Related Research Articles

An exoplanet or extrasolar planet is a planet outside the Solar System. The first possible evidence of an exoplanet was noted in 1917 but was not then recognized as such. The first confirmation of the detection occurred in 1992. A different planet, first detected in 1988, was confirmed in 2003. According to statistics from the NASA Exoplanet Archive, As of 25 July 2024, there are 5,741 confirmed exoplanets in 4,285 planetary systems, with 960 systems having more than one planet. The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) is expected to discover more exoplanets, and to give more insight into their traits, such as their composition, environmental conditions, and potential for life.
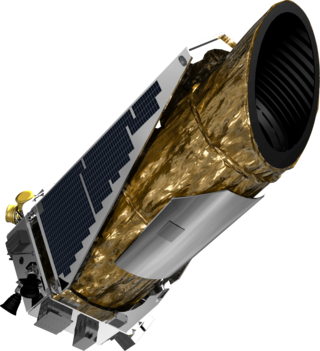
The Kepler space telescope is a defunct space telescope launched by NASA in 2009 to discover Earth-sized planets orbiting other stars. Named after astronomer Johannes Kepler, the spacecraft was launched into an Earth-trailing heliocentric orbit. The principal investigator was William J. Borucki. After nine and a half years of operation, the telescope's reaction control system fuel was depleted, and NASA announced its retirement on October 30, 2018.

Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) is a space telescope for NASA's Explorer program, designed to search for exoplanets using the transit method in an area 400 times larger than that covered by the Kepler mission. It was launched on 18 April 2018, atop a Falcon 9 launch vehicle and was placed into a highly elliptical 13.70-day orbit around the Earth. The first light image from TESS was taken on 7 August 2018, and released publicly on 17 September 2018.

The 215th meeting of the American Astronomical Society (AAS) took place in Washington, D.C., Jan. 3 to Jan. 7, 2010. It is one of the largest astronomy meetings ever to take place as 3,500 astronomers and researchers were expected to attend and give more than 2,200 scientific presentations. The meeting was actually billed as the "largest Astronomy meeting in the universe". An array of discoveries were announced, along with new views of the universe that we inhabit; such as quiet planets like Earth - where life could develop are probably plentiful, even though an abundance of cosmic hurdles exist - such as experienced by our own planet in the past.

An exoplanet is a planet located outside the Solar System. The first evidence of an exoplanet was noted as early as 1917, but was not recognized as such until 2016; no planet discovery has yet come from that evidence. What turned out to be the first detection of an exoplanet was published among a list of possible candidates in 1988, though not confirmed until 2003. The first confirmed detection came in 1992, with the discovery of terrestrial-mass planets orbiting the pulsar PSR B1257+12. The first confirmation of an exoplanet orbiting a main-sequence star was made in 1995, when a giant planet was found in a four-day orbit around the nearby star 51 Pegasi. Some exoplanets have been imaged directly by telescopes, but the vast majority have been detected through indirect methods, such as the transit method and the radial-velocity method. As of 24 July 2024, there are 7,026 confirmed exoplanets in 4,949 planetary systems, with 1007 systems having more than one planet. This is a list of the most notable discoveries.

The NASA Exoplanet Archive is an online astronomical exoplanet catalog and data service that collects and serves public data that support the search for and characterization of extra-solar planets (exoplanets) and their host stars. It is part of the Infrared Processing and Analysis Center and is on the campus of the California Institute of Technology (Caltech) in Pasadena, CA. The archive is funded by NASA and was launched in early December 2011 by the NASA Exoplanet Science Institute as part of NASA's Exoplanet Exploration Program. In June 2019, the archive's collection of confirmed exoplanets surpassed 4,000.
Kepler-47 is a binary star system in the constellation Cygnus located about 3,420 light-years away from Earth. The stars have three exoplanets, all of which orbit both stars at the same time, making this a circumbinary system. The first two planets announced are designated Kepler-47b, and Kepler-47c, and the third, later discovery is Kepler-47d. Kepler-47 is the first circumbinary multi-planet system discovered by the Kepler mission. The outermost of the planets is a gas giant orbiting within the habitable zone of the stars. Because most stars are binary, the discovery that multi-planet systems can form in such a system has impacted previous theories of planetary formation.

Kepler-37, also known as UGA-1785, is a G-type main-sequence star located in the constellation Lyra 209 light-years from Earth. It is host to exoplanets Kepler-37b, Kepler-37c, Kepler-37d and possibly Kepler-37e, all of which orbit very close to it. Kepler-37 has a mass about 80.3 percent of the Sun's and a radius about 77 percent as large. It has a temperature similar to that of the Sun, but a bit cooler at 5,357 K. It has about half the metallicity of the Sun. With an age of roughly 6 billion years, it is slightly older than the Sun, but is still a main-sequence star. Until January 2015, Kepler-37 was the smallest star to be measured via asteroseismology.

Kepler-62e is a super-Earth exoplanet discovered orbiting within the habitable zone of Kepler-62, the second outermost of five such planets discovered by NASA's Kepler spacecraft. Kepler-62e is located about 990 light-years from Earth in the constellation of Lyra. The exoplanet was found using the transit method, in which the dimming effect that a planet causes as it crosses in front of its star is measured. Kepler-62e may be a terrestrial or ocean-covered planet; it lies in the inner part of its host star's habitable zone.

