Related Research Articles

An agricultural subsidy is a government incentive paid to agribusinesses, agricultural organizations and farms to supplement their income, manage the supply of agricultural commodities, and influence the cost and supply of such commodities.
In marketing, market segmentation or customer segmentation is the process of dividing a consumer or business market into meaningful sub-groups of current or potential customers known as segments. Its purpose is to identify profitable and growing segments that a company can target with distinct marketing strategies.
Yield management is a variable pricing strategy, based on understanding, anticipating and influencing consumer behavior in order to maximize revenue or profits from a fixed, time-limited resource. As a specific, inventory-focused branch of revenue management, yield management involves strategic control of inventory to sell the right product to the right customer at the right time for the right price. This process can result in price discrimination, in which customers consuming identical goods or services are charged different prices. Yield management is a large revenue generator for several major industries; Robert Crandall, former Chairman and CEO of American Airlines, gave yield management its name and has called it "the single most important technical development in transportation management since we entered deregulation."
The Commodity Credit Corporation (CCC) is a wholly owned United States government corporation that was created in 1933 to "stabilize, support, and protect farm income and prices". The CCC is authorized to buy, sell, lend, make payments, and engage in other activities for the purpose of increasing production, stabilizing prices, assuring adequate supplies, and facilitating the efficient marketing of agricultural commodities.

The Federal Agriculture Improvement and Reform Act of 1996, known informally as the Freedom to Farm Act, the FAIR Act, or the 1996 U.S. Farm Bill, was the omnibus 1996 farm bill that, among other provisions, revises and simplifies direct payment programs for crops and eliminates milk price supports through direct government purchases.
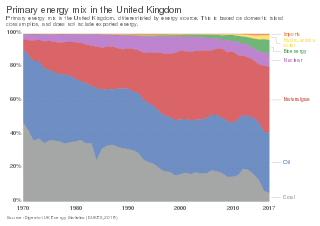
The energy policy of the United Kingdom refers to the United Kingdom's efforts towards reducing energy intensity, reducing energy poverty, and maintaining energy supply reliability. The United Kingdom has had success in this, though energy intensity remains high. There is an ambitious goal to reduce carbon dioxide emissions in future years, but it is unclear whether the programmes in place are sufficient to achieve this objective. Regarding energy self-sufficiency, UK policy does not address this issue, other than to concede historic energy security is currently ceasing to exist.
National Empowerment Television (NET), later known as America's Voice and eventually The Renaissance Network, was a cable TV network designed to rapidly mobilize politically conservative individuals for grassroots lobbying on behalf of the movement's policy aims. It was created by Paul Weyrich, a veteran strategist for the paleoconservative movement. At its peak, NET claimed to reach more than 11 million homes on selected cable systems or, in some markets, low-powered television stations. It accompanied the contemporaneous explosion of the popularity of talk radio, practically all of which was dedicated to propagating conservative political positions, on numerous issues in the United States during the 1990s.

Agriculture is one of the dominant parts of Senegal's economy, even though Senegal lies within the drought-prone Sahel region. As only about 5% of the land is irrigated, Senegal continues to rely on rain-fed agriculture. Agriculture occupies about 75% of the workforce. Despite a relatively wide variety of agricultural production, the majority of farmers produce for subsistence needs. Millet, rice, corn, and sorghum are the primary food crops grown in Senegal. Production is subject to drought and threats of pests such as locusts, birds, fruit flies, and white flies. Moreover, the effects of climate change in Senegal are expected to severely harm the agricultural economy due to extreme weather such as drought, as well as increased temperatures.
Industrial market segmentation is a scheme for categorizing industrial and business customers to guide strategic and tactical decision-making. Government agencies and industry associations use standardized segmentation schemes for statistical surveys. Most businesses create their own segmentation scheme to meet their particular needs. Industrial market segmentation is important in sales and marketing.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to marketing:

