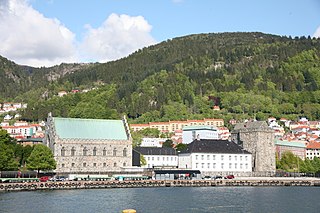Horten (help·info) is a town and municipality in Vestfold in Vestfold og Telemark county, Norway—located along the Oslofjord. The administrative centre of the municipality is the town of Horten. The municipality also includes the town of Åsgårdstrand and the villages of Borre, Skoppum, and Nykirke.

The Hilsea Lines are a line of 18th- and 19th-century fortifications built at Hilsea to protect the northern approach to Portsea Island, an island off the southern coast of England which forms the majority of the city of Portsmouth and its key naval base. They are now used as a greenspace and leisure area, also known locally as Foxes Forest.

Newhaven Fort is a Palmerston fort built in the 19th century to defend the harbour at Newhaven, on the south coast of England. It was the largest defence work ever built in Sussex and is now open as a museum.

A casemate is a fortified gun emplacement or armored structure from which guns are fired, in a fortification, warship, or armoured fighting vehicle.

The Fort Zachary Taylor Historic State Park, also known simply as Fort Taylor, is a Florida State Park and National Historic Landmark centered on a Civil War-era fort located near the southern tip of Key West, Florida.

Fredriksvern was an important Norwegian naval base, just south of Larvik in Vestfold. It is named after Fredrik V Denmark-Norway. The town of Stavern has in many ways come to be because of this naval base.

Staverns Fortress was a military facility located on the island of Citadelløya at Stavern in Vestfold, Norway.
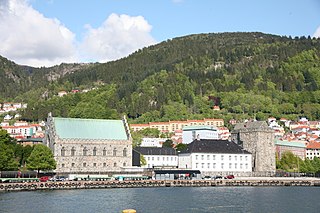
Bergenhus fortress is a fortress located in Bergen, Norway. Located at the entrance of Bergen harbour, the castle is one of the oldest and best preserved stone fortifications in Norway.

The Royal Norwegian Navy Museum is a museum documenting the history of the Royal Norwegian Navy. It is located at the former main naval base of Karljohansvern in Horten. The museum was founded by C.F. Klinck on 24 August 1853. The museum is sometimes regarded as the world's first naval museum, as it was the first collection of naval memorabilia open to the public.

Baltazar Nicolai Garben was a Norwegian military officer, engineer and government minister. He is most associated with the design and construction of various buildings including Tøyhuset at Halden, Norway.

A scarp and a counterscarp are the inner and outer sides, respectively, of a ditch or moat used in fortifications. Attackers must descend the counterscarp and ascend the scarp. In permanent fortifications the scarp and counterscarp may be encased in stone. In less permanent fortifications, the counterscarp may be lined with paling fence set at an angle so as to give no cover to the attackers but to make advancing and retreating more difficult.

Citadellet (Citadel) was a 19th-century Norwegian fortress. The last day of military activity was in 1970. The fort was demolished in 1971.

Karjohansvern at Horten was the main base for the Royal Norwegian Navy from 1850 to 1963.
German submarine U-735 was a Type VIIC U-boat built for Nazi Germany's Kriegsmarine for service during World War II.

Borre is a village in the municipality of Horten, Vestfold county, Norway. The village of Borre had provided the name of the former Borre municipality.

The siege of Fredriksten was an attack on the Norwegian fortress of Fredriksten in the city of Fredrikshald by King Charles XII of Sweden. While inspecting his troops' lines, Charles XII was killed by a projectile. The Swedes broke off the siege, and the Norwegians held the fortress. Along with the Treaty of Nystad three years later, the death of Charles XII marked the end of the imperial era in Sweden, and the beginning of the Age of Liberty in that country.

Kristiansand Cannon Museum is a museum at Møvik, 8 kilometers west of the town centre of Kristiansand, Norway. The museum has collected authentic equipment from a former military installation.

Fort Bourguignon is one of many fortresses in Pula, Croatia that were built by the Austrian Empire in the second half of the 19th century.

The New Fortress of Corfu is a Venetian fortress built on the hill of St. Mark in Corfu in stages. The original architect of the fort was the military engineer Ferrante Vitelli. The current buildings which exist within the fortress were built by the British during their rule of the island (1815–63).
The Battle of Horten Harbour or the Action at Horten was an engagement that occurred on 9 April 1940. It took place during Operation Weserübung, when the Germans launched an amphibious assault on Karljohansvern, the Norwegian naval base at Horten. After being initially repulsed by Norwegian naval units, German troops headed overland to outflank the base, forcing it to capitulate.