Kepler-62f is a super-Earth exoplanet orbiting within the habitable zone of the star Kepler-62, the outermost of five such planets discovered around the star by NASA's Kepler spacecraft. It is located about 980 light-years from Earth in the constellation of Lyra.

Kepler-438b is a confirmed near-Earth-sized exoplanet. It is likely rocky. It orbits on the inner edge of the habitable zone of a red dwarf, Kepler-438, about 472.9 light-years from Earth in the constellation Lyra. It receives 1.4 times our solar flux. The planet was discovered by NASA's Kepler spacecraft using the transit method, in which the dimming effect that a planet causes as it crosses in front of its star is measured. NASA announced the confirmation of the exoplanet on 6 January 2015.

Kepler-442b is a confirmed near-Earth-sized exoplanet, likely rocky, orbiting within the habitable zone of the K-type main-sequence star Kepler-442, about 1,206 light-years (370 pc) from Earth in the constellation of Lyra.
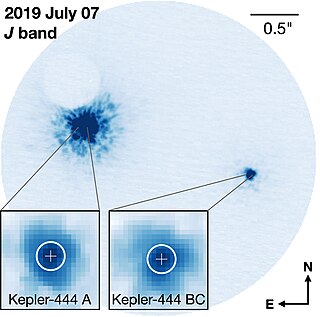
Kepler-444 is a triple star system, estimated to be 11.2 billion years old, approximately 119 light-years (36 pc) away from Earth in the constellation Lyra. On 27 January 2015, the Kepler spacecraft is reported to have confirmed the detection of five sub-Earth-sized rocky exoplanets orbiting the main star. The star is a K-type main sequence star. All of the planets are far too close to their star to harbour life forms.

Kepler-1229b is a confirmed super-Earth exoplanet, likely rocky, orbiting within the habitable zone of the red dwarf Kepler-1229, located about 870 light years from Earth in the constellation of Cygnus. It was discovered in 2016 by the Kepler space telescope. The exoplanet was found by using the transit method, in which the dimming effect that a planet causes as it crosses in front of its star is measured.
K2-155d is a potentially habitable Super-Earth exoplanet in the K2-155 system. It is the outermost of three known planets orbiting around the K-type star K2-155 in the constellation Taurus. It is one of 15 new exoplanets around red dwarf stars discovered by Japanese astronomer Teruyuki Hirano of the Tokyo Institute of Technology and his team. The team used data from NASA's Kepler Space Telescope during its extended K2 "Second Light" mission. K2-155d orbits near the so-called habitable zone of its system, and has the potential to host liquid water.
TOI-700 is a red dwarf 101.4 light-years away from Earth located in the Dorado constellation that hosts TOI-700 d, the first Earth-sized exoplanet in the habitable zone discovered by the Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS).

TOI-700 d is a near-Earth-sized exoplanet, likely rocky, orbiting within the habitable zone of the red dwarf TOI-700, the outermost planet within the system. It is located roughly 101.4 light-years (31.1 pc) away from Earth in the constellation of Dorado. The exoplanet is the first Earth-sized exoplanet in the habitable zone discovered by the Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS).

Habitability of G V stars of G V stars systems defines the suitability for life of exoplanets belonging to yellow dwarf stars. These systems are the object of study among the scientific community because they are considered the most suitable for harboring living organisms, together with those belonging to K-type stars.
TOI-1452 b is a confirmed super-Earth exoplanet, possibly a water world, orbiting a red-dwarf star TOI-1452 about 100 light-years away in the Draco constellation. The exoplanet is about 70% larger in diameter than Earth, and roughly five times as massive.
References
- ↑ "White Dwarf Research Corporation". ProPublica Nonprofit Explorer.
- ↑ Hylkema, Chloë (June 2023). "Adopt a Star Offers Out-of-This-World Gifts for Couples". DatingNews.com.
- ↑ Moskowitz, Clara (August 2009). "Adopt a Star, Help Fund Science". Space.com.
- ↑ NASA (November 2013). "How NASA revived the Kepler Space Telescope". phys.org.
- ↑ Plait, Phil (February 2013). "Astronomers Find the Tiniest Exoplanet Yet". Slate.
- ↑ Atkinson, Nancy (January 2015). "Oldest Planetary System Discovered, Improving the Chances for Intelligent Life Everywhere". Universe Today.
- ↑ United States Patent and Trademark Office (April 2024). "Status Search SN 7371313". uspto.gov.
- ↑ "The Curious Adventures of an Astronomer-Turned-Crowdfunder". MIT Technology Review. March 2015.
- ↑ Grossman, Lisa (August 2009). "Stars put up for adoption to fund exoplanet research". New Scientist.
- ↑ Feeney, Nolan (July 2014). "A Star With a Not-So-Nice Nickname for Putin Won't Have to Change". TIME.
- ↑ Jain, Akshita Nahar (May 2022). "Gucci gifts each person who attended their Cosmogonie Cruise 2023 show a star". Lifestyle Asia.