Related Research Articles

A ballpoint pen, also known as a biro, ball pen, or dot pen (Nepali) is a pen that dispenses ink over a metal ball at its point, i.e. over a "ball point". The metal commonly used is steel, brass, or tungsten carbide. The design was conceived and developed as a cleaner and more reliable alternative to dip pens and fountain pens, and it is now the world's most-used writing instrument; millions are manufactured and sold daily. It has influenced art and graphic design and spawned an artwork genre.

Ink is a gel, sol, or solution that contains at least one colourant, such as a dye or pigment, and is used to color a surface to produce an image, text, or design. Ink is used for drawing or writing with a pen, brush, reed pen, or quill. Thicker inks, in paste form, are used extensively in letterpress and lithographic printing.

A quill is a writing tool made from a moulted flight feather of a large bird. Quills were used for writing with ink before the invention of the dip pen, the metal-nibbed pen, the fountain pen, and, eventually, the ballpoint pen.

Calligraphy is a visual art related to writing. It is the design and execution of lettering with a pen, ink brush, or other writing instrument. A contemporary calligraphic practice can be defined as "the art of giving form to signs in an expressive, harmonious, and skillful manner".

A fountain pen is a writing instrument which uses a metal nib to apply a water-based ink to paper. It is distinguished from earlier dip pens by using an internal reservoir to hold ink, eliminating the need to repeatedly dip the pen in an inkwell during use. The pen draws ink from the reservoir through a feed to the nib and deposits the ink on paper via a combination of gravity and capillary action. Filling the reservoir with ink may be achieved manually, via the use of an eyedropper or syringe, or via an internal filling mechanism which creates suction or a vacuum to transfer ink directly through the nib into the reservoir. Some pens employ removable reservoirs in the form of pre-filled ink cartridges.

Invisible ink, also known as security ink or sympathetic ink, is a substance used for writing, which is invisible either on application or soon thereafter, and can later be made visible by some means. Invisible ink is one form of steganography.

A pen is a common writing instrument that applies ink to a surface, usually paper, for writing or drawing. Early pens such as reed pens, quill pens, dip pens and ruling pens held a small amount of ink on a nib or in a small void or cavity which had to be periodically recharged by dipping the tip of the pen into an inkwell. Today, such pens find only a small number of specialized uses, such as in illustration and calligraphy. Reed pens, quill pens and dip pens, which were used for writing, have been replaced by ballpoint pens, rollerball pens, fountain pens and felt or ceramic tip pens. Ruling pens, which were used for technical drawing and cartography, have been replaced by technical pens such as the Rapidograph. All of these modern pens contain internal ink reservoirs, such that they do not need to be dipped in ink while writing.

Stationery refers to commercially manufactured writing materials, including cut paper, envelopes, writing implements, continuous form paper, and other office supplies. Stationery includes materials to be written on by hand or by equipment such as computer printers.

A stylus is a writing utensil or a small tool for some other form of marking or shaping, for example, in pottery. It can also be a computer accessory that is used to assist in navigating or providing more precision when using touchscreens. It usually refers to a narrow elongated staff, similar to a modern ballpoint pen. Many styluses are heavily curved to be held more easily. Another widely used writing tool is the stylus used by blind users in conjunction with the slate for punching out the dots in Braille.

A dip pen or nib pen or pen nib usually consists of a metal nib with capillary channels like those of fountain pen nibs, mounted in a handle or holder, often made of wood. Other materials can be used for the holder, including bone, metal and plastic; some pens are made entirely of glass.

A marker pen, fine liner, marking pen, felt-tip pen, flowmarker, sign pen, vivid, texta, sketch pen or koki, is a pen which has its own ink source and a tip made of porous, pressed fibers such as felt.

A permanent marker or indelible marker is a type of marker pen that is used to create permanent or semi-permanent writing on an object. In general, the ink comprises a main carrier solvent, a glyceride, a pyrrolidone, a resin and a colorant, making it water resistant. It is capable of writing on a variety of surfaces from paper to metal to stone. They come in a variety of tip sizes, shapes, and colors. Like spray paint, these markers contain volatile organic compounds which evaporate to dry the ink. Due to compounds such as toluene and xylene often being present in permanent markers, they have a potential for abuse as a recreational drug.
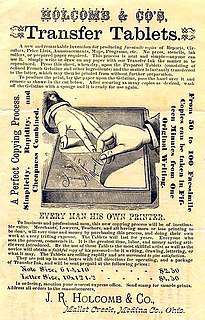
The hectograph, gelatin duplicator or jellygraph is a printing process that involves transfer of an original, prepared with special inks, to a pan of gelatin or a gelatin pad pulled tight on a metal frame.

Iron gall ink is a purple-black or brown-black ink made from iron salts and tannic acids from vegetable sources. It was the standard ink formulation used in Europe for the 1400-year period between the 5th and 19th centuries, remained in widespread use well into the 20th century, and is still sold today.
A writing implement or writing instrument is an object used to produce writing. Writing consists of different figures, lines, and or forms. Most of these items can be also used for other functions such as painting, drawing and technical drawing, but writing instruments generally have the ordinary requirement to create a smooth, controllable line.
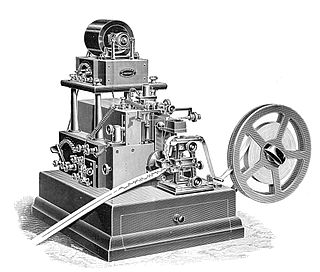
The syphon or siphon recorder is an obsolete electromechanical device used as a receiver for submarine telegraph cables invented by William Thomson, 1st Baron Kelvin in 1867. It automatically records an incoming telegraph message as a wiggling ink line on a roll of paper tape. Later a trained telegrapher would read the tape, translating the pulses representing the "dots" and "dashes" of the Morse code to characters of the text message.

Roller ball pens or roll pens are pens which use ball point writing mechanisms with water-based liquid or gelled ink, as opposed to the oil-based viscous inks found in ballpoint pens. These less viscous inks, which tend to saturate more deeply and more widely into paper than other types of ink, give roller ball pens their distinctive writing qualities. The writing point is a tiny ball, usually 0.5 or 0.7 mm in diameter, that transfers the ink from the reservoir onto the paper as the pen moves.

Blotting paper, called bibulous paper, is a highly absorbent type of paper or other material. It is used to absorb an excess of liquid substances from the surface of writing paper or objects. Blotting paper referred to as bibulous paper is mainly used in microscopy to remove excess liquids from the slide before viewing. Blotting paper has also been sold as a cosmetic to aid in the removal of skin oils and makeup.

A nib is the part of a quill, dip pen, fountain pen, ball point or stylus which comes into contact with the writing surface in order to deposit ink. Different types of nibs vary in their purpose, shape and size, as well as the material from which they are made.

Several instruments have been used to write in outer space, including different types of pencils and pens. Some of them have been unmodified versions of conventional writing instruments; others have been invented specifically to counter the problems with writing in space conditions.
References
- ↑ W R Wedgewood's advertisement of 1842 - Archived 2017-05-10 at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ William H. Prescott - Encyclopædia Britannica v. 14, p. 993. 1974
- ↑ "Siberia 19th century to 1890 - extreme tourism".