Related Research Articles
Twelve-step programs are international mutual aid programs supporting recovery from substance addictions, behavioral addictions and compulsions. Developed in the 1930s, the first twelve-step program, Alcoholics Anonymous (AA), founded by Bill Wilson and Bob Smith, aided its membership to overcome alcoholism. Since that time dozens of other organizations have been derived from AA's approach to address problems as varied as drug addiction, compulsive gambling, sex, and overeating. All twelve-step programs utilize a version of AA's suggested twelve steps first published in the 1939 book Alcoholics Anonymous: The Story of How More Than One Hundred Men Have Recovered from Alcoholism.
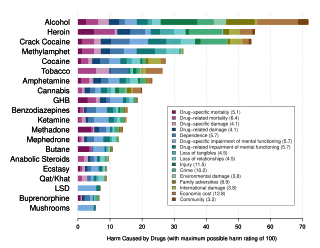
Drug rehabilitation is the process of medical or psychotherapeutic treatment for dependency on psychoactive substances such as alcohol, prescription drugs, and street drugs such as cannabis, cocaine, heroin, and amphetamines. The general intent is to enable the patient to confront substance dependence, if present, and stop substance misuse to avoid the psychological, legal, financial, social, and medical consequences that can be caused.

Problem gambling, ludophaty or ludomania is repetitive gambling behavior despite harm and negative consequences. Problem gambling may be diagnosed as a mental disorder according to DSM-5 if certain diagnostic criteria are met. Pathological gambling is a common disorder associated with social and family costs.
Substance dependence, also known as drug dependence, is a biopsychological situation whereby an individual's functionality is dependent on the necessitated re-consumption of a psychoactive substance because of an adaptive state that has developed within the individual from psychoactive substance consumption that results in the experience of withdrawal and that necessitates the re-consumption of the drug. A drug addiction, a distinct concept from substance dependence, is defined as compulsive, out-of-control drug use, despite negative consequences. An addictive drug is a drug which is both rewarding and reinforcing. ΔFosB, a gene transcription factor, is now known to be a critical component and common factor in the development of virtually all forms of behavioral and drug addictions, but not dependence.
A methadone clinic is a medical facility where medications for opioid use disorder (MOUD) are dispensed-—historically and most commonly methadone, although buprenorphine is also increasingly prescribed. Medically assisted drug therapy treatment is indicated in patients who are opioid-dependent or have a history of opioid dependence. Methadone is a schedule II (USA) opioid analgesic, that is also prescribed for pain management. It is a long-acting opioid that can delay the opioid withdrawal symptoms that patients experience from taking short-acting opioids, like heroin, and allow time for withdrawal management. In the United States, by law, patients must receive methadone under the supervision of a physician, and dispensed through the Opioid Treatment Program (OTP) certified by the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration and registered with the Drug Enforcement Administration.

Pine Rest Christian Mental Health Services is a psychiatric hospital and behavioral health provider, with the main treatment campus located in Grand Rapids, Michigan. The Chief Executive Officer and President is Dr. Mark Eastburg, appointed December, 2006.
St. Cloud Hospital is a hospital in St. Cloud, Minnesota, United States. It is a Catholic-affiliated, not-for-profit institution and part of CentraCare Health. The hospital has more than 9,000 employees, 400 physicians and 1,200 volunteers. It serves 690,000 people in a 12-county area.
Sober living houses (SLHs), also called sober homes and sober living environments, are facilities that provide safe housing and supportive, structured living conditions for people exiting drug rehabilitation programs. SLHs serve as a transitional environment between such programs and mainstream society. Many SLHs also accept people who are in recovery from substance use disorders but have not recently completed a rehabilitation program.

Polysubstance dependence refers to a type of substance use disorder in which an individual uses at least three different classes of substances indiscriminately and does not have a favorite substance that qualifies for dependence on its own. Although any combination of three substances can be used, studies have shown that alcohol is commonly used with another substance. One study on polysubstance use categorized participants who used multiple substances according to their substance of preference. The results of a longitudinal study on substance use led the researchers to observe that excessively using or relying on one substance increased the probability of excessively using or relying on another substance.
Services for mental health disorders provide treatment, support, or advocacy to people who have psychiatric illnesses. These may include medical, behavioral, social, and legal services.
Willingway, located in Statesboro, Georgia, is a privately owned Substance Use Disorder facility which specializes in treating alcoholism and drug addiction. The treatment modality at Willingway is based on the principles of the twelve-step program, Alcoholics Anonymous. It is referred to by many as "The Betty Ford Center of the South."

