
Inorganic chemistry deals with synthesis and behavior of inorganic and organometallic compounds. This field covers chemical compounds that are not carbon-based, which are the subjects of organic chemistry. The distinction between the two disciplines is far from absolute, as there is much overlap in the subdiscipline of organometallic chemistry. It has applications in every aspect of the chemical industry, including catalysis, materials science, pigments, surfactants, coatings, medications, fuels, and agriculture.

Organometallic chemistry is the study of organometallic compounds, chemical compounds containing at least one chemical bond between a carbon atom of an organic molecule and a metal, including alkali, alkaline earth, and transition metals, and sometimes broadened to include metalloids like boron, silicon, and selenium, as well. Aside from bonds to organyl fragments or molecules, bonds to 'inorganic' carbon, like carbon monoxide, cyanide, or carbide, are generally considered to be organometallic as well. Some related compounds such as transition metal hydrides and metal phosphine complexes are often included in discussions of organometallic compounds, though strictly speaking, they are not necessarily organometallic. The related but distinct term "metalorganic compound" refers to metal-containing compounds lacking direct metal-carbon bonds but which contain organic ligands. Metal β-diketonates, alkoxides, dialkylamides, and metal phosphine complexes are representative members of this class. The field of organometallic chemistry combines aspects of traditional inorganic and organic chemistry.

High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), formerly referred to as high-pressure liquid chromatography, is a technique in analytical chemistry used to separate, identify, and quantify specific components in mixtures. The mixtures can originate from food, chemicals, pharmaceuticals, biological, environmental and agriculture, etc, which have been dissolved into liquid solutions.
The Heck reaction is the chemical reaction of an unsaturated halide with an alkene in the presence of a base and a palladium catalyst to form a substituted alkene. It is named after Tsutomu Mizoroki and Richard F. Heck. Heck was awarded the 2010 Nobel Prize in Chemistry, which he shared with Ei-ichi Negishi and Akira Suzuki, for the discovery and development of this reaction. This reaction was the first example of a carbon-carbon bond-forming reaction that followed a Pd(0)/Pd(II) catalytic cycle, the same catalytic cycle that is seen in other Pd(0)-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions. The Heck reaction is a way to substitute alkenes.
The Stille reaction is a chemical reaction widely used in organic synthesis. The reaction involves the coupling of two organic groups, one of which is carried as an organotin compound (also known as organostannanes). A variety of organic electrophiles provide the other coupling partner. The Stille reaction is one of many palladium-catalyzed coupling reactions.
The Suzuki reaction is an organic reaction, classified as a cross-coupling reaction, where the coupling partners are a boronic acid and an organohalide and the catalyst is a palladium(0) complex. It was first published in 1979 by Akira Suzuki, and he shared the 2010 Nobel Prize in Chemistry with Richard F. Heck and Ei-ichi Negishi for their contribution to the discovery and development of palladium-catalyzed cross-couplings in organic synthesis. This reaction is also known as the Suzuki–Miyaura reaction or simply as the Suzuki coupling. It is widely used to synthesize polyolefins, styrenes, and substituted biphenyls. Several reviews have been published describing advancements and the development of the Suzuki reaction. The general scheme for the Suzuki reaction is shown below, where a carbon-carbon single bond is formed by coupling a halide (R1-X) with an organoboron species (R2-BY2) using a palladium catalyst and a base. The organoboron species is usually synthesized by hydroboration or carboboration, allowing for rapid generation of molecular complexity.
The Sonogashira reaction is a cross-coupling reaction used in organic synthesis to form carbon–carbon bonds. It employs a palladium catalyst as well as copper co-catalyst to form a carbon–carbon bond between a terminal alkyne and an aryl or vinyl halide.
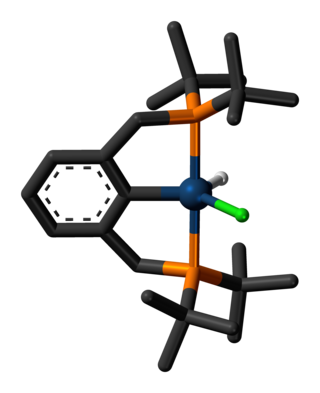
In chemistry, a transition metal pincer complex is a type of coordination complex with a pincer ligand. Pincer ligands are chelating agents that binds tightly to three adjacent coplanar sites in a meridional configuration. The inflexibility of the pincer-metal interaction confers high thermal stability to the resulting complexes. This stability is in part ascribed to the constrained geometry of the pincer, which inhibits cyclometallation of the organic substituents on the donor sites at each end. In the absence of this effect, cyclometallation is often a significant deactivation process for complexes, in particular limiting their ability to effect C-H bond activation. The organic substituents also define a hydrophobic pocket around the reactive coordination site. Stoichiometric and catalytic applications of pincer complexes have been studied at an accelerating pace since the mid-1970s. Most pincer ligands contain phosphines. Reactions of metal-pincer complexes are localized at three sites perpendicular to the plane of the pincer ligand, although in some cases one arm is hemi-labile and an additional coordination site is generated transiently. Early examples of pincer ligands were anionic with a carbanion as the central donor site and flanking phosphine donors; these compounds are referred to as PCP pincers.

