mammals or fowl is classified as red or white. In nutritional science, red meat is defined as any meat that has more of the protein myoglobin than white meat. White meat is defined as non-dark meat from fish or chicken.

Processed meat is considered to be any meat that has been modified in order to either improve its taste or to extend its shelf life. Methods of meat processing include salting, curing, fermentation, smoking, and/or the addition of chemical preservatives. Processed meat is usually composed of pork or beef or, less frequently, poultry. It can also contain offal or meat by-products such as blood. Processed meat products include bacon, ham, sausages, salami, corned beef, jerky, hot dogs, lunch meat, canned meat, chicken nuggets, and meat-based sauces. Meat processing includes all the processes that change fresh meat with the exception of simple mechanical processes such as cutting, grinding or mixing.

Nitrosation and nitrosylation are two names for the process of converting organic compounds or metal complexes into nitroso derivatives, i.e., compounds containing the R−NO functionality. The synonymy arises because the R-NO functionality can be interpreted two different ways, depending on the physico-chemical environment:

Pickling is the process of preserving or extending the shelf life of food by either anaerobic fermentation in brine or immersion in vinegar. The pickling procedure typically affects the food's texture and flavor. The resulting food is called a pickle, or, if named, the name is prefaced with the word "pickled". Foods that are pickled include vegetables, fruits, mushrooms, meats, fish, dairy and eggs.

N-Nitrosonornicotine (NNN) is a tobacco-specific nitrosamine produced during the curing and processing of tobacco.

In organic chemistry, nitroso refers to a functional group in which the nitric oxide group is attached to an organic moiety. As such, various nitroso groups can be categorized as C-nitroso compounds, S-nitroso compounds, N-nitroso compounds, and O-nitroso compounds.

Curing is any of various food preservation and flavoring processes of foods such as meat, fish and vegetables, by the addition of salt, with the aim of drawing moisture out of the food by the process of osmosis. Because curing increases the solute concentration in the food and hence decreases its water potential, the food becomes inhospitable for the microbe growth that causes food spoilage. Curing can be traced back to antiquity, and was the primary method of preserving meat and fish until the late 19th century. Dehydration was the earliest form of food curing. Many curing processes also involve smoking, spicing, cooking, or the addition of combinations of sugar, nitrate, and nitrite.