In the United States, the farm bill is comprehensive omnibus bill that is the primary agricultural and food policy instrument of the federal government. Congress typically passes a new farm bill every five to six years.
A target market, also known as serviceable obtainable market (SOM), is a group of customers within a business's serviceable available market at which a business aims its marketing efforts and resources. A target market is a subset of the total market for a product or service.
The agricultural policy of the United States is composed primarily of the periodically renewed federal U.S. farm bills. The Farm Bills have a rich history which initially sought to provide income and price support to US farmers and prevent them from adverse global as well as local supply and demand shocks. This implied an elaborate subsidy program which supports domestic production by either direct payments or through price support measures. The former incentivizes farmers to grow certain crops which are eligible for such payments through environmentally conscientious practices of farming. The latter protects farmers from vagaries of price fluctuations by ensuring a minimum price and fulfilling their shortfalls in revenue upon a fall in price. Lately, there are other measures through which the government encourages crop insurance and pays part of the premium for such insurance against various unanticipated outcomes in agriculture.
A go-to-market strategy, or GTM strategy, is the plan of an organization, utilizing their outside resources, to deliver their unique value proposition to customers ("go-to-market") and to achieve a competitive advantage. The goal is to enhance the overall customer experience by not only offering a superior product and/or more competitive pricing, but also creating a clear framework and plan to penetrate a defined market and/or target audience.
The Tobacco Price Support Program used a combination of marketing quotas and nonrecourse loans to keep prices stable and higher than they would be otherwise in the United States. The tobacco quota limited production to raise prices. Nonrecourse loans allowed producers to hold tobacco stocks for long periods to balance supplies with market demand conditions.
A poundage quota, also called a marketing quota, is a quantitative limit on the amount of a commodity that can be marketed under the provisions of a permanent law. Once a common feature of price support programs, this supply control mechanism ended with the quota buyouts for peanuts in 2002 and tobacco in 2004.

The No Net Cost Tobacco Act of 1982 required that the Tobacco Price Support Program operate at no net cost to taxpayers, other than for the administrative expenses common to all price support programs. To satisfy this mandate, sellers and buyers of tobacco were assessed equally to build a capital account that was drawn upon to reimburse the Commodity Credit Corporation (CCC) for any losses of principal and interest resulting from nonrecourse loan operations. Other provisions of this law provided for reducing the level of support for tobacco and made various modifications to the marketing quota and acreage allotment programs. No net cost assessments ended when price support was terminated after the 2004 crop.
Poundage quotas were authorized by the Agricultural Adjustment Act of 1938, so the peanut poundage quota was the supply control mechanism for the peanut price support program until its revision in the 2002 farm bill.
Two-tiered pricing refers to a system under which commodities for domestic use are supported at one level and those for export markets at another, lower level.
Marketing assessments are payments in United States agricultural policy. At times, producers and first purchasers of some supported commodities are required to pay assessments as a contribution towards achieving budget deficit reduction targets. Under the 1996 farm bill, assessments were imposed on sugar processors, producers, and first buyers of peanuts. However, the 1996 farm bill eliminated a milk marketing assessment. The 2002 farm bill eliminated the assessments for peanuts and sugar. Tobacco was subject to a no-net-cost assessment on all marketings to offset Commodity Credit Corporation (CCC) losses on price support loan operations until support was ended in 2005 under the quota buyout provision.
References
- ↑ "Tobacco industry pricing strategies and price segmentation of the UK tobacco market". Tobacco industry pricing strategies and price segmentation of the UK tobacco market on NCBI. NIHR Journals Library. April 2020.
 This article incorporates public domain material from Jasper Womach. Report for Congress: Agriculture: A Glossary of Terms, Programs, and Laws, 2005 Edition (PDF). Congressional Research Service.
This article incorporates public domain material from Jasper Womach. Report for Congress: Agriculture: A Glossary of Terms, Programs, and Laws, 2005 Edition (PDF). Congressional Research Service.