Related Research Articles

The SEA IV was a French two-seat military aircraft of World War I and the immediate post-war era.

The Dassault MD 315 Flamant is a French light twin-engined transport airplane built shortly after World War II by Dassault Aviation for the French Air Force.

The Nord Aviation 3202 is a 1950s French military trainer aircraft designed and built by Nord Aviation to meet a French Army requirement for a two-seat basic trainer, as a replacement for the biplane Stampe SV.4. Altogether, 101 examples were built, with the first flying on 17 April 1957.

The CAB GY-30 Supercab was a two-seat light aircraft built in France in 1954, as a further development of the CAB Minicab. The design was performed by Yves Gardan, a onetime employee of French aeronautical company SIPA. Changes incorporated in the Supercab included a more powerful engine, greater wingspan, manually retractable undercarriage, and slotted flaps that replaced the split flaps of the Minicab.
The Dassault M.D.320 Hirondelle was a French 14-seat utility transport aircraft of the 1960s, designed and built by Dassault Aviation, in prototype form only.
The SNCASE SE.3120 Alouette ("Lark") was a utility helicopter developed in France in the early 1950s but which did not enter production. Designed in parallel with the SE.3110, the Alouette shared that machine's dynamic components, with the exception of the SE.3110's unusual twin tail rotor, which was replaced by a single rotor, and the addition of a three-bladed gyroscopic stabiliser under the main rotor (similar to the stabiliser bar used by Bell helicopters. The Alouette featured an open-framework fuselage behind a cockpit that was enclosed by a bubble canopy. Skid undercarriage and tricycle gear were both tested.

The Morane-Saulnier MS.230 aircraft was the main elementary trainer for the French Armée de l'Air throughout the 1930s. Almost all French pilots flying for the Armée de l'Air at the outbreak of World War II had had their earliest flight training in this machine. It was the equivalent of the Stearman trainer in the United States air services and the de Havilland Tiger Moth in the British Royal Air Force.

The SCAN 20 was a 1940s French flying-boat training monoplane designed and built by Société de Constructions Aéro-Navales de Port-Neuf (SCAN). The prototype was built in secret in 1941. It was hidden until the liberation of France and first flown in 1945.
The Hanriot HD.17 was a French trainer seaplane of the 1920s. It was essentially a floatplane version of the ubiquitous HD.14 with a revised tail and a more powerful engine. Over 50 examples were operated by the Aéronautique Maritime, of which seven were converted to landplanes. A small number of HD.17s were exported to Estonia and Latvia. Further development resulted in the HD.41H.
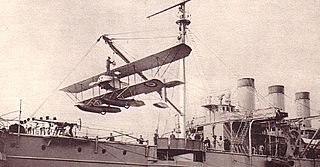
The Caudron J Marine was an amphibious, two-seat, biplane equipped with floats and wheels, similar to the earlier Caudron J floatplane.
The Morane-Saulnier MS.560 was a French civil aerobatic monoplane designed and built by Morane-Saulnier.
The Dewoitine HD.730 was a prototype French reconnaissance floatplane of the 1940s. It was a single-engined, low-wing monoplane that was designed as a catapult-launched reconnaissance aircraft to operate from warships of the French Navy. Two flew in 1940, and a third aircraft was built to a modified design in 1941, but no production followed.
The Nord 1700 Norélic or SNCAN N.1700 Norélic was a French helicopter with several novel control features. Only one prototype was built, though it was intended to lead to series production.

The Barber Snark is a two-seater kit-plane, designed and built in New Zealand by Bill Barber. It first flew in late 1987. Only some five aircraft have been built.
The Bloch MB.60, initially known as the MB.VI, was a tri-motor mailplane designed and built in France from 1930 to 1931 to an order for an aircraft suitable for use as a postal, commercial or medical transport.
The Blériot XLIII was a First World War French reconnaissance plane designed and built by Blériot.
The Lioré et Olivier LeO H-46 was a bomber seaplane built in France in 1936.
The Dewoitine D.720 T3 was a French reconnaissance/cooperation aircraft built by Dewoitine in the late 1930s.
The Bloch MB.800 was a French low-wing monoplane three-seat trainer / mailplane developed by Société des Avions Marcel Bloch. It was of all-wood construction.
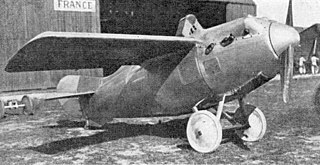
The Hanriot HD.22 was a racer aircraft built by Hanriot in the early 1920s.
References
- ↑ de Narbonne 2010, p. 79
- ↑ "Dassault M.D.80 ABC". 1000aircraftphotos.com. Retrieved 6 February 2019.
- 1 2 "Nord 2800". 1000aircraftphotos.com. Retrieved 6 February 2019.
- ↑ Parmentier, Bruno (3 July 1997). "S.N.C.A.N. Nord 2800". Aviafrance (in French). Paris. Retrieved 6 February 2019.
- de Narbonne, Roland (August 2010). "Août 1950, dans l'aéronautique française: Le Nord 2800: Un petit tour et puis s'en va". Le Fana de l'Aviation (in French). No. 489. pp. 78–79.