Related Research Articles
Thrombosis is the formation of a blood clot inside a blood vessel, obstructing the flow of blood through the circulatory system. When a blood vessel is injured, the body uses platelets (thrombocytes) and fibrin to form a blood clot to prevent blood loss. Even when a blood vessel is not injured, blood clots may form in the body under certain conditions. A clot, or a piece of the clot, that breaks free and begins to travel around the body is known as an embolus.

Kidney failure, also known as end-stage kidney disease, is a medical condition in which the kidneys can no longer adequately filter waste products from the blood, functioning at less than 15% of normal levels. Kidney failure is classified as either acute kidney failure, which develops rapidly and may resolve; and chronic kidney failure, which develops slowly and can often be irreversible. Symptoms may include leg swelling, feeling tired, vomiting, loss of appetite, and confusion. Complications of acute and chronic failure include uremia, hyperkalaemia, and volume overload. Complications of chronic failure also include heart disease, high blood pressure, and anaemia.

Peripheral artery disease (PAD) is an abnormal narrowing of arteries other than those that supply the heart or brain. PAD can happen in any blood vessel, but it is more common in the legs than the arms.

Ischemia or ischaemia is a restriction in blood supply to any tissue, muscle group, or organ of the body, causing a shortage of oxygen that is needed for cellular metabolism. Ischemia is generally caused by problems with blood vessels, with resultant damage to or dysfunction of tissue i.e. hypoxia and microvascular dysfunction. It also implies local hypoxia in a part of a body resulting from constriction. Ischemia causes not only insufficiency of oxygen, but also reduced availability of nutrients and inadequate removal of metabolic wastes. Ischemia can be partial or total blockage. The inadequate delivery of oxygenated blood to the organs must be resolved either by treating the cause of the inadequate delivery or reducing the oxygen demand of the system that needs it. For example, patients with myocardial ischemia have a decreased blood flow to the heart and are prescribed with medications that reduce chronotrophy and ionotrophy to meet the new level of blood delivery supplied by the stenosed vasculature so that it is adequate.
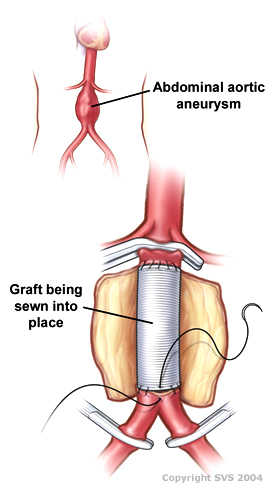
Vascular surgery is a surgical subspecialty in which vascular diseases involving the arteries, veins, or lymphatic vessels, are managed by medical therapy, minimally-invasive catheter procedures and surgical reconstruction. The specialty evolved from general and cardiovascular surgery where it refined the management of just the vessels, no longer treating the heart or other organs. Modern vascular surgery includes open surgery techniques, endovascular techniques and medical management of vascular diseases - unlike the parent specialities. The vascular surgeon is trained in the diagnosis and management of diseases affecting all parts of the vascular system excluding the coronaries and intracranial vasculature. Vascular surgeons also are called to assist other physicians to carry out surgery near vessels, or to salvage vascular injuries that include hemorrhage control, dissection, occlusion or simply for safe exposure of vascular structures.

Abdominal pain, also known as a stomach ache, is a symptom associated with both non-serious and serious medical issues.
Intestinal malrotation is a congenital anomaly of rotation of the midgut. It occurs during the first trimester as the fetal gut undergoes a complex series of growth and development. Malrotation can lead to a dangerous complication called volvulus. Malrotation can refer to a spectrum of abnormal intestinal positioning, often including:

Cerebral infarction is the pathologic process that results in an area of necrotic tissue in the brain. It is caused by disrupted blood supply (ischemia) and restricted oxygen supply (hypoxia), most commonly due to thromboembolism, and manifests clinically as ischemic stroke. In response to ischemia, the brain degenerates by the process of liquefactive necrosis.

Unstable angina is a type of angina pectoris that is irregular or more easily provoked. It is classified as a type of acute coronary syndrome (ACS).

Ischemic colitis is a medical condition in which inflammation and injury of the large intestine result from inadequate blood supply. Although uncommon in the general population, ischemic colitis occurs with greater frequency in the elderly, and is the most common form of bowel ischemia. Causes of the reduced blood flow can include changes in the systemic circulation or local factors such as constriction of blood vessels or a blood clot. In most cases, no specific cause can be identified.
An acute abdomen refers to a sudden, severe abdominal pain. It is in many cases a medical emergency, requiring urgent and specific diagnosis. Several causes need immediate surgical treatment.
Abdominal angina is abdominal pain after eating that occurs in individuals with ongoing poor blood supply to their small intestines known as chronic mesenteric ischemia. Although the term angina alone usually denotes angina pectoris, angina by itself can also mean "any spasmodic, choking, or suffocative pain", with an anatomic adjective defining its focus; so, in this case, spasmodic pain in the abdomen. Stedman's Medical Dictionary Online defines abdominal angina as "intermittent abdominal pain, frequently occurring at a fixed time after eating, caused by inadequacy of the mesenteric circulation resulting from arteriosclerosis or other arterial disease. Synonym: intestinal angina."