Molecular imprinting is a technique to create template-shaped cavities in polymer matrices with predetermined selectivity and high affinity. This technique is based on the system used by enzymes for substrate recognition, which is called the "lock and key" model. The active binding site of an enzyme has a shape specific to a substrate. Substrates with a complementary shape to the binding site selectively bind to the enzyme; alternative shapes that do not fit the binding site are not recognized.
The Ullmann reaction or Ullmann coupling is a coupling reaction between aryl halides. Traditionally this reaction is effected by copper, but palladium and nickel are also effective catalysts. The reaction is named after Fritz Ullmann.

Organozinc chemistry is the study of the physical properties, synthesis, and reactions of organozinc compounds, which are organometallic compounds that contain carbon (C) to zinc (Zn) chemical bonds.
Reversed-phase Liquid chromatography (RP-LC) is a mode of liquid chromatography in which non-polar stationary phase and polar mobile phases are used for the separation of organic compounds. The vast majority of separations and analyses using High Performance Liquid Chromatography-HPLC in recent years are done using the Reversed Phase mode. In the Reversed Phase mode, the sample components are retained in the system, the more hydrophobic they are.

Organocopper chemistry is the study of the physical properties, reactions, and synthesis of organocopper compounds, which are organometallic compounds containing a carbon to copper chemical bond. They are reagents in organic chemistry.
Silanization is the attachment of an organosilyl group to some chemical species. Almost always, the silanization refers to conversion of a silanol-terminated surface to a alkylsiloxy-terminated surface. This conversion confers hydrophobicity to a previously hydrophilic surface. This process is often used to modify the surface properties of glass, silicon, alumina, quartz, and metal oxide substrates, which all have an abundance of hydroxyl groups. Silanization differs from silylation, which usually refers to attachment of organosilicon groups to molecular substrates.
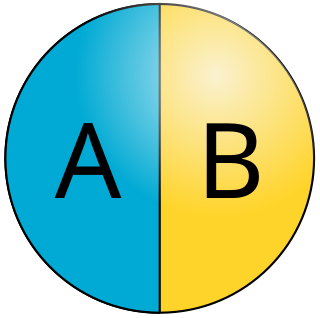
Janus particles are special types of nanoparticles or microparticles whose surfaces have two or more distinct physical properties. This unique surface of Janus particles allows two different types of chemistry to occur on the same particle. The simplest case of a Janus particle is achieved by dividing the particle into two distinct parts, each of them either made of a different material, or bearing different functional groups. For example, a Janus particle may have one half of its surface composed of hydrophilic groups and the other half hydrophobic groups, the particles might have two surfaces of different color, fluorescence, or magnetic properties. This gives these particles unique properties related to their asymmetric structure and/or functionalization.
In chemistry, π-effects or π-interactions are a type of non-covalent interaction that involves π systems. Just like in an electrostatic interaction where a region of negative charge interacts with a positive charge, the electron-rich π system can interact with a metal, an anion, another molecule and even another π system. Non-covalent interactions involving π systems are pivotal to biological events such as protein-ligand recognition.
1-Decyne is the organic compound with the formula C8H17C≡CH. It is a terminal alkyne. A colorless liquid, 1-decyne is used as a model substrate when evaluating methodology in organic synthesis. It participates in a number of classical reactions including Suzuki-Miyaura couplings, Sonogashira couplings, Huisgen cycloadditions, and borylations.
Hybrid materials are composites consisting of two constituents at the nanometer or molecular level. Commonly one of these compounds is inorganic and the other one organic in nature. Thus, they differ from traditional composites where the constituents are at the macroscopic level. Mixing at the microscopic scale leads to a more homogeneous material that either show characteristics in between the two original phases or even new properties.

In organometallic chemistry, palladium-NHC complexes are a family of organopalladium compounds in which palladium forms a coordination complex with N-heterocyclic carbenes (NHCs). They have been investigated for applications in homogeneous catalysis, particularly cross-coupling reactions.

Copper forms a rich variety of compounds, usually with oxidation states +1 and +2, which are often called cuprous and cupric, respectively. Copper compounds, whether organic complexes or organometallics, promote or catalyse numerous chemical and biological processes.











