
The Frisian languages are a closely related group of West Germanic languages, spoken by about 400,000 Frisian people, who live on the southern fringes of the North Sea in the Netherlands and Germany. The Frisian languages are the closest living language group to the Anglic languages; the two groups make up the Anglo-Frisian languages group and together with the Low German dialects these form the North Sea Germanic languages. However, modern English and Frisian are not mutually intelligible, nor are Frisian languages intelligible among themselves, owing to independent linguistic innovations and language contact with neighboring languages.
The Frisians are an ethnic group indigenous to the coastal regions of the Netherlands, north-western Germany and southern Denmark, and during the Early Middle Ages in the north-western coastal zone of Flanders, Belgium. They inhabit an area known as Frisia and are concentrated in the Dutch provinces of Friesland and Groningen and, in Germany, East Frisia and North Frisia.

Schleswig-Holstein is the northernmost of the 16 states of Germany, comprising most of the historical Duchy of Holstein and the southern part of the former Duchy of Schleswig. Its capital city is Kiel; other notable cities are Lübeck and Flensburg. It covers an area of 15,763 km2 (6,086 sq mi), making it the 5th smallest German federal state by area. Historically, the name can also refer to a larger region, containing both present-day Schleswig-Holstein and the former South Jutland County in Denmark.

The Duchy of Schleswig was a duchy in Southern Jutland covering the area between about 60 km north and 70 km (45 mi) south of the current border between Germany and Denmark. The territory has been divided between the two countries since 1920, with Northern Schleswig in Denmark and Southern Schleswig in Germany. The region is also called Sleswick in English.

Nordfriesland, also known as North Frisia, is the northernmost district of Germany, part of the state of Schleswig-Holstein. It includes almost all of traditional North Frisia, as well as adjacent parts of the Schleswig Geest to the east and Stapelholm to the south, and is bounded by the districts of Schleswig-Flensburg and Dithmarschen, the North Sea and the Danish county of South Jutland. The district is called Kreis Nordfriesland in German, Kreis Noordfreesland in Low German, Kris Nordfraschlönj in Mooring North Frisian, Kreis Nuurdfresklun in Fering North Frisian and Nordfrislands amt in Danish.
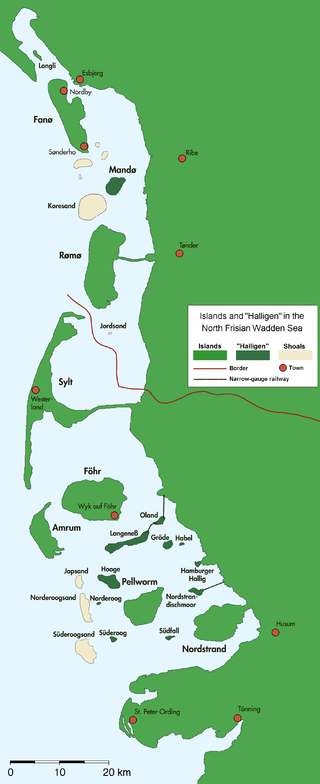
The North Frisian Islands are the Frisian Islands off the coast of North Frisia.

Frisia is a cross-border cultural region in Northwestern Europe. Stretching along the Wadden Sea, it encompasses the north of the Netherlands and parts of northwestern Germany. Wider definitions of "Frisia" may include the island of Rem and the other Danish Wadden Sea Islands. The region is traditionally inhabited by the Frisians, a West Germanic ethnic group.

Föhr is one of the North Frisian Islands on the German coast of the North Sea. It is part of the Nordfriesland district in the federal state of Schleswig-Holstein. Föhr is the second-largest North Sea island of Germany and a popular destination for tourists. A town and eleven distinct municipalities are located on the island. The climate is oceanic with moderate winters and relatively cool summers.
Amrum is one of the North Frisian Islands on the German North Sea coast, south of Sylt and west of Föhr. It is part of the Nordfriesland district in the federal state of Schleswig-Holstein and has approximately 2,300 inhabitants.

is a peninsula and former island in North Frisia on the North Sea coast of Germany. It is part of the Nordfriesland district in the federal state of Schleswig-Holstein. Its area is 50 km² and its population is 2,300. Nordstrand has two municipalities, Nordstrand and smaller Elisabeth-Sophien-Koog, which are part of the Amt Nordsee-Treene.