Addiction is a neuropsychological disorder characterized by a persistent and intense urge to use a drug or engage in a behavior that produces natural reward, despite substantial harm and other negative consequences. Repetitive drug use often alters brain function in ways that perpetuate craving, and weakens self-control. This phenomenon – drugs reshaping brain function – has led to an understanding of addiction as a brain disorder with a complex variety of psychosocial as well as neurobiological factors that are implicated in addiction's development.
Brighton Hospital is one of the oldest alcoholism and addiction treatment centers in North America.
Recovery coaching is a form of strengths-based support for people with addictions or in recovery from alcohol, other drugs, codependency, or other addictive behaviors. There are multiple models, with some programs using self-identified peers who draw from their own lived experience with substance use and recovery and some utilizing people who have no lived experience but some training in support, depending on local standards and availability. They help clients find ways to stop addiction (abstinence) or reduce harm associated with addictive behaviors. These coaches can help a client find resources for harm reduction, detox, treatment, family support and education, local or online support groups; or help a client create a change plan to recover on their own.
Addiction psychiatry is a medical subspecialty within psychiatry that focuses on the evaluation, diagnosis, and treatment of people who have one or more disorders related to addiction. This may include disorders involving legal and illegal drugs, gambling, sex, food, and other impulse control disorders. Addiction psychiatrists are substance use disorder experts. Growing amounts of scientific knowledge, such as the health effects and treatments for substance use disorders, have led to advancements in the field of addiction psychiatry. These advancements in understanding the neurobiology of rewarding behavior, along with federal funding, has allowed for ample opportunity for research in the discipline of addiction psychiatry. Addiction psychiatry is an expanding field, and currently there is a high demand for substance use disorder experts in both the private and public sector.
The Psychiatric Institute of Washington (PIW) is an acute psychiatric hospital in Washington, D.C. Opened in 1967, PIW is a short-term, private hospital. It offers behavioral healthcare to patients with mental and addictive illnesses, including children, adolescents, adults and the elderly. Services offered by PIW include inpatient, partial and intensive outpatient hospitalization, and group treatment programs for substance abuse and addiction.
About 1 in 7 Americans reportedly suffered from active addiction to a particular substance. Addiction can cause physical, emotional and psychological harm to those affected by it. The American Society of Addiction Medicine defines addiction as "a treatable, chronic medical disease involving complex interactions among brain circuits, genetics, the environment, and an individual's life experiences. People with addiction use substances or engage in behaviors that become compulsive and often continue despite harmful consequences."

The Cabin Rehab is a drug and alcohol rehabilitation facility in Chiang Mai, Thailand. The center has offered treatment for alcohol, drug and behavioral addiction since 2009. The centre is a medical tourism location for international patients from countries such as Australia, Bangladesh, India, Oman, Singapore, the United Kingdom and the United States.
AdCare Hospital of Worcester is a substance abuse treatment hospital located in Worcester, Massachusetts. With 114 inpatient beds and a variety of outpatient services in Massachusetts and Rhode Island, AdCare is the only private hospital in Massachusetts specifically dedicated to substance abuse treatment.
References
- ↑ "INPATIENT, RESIDENTIAL AND INTENSIVE OUTPATIENT TREATMENT FACILITY LIST" . Retrieved May 27, 2015.
- ↑ Potenza, M. N (12 October 2008). "The neurobiology of pathological gambling and drug addiction: an overview and new findings". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 363 (1507): 3181–3189. doi:10.1098/rstb.2008.0100. PMC 2607329 . PMID 18640909.
- ↑ Algamus Gambling Treatment Center https://www.algamus.org/ . Retrieved 13 November 2024.
{{cite web}}: Missing or empty|title=(help) - ↑ "Is drug addiction treatment worth its cost?" . Retrieved May 27, 2015.