
Amarna is an extensive ancient Egyptian archaeological site containing the remains of what was the capital city during the late Eighteenth Dynasty. The city of Akhetaten was established in 1346 BC, built at the direction of the Pharaoh Akhenaten, and abandoned shortly after his death in 1332 BC. The name that the ancient Egyptians used for the city is transliterated as Akhetaten or Akhetaton, meaning "the horizon of the Aten".

Nefertiti was a queen of the 18th Dynasty of Ancient Egypt, the great royal wife of Pharaoh Akhenaten. Nefertiti and her husband were known for their radical overhaul of state religious policy, in which they promoted the earliest known form of monotheism, Atenism, centered on the sun disc and its direct connection to the royal household. With her husband, she reigned at what was arguably the wealthiest period of ancient Egyptian history. After her husband's death, some scholars believe that Nefertiti ruled briefly as the female king known by the throne name, Neferneferuaten and before the ascension of Tutankhamun, although this identification is a matter of ongoing debate. If Nefertiti did rule as Pharaoh, her reign was marked by the fall of Amarna and relocation of the capital back to the traditional city of Thebes.

Smenkhkare was an ancient Egyptian pharaoh of unknown background who lived and ruled during the Amarna Period of the 18th Dynasty. Smenkhkare was husband to Meritaten, the daughter of his likely co-regent, Akhenaten. Since the Amarna period was subject to a large-scale condemnation of memory by later pharaohs, very little can be said of Smenkhkare with certainty, and he has hence been subject to immense speculation.

Kiya was one of the wives of the Egyptian Pharaoh Akhenaten. Little is known about her, and her actions and roles are poorly documented in the historical record, in contrast to those of Akhenaten's 'Great royal wife', Nefertiti. Her unusual name suggests that she may originally have been a Mitanni princess. Surviving evidence demonstrates that Kiya was an important figure at Akhenaten's court during the middle years of his reign, when she had a daughter with him. She disappears from history a few years before her royal husband's death. In previous years, she was thought to be mother of Tutankhamun, but recent DNA evidence suggests this is unlikely.

Meritaten, also spelled Merytaten, Meritaton or Meryetaten, was an ancient Egyptian royal woman of the Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt. Her name means "She who is beloved of Aten"; Aten being the sun-deity whom her father, Pharaoh Akhenaten, worshipped. She held several titles, performing official roles for her father and becoming the Great Royal Wife to Pharaoh Smenkhkare, who may have been a brother or son of Akhenaten. Meritaten also may have served as pharaoh in her own right under the name Ankhkheperure Neferneferuaten.
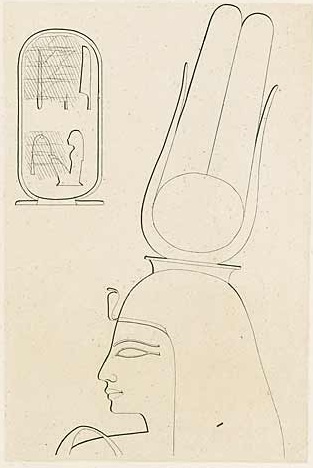
Tey was the Great Royal Wife of Kheperkheprure Ay, who was the penultimate pharaoh of Ancient Egypt's Eighteenth Dynasty. She also had been the wet nurse of Nefertiti.
Ankhesenpaaten Tasherit was an ancient Egyptian princess of the 18th Dynasty. Ankhesenpaaten Tasherit and another princess, Meritaten Tasherit are two princesses who appear in scenes dating to the later part of the reign of Akhenaten. The titles of at least one of the princess is of the form "[...-ta]sherit, born of [...], born of the King's Great Wife [...]. The inscription is damaged and the name of the mother and grandmother of the princesses has not been preserved. Ankhesenpaaten Tasherit has been known to archaeologists since 1938, when a talatat block with her picture and name was found in Hermopolis.
The Amarna Period was an era of Egyptian history during the later half of the Eighteenth Dynasty when the royal residence of the pharaoh and his queen was shifted to Akhetaten in what is now Amarna. It was marked by the reign of Amenhotep IV, who changed his name to Akhenaten in order to reflect the dramatic change of Egypt's polytheistic religion into one where the sun disc Aten was worshipped over all other gods. The Egyptian pantheon was restored under Akhenaten's successor, Tutankhamun.

Panehesy was an Egyptian noble who bore the titles of 'Chief servitor of the Aten in the temple of Aten in Akhetaten'.

Meryre II was an ancient Egyptian noble known as the superintendent of Queen Nefertiti, and held the title of royal scribe, steward, overseer of the two treasuries, overseer of the royal harem of Nefertiti. He had a tomb constructed at Amarna, although his remains have never been identified. The tomb has the last dated appearance of Akhenaten and the Amarna family.

Neferneferuaten Tasherit or Neferneferuaten the younger was an ancient Egyptian princess of the 18th Dynasty and the fourth daughter of Pharaoh Akhenaten and his Great Royal Wife Nefertiti.

Neferneferure was an ancient Egyptian princess of the 18th Dynasty. She was the fifth of six known daughters of Pharaoh Akhenaten and his Great Royal Wife Nefertiti.
Ankhkheperure-Merit-Neferkheperure/Waenre/Aten Neferneferuaten was a name used to refer to a female king who reigned toward the end of the Amarna Period during the Eighteenth Dynasty. Her gender is confirmed by feminine traces occasionally found in the name and by the epithet Akhet-en-hyes, incorporated into one version of her nomen cartouche. She is distinguished from the king Smenkhkare who used the same throne name, Ankhkheperure, by the presence of epithets in both cartouches. She is suggested to have been either Smenkhkare's wife, Meritaten or, his predecessor's widow, Nefertiti. If this person is Nefertiti ruling as sole king, it has been theorized by Egyptologist and archaeologist Zahi Hawass that her reign was marked by the fall of Amarna and relocation of the capital back to the traditional city of Thebes.
Mahu was Chief of Police at Akhetaten.
Dakhamunzu is the name of an Egyptian queen known from the Hittite annals The Deeds of Suppiluliuma, which were composed by Suppiluliuma I's son Mursili II. The identity of this queen has not yet been established with any degree of certainty and Dakhamunzu has variously been identified as either Nefertiti, Meritaten or Ankhesenamen. The identification of this queen is of importance both for Egyptian chronology and for the reconstruction of events during the late Eighteenth Dynasty.
Setepenre or Sotepenre was an ancient Egyptian princess of the 18th Dynasty; sixth and last daughter of Pharaoh Akhenaten and his chief queen Nefertiti.

Amarna tomb 7 was one of the Southern tombs at Amarna, Egypt. It belonged to Parennefer, who was a pure handed cupbearer of the king's Person.
The North Riverside Palace was a royal residence in the former Egyptian city of Amarna. This palace should not be confused with the North Palace, which was the residence of first Queen Kiya and later Meritaten.

The Tomb of Panehsy is a sepulchre in Amarna, Upper Egypt. It was erected for the noble Panehsy who bore the titles the First servant of the Aten in the house of Aten in Akhet-Aten, Second prophet of the Lord of the Two Lands Neferkheprure-Waenre (Akhenaten), the sealbearer of the King of Lower Egypt, Overseer of the storehouse of the Aten in Akhetaten, Overseer of cattle of the Aten in Akhet-Aten.
The Anonymous Tombs in Amarna are ancient Tombs of Nobles at the Royal Wadi in Amarna, Upper Egypt. They consist of both sepulchres and burial pits in varying stages of construction.