North Frisian is a minority language of Germany, spoken by about 10,000 people in North Frisia. The language is part of the larger group of the West Germanic Frisian languages. The language comprises 10 dialects which are themselves divided into an insular and a mainland group.

Dagebüll is a municipality located at the west coast of Schleswig-Holstein in the Nordfriesland district, Germany. Today's Dagebüll was created in 1978 as a merger of the municipalities of Fahretoft, Juliane-Marien-Koog and Waygaard. Dagebüll used to be a Hallig, the oldest houses were built on artificial dwelling hills which in parts can still be seen today. In 1704 the area was secured by sea dikes.

The German Bight is the southeastern bight of the North Sea bounded by the Netherlands and Germany to the south, and Denmark and Germany to the east. To the north and west it is limited by the Dogger Bank. The Bight contains the Frisian and Danish Islands. The Wadden Sea is approximately ten to twelve kilometres wide at the location of the German Bight. The Frisian islands and the nearby coastal areas are collectively known as Frisia. The southern portion of the bight is also known as the Heligoland Bight. Between 1949 and 1956 the BBC Sea Area Forecast used "Heligoland" as the designation for the area now referred to as German Bight.

A terp, also known as a wierde, woerd, warf, warft, werf, werve, wurt or værft, is an artificial dwelling mound found on the North European Plain that has been created to provide safe ground during storm surges, high tides and sea or river flooding. The various terms used reflect the regional dialects of the North European region.

North Frisia is the northernmost portion of Frisia, located in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany, between the rivers Eider and Wiedau. It also includes the North Frisian Islands and Heligoland. The region is traditionally inhabited by the North Frisians.

The flag of Schleswig-Holstein is a horizontal tricolour of blue, white, and red. Schleswig-Holstein is one of the 16 states of Germany, comprising most of the historical duchy of Holstein and the southern part of the former Duchy of Schleswig.

Frisia is a small region in the north of the modern day country known as the Netherlands. In the Iron Age, the ancestors of the modern Frisians first migrated south out of modern day Scandinavia to the south west where they began to settle along the coast. The archeological record goes all the way back to the Neolithic era, however, the first written sources for Frisian history come from Roman records, like Tacitus' account of an unsuccessful Frisian attack on a Roman fort. Frisia would go on to distinguish itself culturally from other Germanic peoples but remained recognizably Germanic nonetheless. In the Early Medieval era, Frisians took the seas with well crafted ships to perform trade and to raid other ports, cities, and towns in other parts of Europe. For most of its modern history, Frisia, or Frysland, has been under the control of the Netherlands but today their language is co-official with Dutch at the provincial level. Frisian is the most closely related language to English aside from Scots.

The flags of Frisia are the flags that are used to represent Frisia, a cross-border cultural region in Northwestern Europe. Some designs are in official use on a local or provincial level, while others are used unofficially on a regional, linguistic or international level.

Uthlande, Utlande is a term for the islands, halligen and marshes off the mainland of North Frisia in the Southwest Jutland, modern Nordfriesland district, Germany.

Frisian nationalism refers to the nationalism which views Frisians as a nation with a shared culture. Frisian nationalism seeks to achieve greater levels of autonomy for Frisian people, and also supports the cultural unity of all Frisians regardless of modern-day territorial borders. The Frisians derive their name from the Frisii, an ancient Germanic tribe which inhabited the northern coastal areas in what today is the northern Netherlands, although historical research has indicated a lack of direct ethnic continuity between the ancient Frisii and later medieval 'Frisians' from whom modern Frisians descend. In the Middle Ages, these Frisians formed the Kingdom of Frisia and later the Frisian freedom confederation, before being subsumed by stronger foreign powers up to this day.



