A bowel resection or enterectomy is a surgical procedure in which a part of an intestine (bowel) is removed, from either the small intestine or large intestine. Often the word enterectomy is reserved for the sense of small bowel resection, in distinction from colectomy, which covers the sense of large bowel resection. Bowel resection may be performed to treat gastrointestinal cancer, bowel ischemia, necrosis, or obstruction due to scar tissue, volvulus, and hernias. Some patients require ileostomy or colostomy after this procedure as alternative means of excretion. Complications of the procedure may include anastomotic leak or dehiscence, hernias, or adhesions causing partial or complete bowel obstruction. Depending on which part and how much of the intestines are removed, there may be digestive and metabolic challenges afterward, such as short bowel syndrome.
Ischemic preconditioning (IPC) is an experimental technique for producing resistance to the loss of blood supply, and thus oxygen, to tissues of many types. In the heart, IPC is an intrinsic process whereby repeated short episodes of ischaemia protect the myocardium against a subsequent ischaemic insult. It was first identified in 1986 by Murry et al. This group exposed anesthetised open-chest dogs to four periods of 5 minute coronary artery occlusions followed by a 5-minute period of reperfusion before the onset of a 40-minute sustained occlusion of the coronary artery. The control animals had no such period of “ischaemic preconditioning” and had much larger infarct sizes compared with the dogs that did. The exact molecular pathways behind this phenomenon have yet to be fully understood.

Bowel infarction or gangrenous bowel represents an irreversible injury to the intestine resulting from insufficient blood flow. It is considered a medical emergency because it can quickly result in life-threatening infection and death. Any cause of bowel ischemia, the earlier reversible form of injury, may ultimately lead to infarction if uncorrected. The causes of bowel ischemia or infarction include primary vascular causes and other causes of bowel obstruction.
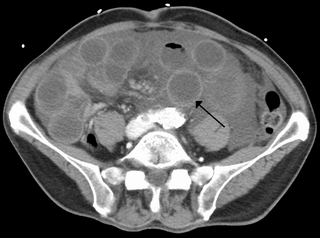
Intestinal ischemia is a medical condition in which injury to the large or small intestine occurs due to not enough blood supply. It can come on suddenly, known as acute intestinal ischemia, or gradually, known as chronic intestinal ischemia. The acute form of the disease often presents with sudden severe abdominal pain and is associated with a high risk of death. The chronic form typically presents more gradually with abdominal pain after eating, unintentional weight loss, vomiting, and fear of eating.
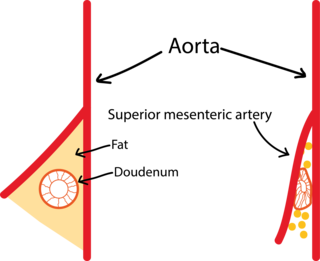
Superior mesenteric artery (SMA) syndrome is a gastro-vascular disorder in which the third and final portion of the duodenum is compressed between the abdominal aorta (AA) and the overlying superior mesenteric artery. This rare, potentially life-threatening syndrome is typically caused by an angle of 6–25° between the AA and the SMA, in comparison to the normal range of 38–56°, due to a lack of retroperitoneal and visceral fat. In addition, the aortomesenteric distance is 2–8 millimeters, as opposed to the typical 10–20. However, a narrow SMA angle alone is not enough to make a diagnosis, because patients with a low BMI, most notably children, have been known to have a narrow SMA angle with no symptoms of SMA syndrome.

ST depression refers to a finding on an electrocardiogram, wherein the trace in the ST segment is abnormally low below the baseline.

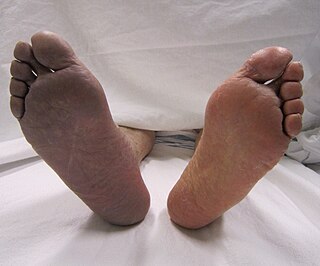
Acute limb ischaemia (ALI) occurs when there is a sudden lack of blood flow to a limb, within 14 days of symptoms onset. It is different from another condition which is more chronic called critical limb ischemia (CLD). CLD is the end stage of peripheral vascular disease where there is still some collateral circulation (alternate circulation pathways} that bring some blood to the distal parts of the limbs. While limbs in both acute and chronic limb ischemia may be pulseless, a chronically ischemic limb is typically warm and pink due to a well-developed collateral artery network and does not need emergency intervention to avoid limb loss.
Chronic limb threatening ischemia (CLTI), also known as critical limb ischemia (CLI), is an advanced stage of peripheral artery disease (PAD). It is defined as ischemic rest pain, arterial insufficiency ulcers, and gangrene. The latter two conditions are jointly referred to as tissue loss, reflecting the development of surface damage to the limb tissue due to the most severe stage of ischemia. Compared to the other manifestation of PAD, intermittent claudication, CLI has a negative prognosis within a year after the initial diagnosis, with 1-year amputation rates of approximately 12% and mortality of 50% at 5 years and 70% at 10 years.
References
- 1 2 Krämer, S. C.; Görich, J.; Oertel, F.; Scheld, H.; Heindel, W. (1 September 2003). "[Non-occlusive mesenteric ischemia]". RöFo. 175 (9): 1177–1183. doi:10.1055/s-2003-41923. PMID 12964071.
- ↑ Trompeter, Markus; Brazda, Thurid; Remy, Christopher T.; Vestring, Thomas; Reimer, Peter (1 May 2002). "Non-occlusive mesenteric ischemia: etiology, diagnosis, and interventional therapy". Eur Radiol. 12 (5): 1179–1187. doi:10.1007/s00330-001-1220-2. PMID 11976865. S2CID 19135271.
- 1 2 Longmore, Murray; Wilkinson, Ian; Baldwin, Andrew; Wallin, Elizabeth (31 March 2017). Oxford Handbook of Clinical Medicine. OUP Oxford. ISBN 9780199609628 – via Google Books.
- ↑ Garden, O. James; Bradbury, Andrew W.; Forsythe, John L. R.; Parks, Rowan W. (28 May 2012). Principles and Practice of Surgery E-Book: With STUDENT CONSULT Online Access. Elsevier Health Sciences. ISBN 978-0702051166 – via Google Books.