Related Research Articles

The Constitution of Norway was adopted on 16 May and signed on 17 May 1814 by the Norwegian Constituent Assembly at Eidsvoll. The latter date is the National Day of Norway; it marks the establishment of the constitution.

Horten is a municipality in Vestfold county, Norway. It is located in the traditional district of Jarlsberg. The administrative centre of the municipality is the town of Horten. Other population centers in Horten Municipality include the town of Åsgårdstrand and the villages of Nykirke, Skoppum, and Borre. The municipality is located on a peninsula along the Ytre Oslofjord.

The Church of Norway is an evangelical Lutheran denomination of Protestant Christianity and by far the largest Christian church in Norway. The church became the state church of Norway around 1020, and was established as a separate church intimately integrated with the state as a result of the Lutheran reformation in Denmark–Norway which broke ties with the Holy See in 1536–1537; the King of Norway was the church's head from 1537 to 2012. Historically the church was one of the main instruments of royal power and official authority, and an important part of the state administration; local government was based on the church's parishes with significant official responsibility held by the parish priest.

Trinity International University (TIU) is an evangelical Christian university headquartered in Bannockburn, Illinois. It comprises Trinity College, a theological seminary, a law school, and a camp called Timber-lee. The university also maintains campuses in North Lauderdale, Florida and Miami, Florida; the camp is located in East Troy, Wisconsin. TIU is the only university affiliated with Evangelical Free Church of America in the United States and enrolls 1,242 students. On February 17, 2023, TIU announced it was moving the undergraduate program to online modalities only and closed the residential campus at the end of the Spring 2023 semester. The online undergraduate program is ending at the end of the Spring 2024 semester.
The Norwegian School of Economics or NHH is a business school situated in Bergen, Norway. It was founded in 1936 as Norway's first business school and is the leading teaching and research institution in Norway for the fields of management and business administration.

Universities and Colleges Christian Fellowship is an evangelical Christian student movement with affiliate groups on university campuses in the United Kingdom. It is a member of the International Fellowship of Evangelical Students. The UCCF endorses a conservative evangelical form of Christian theology.
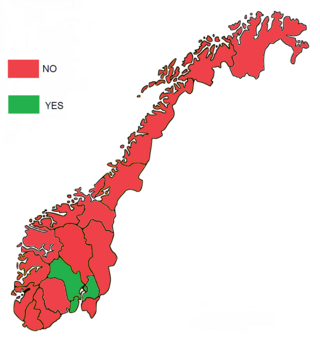
A referendum on joining the European Community was held in Norway on 25 September 1972. After a long period of heated debate, the "no" side won with 53.5% of the vote. Prime Minister Trygve Bratteli, who had championed a "yes" vote, resigned as a result. This was Norway's second attempt at becoming a member, after having been vetoed by France in January 1963 and again temporarily in 1967, but the first attempt with a referendum on a set of fully negotiated accession terms.

The Norwegian University of Life Sciences is a public university located in Ås, Norway. It is located in Akershus county and has around 7,700 students.

Religion in Norway is dominated by Lutheran Christianity, with 63.7% of the population belonging to the Evangelical Lutheran Church of Norway in 2022. The Catholic Church is the next largest Christian church at 3.1%. The unaffiliated make up 18.3% of the population. Islam is followed by 3.4% of the population.

Christian Heinrich Grosch was a Norwegian architect. He was a dominant figure in Norwegian architecture in the first half of the 1800s.

Islam is the second largest religion in Norway after Christianity. As of 2020, the number of Muslims living in Norway was 182,607. The majority of Muslims in Norway are Sunni, with a significant Shia minority. 55 percent of Muslims in the country live in Oslo and Viken. The vast majority of Muslims have an immigrant background, and very few ethnic Norwegians are Muslim.

Carl Fredrik Wisløff was a Norwegian Lutheran theologian and preacher, who spent much of his professional career at the MF Norwegian School of Theology. He is considered among the most important lay preachers in 20th-century Norway.
Kjell Erfjord is a Norwegian former educator and politician for the Christian Democratic Party.

Christianity is the largest religion in Norway and it has historically been called a Christian country. A majority of the population are members of the Church of Norway with 64.9% of the population officially belonging to the Evangelical Lutheran Church of Norway in 2021. At numerous times in history, Norway sent more missionaries per capita than any other country. This changed considerably from the 1960s. In 2004, only 12% of the population attended church services each month. The Church of Norway receives a fixed sum from the Government not based on membership numbers. Other religious organisations receive approximately the same amount per member.

Pentecostal congregations in Norway is the largest Protestant free church in Norway with a total membership of 40,725 people in 2020.
Norge Idag is a Norwegian Christian conservative weekly newspaper published in Bergen that was founded in 1999. The editor-in-chief is Finn Jarle Sæle.

The University of South-Eastern Norway, commonly known as USN, is a Norwegian state university. It has campuses in Bø in Telemark, Porsgrunn, Notodden, Rauland, Drammen, Hønefoss, Kongsberg and Horten. USN is a continuation of the three former university colleges, Telemark University College, Buskerud University College and Vestfold University College, which merged between 2014 and 2016 to form the University College of South-Eastern Norway. The institution was granted the status of a full university by the King-in-Council on 4 May 2018.
Hald International Center is a vocational school offering courses in cross-cultural understanding and international work. The school is owned by the Strømme Foundation, the Norwegian Missionary Society, and the Norwegian Christian Student and School Association, which each have their own exchange program. The academic program is a mix of theory and practice in which all of the students spend six to seven months of student traineeship in another culture. The school has about 40 Norwegian students and 20 students from abroad. The Norwegian students have their traineeship abroad, and the students from abroad have their traineeship in Norway. Those studying at Hald International Center are eligible for full loans and grants from the Norwegian State Educational Loan Fund. The school is located at the Hald Hotel just outside Mandal.
The Dissenter Act is a Norwegian law from 1845 that allowed Christian denominations other than the Church of Norway to establish themselves in the country. It was enacted on 16 July 1845, and remained in effect until it was replaced by the Act Relating to Religious Communities, etc. in 1969.

The Jesuit clause was a provision in the Constitution of Norway, paragraph 2, in force from 1814 to 1956, that denied Jesuits entry into the country. Until 1897, this provision was combined with a ban on monastic orders, and until 1851 a ban on Jews, the so-called Jew clause.
References
- ↑ "Norges Kristelige Student- og Skoleungdomslag (AktiWiki)". Archived from the original on 2015-05-30. Retrieved 2015-05-29.