6-O-Methylguanine is a derivative of the nucleobase guanine in which a methyl group is attached to the oxygen atom. It base-pairs to thymine rather than cytosine, causing a G:C to A:T transition in DNA.
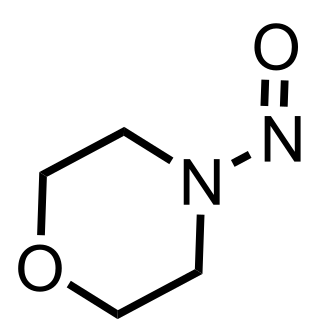
N-Nitrosomorpholine is an organic compound which is known to be a carcinogen and mutagen.
References
- ↑ Honikel, K. O. (2008). "The use an control of nitrate and nitrite for the processing of meat products" (PDF). Meat Science. 78 (1–2): 68–76. doi:10.1016/j.meatsci.2007.05.030. PMID 22062097.
- ↑ Lunn, J.C.; Kuhnle, G.; Mai, V.; Frankenfeld, C.; Shuker, D.E.G.; Glen, R. C.; Goodman, J.M.; Pollock, J.R.A.; Bingham, S.A. (2006). "The effect of haem in red and processed meat on the endogenous formation of N-nitroso compounds in the upper gastrointestinal tract". Carcinogenesis. 28 (3): 685–690. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgl192. PMID 17052997.
- ↑ Bastide, Nadia M.; Pierre, Fabrice H.F.; Corpet, Denis E. (2011). "Heme Iron from Meat and Risk of Colorectal Cancer: A Meta-analysis and a Review of the Mechanisms Involved". Cancer Prevention Research. 4 (2): 177–184. doi: 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-10-0113 . PMID 21209396. S2CID 4951579.
- ↑ Bastide, Nadia M.; Chenni, Fatima; Audebert, Marc; Santarelli, Raphaelle L.; Taché, Sylviane; Naud, Nathalie; Baradat, Maryse; Jouanin, Isabelle; Surya, Reggie; Hobbs, Ditte A.; Kuhnle, Gunter G.; Raymond-Letron, Isabelle; Gueraud, Françoise; Corpet, Denis E.; Pierre, Fabrice H.F. (2015). "A Central Role for Heme Iron in Colon Carcinogenesis Associated with Red Meat Intake". Cancer Research. 75 (5): 870–879. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-2554 . PMID 25592152. S2CID 13274953.
- ↑ Jakszyn, P; Gonzalez, CA (2006). "Nitrosamine and related food intake and gastric and oesophageal cancer risk: A systematic review of the epidemiological evidence". World Journal of Gastroenterology. 12 (27): 4296–4303. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i27.4296 . PMC 4087738 . PMID 16865769.
- ↑ Joyce I. Boye; Yves Arcand (2012-01-10). Green Technologies in Food Production and Processing. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 573. ISBN 978-1-4614-1586-2.
- ↑ Lee, L; Archer, MC; Bruce, WR (October 1981). "Absence of volatile nitrosamines in human feces". Cancer Res. 41 (10): 3992–4. PMID 7285009.
- ↑ Kuhnle, GG; Story, GW; Reda, T; et al. (October 2007). "Diet-induced endogenous formation of nitroso compounds in the GI tract". Free Radic. Biol. Med. 43 (7): 1040–7. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2007.03.011. PMID 17761300.
- 1 2 Combet, E.; Paterson, S; Iijima, K; Winter, J; Mullen, W; Crozier, A; Preston, T; McColl, K. E. (2007). "Fat transforms ascorbic acid from inhibiting to promoting acid-catalysed N-nitrosation". Gut. 56 (12): 1678–1684. doi:10.1136/gut.2007.128587. PMC 2095705 . PMID 17785370.
- ↑ Herrmann, S.S.; Granby, K.; Duedahl-Olesen, L. (May 2015). "Formation and mitigation of N-nitrosamines in nitrite preserved cooked sausages". Food Chemistry. 174: 516–526. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.11.101 .
- ↑ Mirvish, SS; Wallcave, L; Eagen, M; Shubik, P (July 1972). "Ascorbate–nitrite reaction: possible means of blocking the formation of carcinogenic N-nitroso compounds". Science. 177 (4043): 65–8. Bibcode:1972Sci...177...65M. doi:10.1126/science.177.4043.65. PMID 5041776. S2CID 26275960.
- ↑ Mirvish, SS (October 1986). "Effects of vitamins C and E on N-nitroso compound formation, carcinogenesis, and cancer". Cancer. 58 (8 Suppl): 1842–50. doi:10.1002/1097-0142(19861015)58:8+<1842::aid-cncr2820581410>3.0.co;2-#. PMID 3756808. S2CID 196379002.
- ↑ Tannenbaum SR, Wishnok JS, Leaf CD (1991). "Inhibition of nitrosamine formation by ascorbic acid". The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition . 53 (1 Suppl): 247S –250S. Bibcode:1987NYASA.498..354T. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.1987.tb23774.x. PMID 1985394. S2CID 41045030 . Retrieved 2015-06-06.
Evidence now exists that ascorbic acid is a limiting factor in nitrosation reactions in people.
- ↑ Combet, E; El Mesmari, A; Preston, T; Crozier, A; McColl, K. E. (2010). "Dietary phenolic acids and ascorbic acid: Influence on acid-catalyzed nitrosative chemistry in the presence and absence of lipids". Free Radical Biology and Medicine. 48 (6): 763–771. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2009.12.011. PMID 20026204.
- ↑ Pappenberger, Günter; Hohmann, Hans-Peter (2013). "Industrial Production of l-Ascorbic Acid (Vitamin C) and d-Isoascorbic Acid". Biotechnology of Food and Feed Additives. 143: 143–188. doi:10.1007/10_2013_243.