
Territorial waters are informally an area of water where a sovereign state has jurisdiction, including internal waters, the territorial sea, the contiguous zone, the exclusive economic zone, and potentially the extended continental shelf. In a narrower sense, the term is often used as a synonym for the territorial sea.

North Sea oil is a mixture of hydrocarbons, comprising liquid petroleum and natural gas, produced from petroleum reservoirs beneath the North Sea.

An exclusive economic zone (EEZ), as prescribed by the 1982 United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea, is an area of the sea in which a sovereign state has exclusive rights regarding the exploration and use of marine resources, including energy production from water and wind.
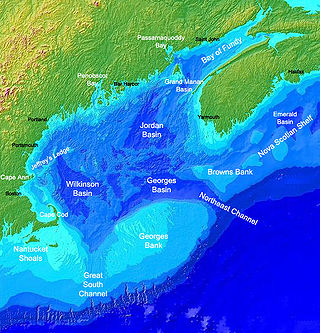
Georges Bank is a large elevated area of the sea floor between Cape Cod, Massachusetts, and Cape Sable Island, Nova Scotia (Canada). It separates the Gulf of Maine from the Atlantic Ocean.

Long Forties is a zone of the northern North Sea that is fairly consistently forty fathoms deep.

The Statfjord oil field is a large oil and gas field covering 580 km2 along the U.K.-Norwegian boundary of the North Sea at a water depth of 145 m, discovered in 1974 by Mobil and since 1987 operated by Equinor.

A passive margin is the transition between oceanic and continental lithosphere that is not an active plate margin. A passive margin forms by sedimentation above an ancient rift, now marked by transitional lithosphere. Continental rifting forms new ocean basins. Eventually the continental rift forms a mid-ocean ridge and the locus of extension moves away from the continent-ocean boundary. The transition between the continental and oceanic lithosphere that was originally formed by rifting is known as a passive margin.
State's Direct Financial Interest (SDFI) is a portfolio of the Norwegian government's directly owned exploration and production licenses for petroleum and natural gas on the Norwegian continental shelf. The Norwegian government-owned company Petoro has managed the SDFI portfolio since 2001.
Gassco is a Norwegian state owned company that operates 7,800 kilometres (4,800 mi) of natural gas pipes transporting annually of 100 billion cubic meter (bcm) of natural gas from the Norwegian continental shelf to Continental Europe and Great Britain.

The Argentine Sea is a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean adjacent to the southern tip of South America. It ranges from the mouth of the estuary of the Río de la Plata in the north to the Isla de los Estados in the south, and from the Argentine coast to the 200 meters isobath. Its width varies between 210 km in front of Mar del Plata and 850 km at the latitude of the Falkland Islands. The coastline extends for 4,725 km. To the east of the Argentine Sea extends much deeper and more extensive Argentine Basin.

Norway is a large energy producer, and one of the world's largest exporters of oil. Most of the electricity in the country is produced by hydroelectricity. Norway is one of the leading countries in the electrification of its transport sector, with the largest fleet of electric vehicles per capita in the world.

Atlantic Petroleum P/FP/F is an oil and gas company situated in Tórshavn, Faroe Islands and has technical offices located in London and Bergen (Norway). It participates in exploration on the Faroese Continental Shelf, offshore Norway, Ireland, and United Kingdom. The company has production from three fields in the United Kingdom's sector of the North Sea and also participates in development projects.

Equinor ASA is a Norwegian state-owned multinational energy company headquartered in Stavanger, Norway. It is primarily a petroleum company operating in 36 countries with additional investments in renewable energy. In the 2020 Forbes Global 2000, Equinor was ranked as the 169th-largest public company in the world. In 2023, the company was ranked 52nd in the same list. As of 2021, the company has 21,126 employees.
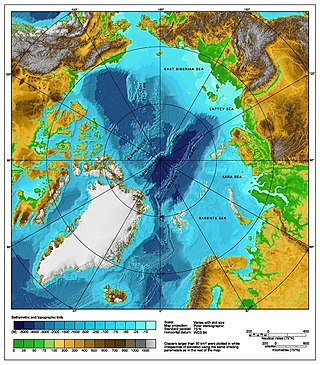
The Arctic consists of land, internal waters, territorial seas, exclusive economic zones (EEZs) and international waters above the Arctic Circle. All land, internal waters, territorial seas and EEZs in the Arctic are under the jurisdiction of one of the eight Arctic coastal states: Canada, Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway, Russia, Sweden and the United States. International law regulates this area as with other portions of Earth.

The geology of Norway encompasses the history of Earth that can be interpreted by rock types found in Norway, and the associated sedimentological history of soils and rock types.

The Norwegian Offshore Directorate is a Norwegian government agency responsible for the regulation of the petroleum resources on the Norwegian continental shelf. Based in Stavanger, its mission is to ensure that the petroleum resources are allocated in an optimal way, at the same time incurring minimal environmental impact. It is subordinate to the Norwegian Ministry of Petroleum and Energy.

The Jan Mayen Microcontinent is a fragment of continental crust within the oceanic part of the western Eurasian Plate lying northeast of Iceland. At the onset of separation between the Greenland and Eurasian plates 55 million years ago, it formed part of the eastern margin of the Greenland Plate. Propagation of a new spreading center from the Reykjanes Ridge separated this microcontinent from the Greenland Plate. For a short period it formed a microplate, until the Aegir Ridge became inactive, after which it formed part of the Eurasian Plate. The island of Jan Mayen is a much younger feature, formed of volcanic rock, built up at the northernmost tip of the microcontinent.
Malaysia and Vietnam are two Southeast Asian countries with maritime boundaries which meet in the Gulf of Thailand and South China Sea. The two countries have overlapping claims over the continental shelf in the Gulf of Thailand. Both countries have, however, come to an agreement to jointly exploit the natural resources in the disputed area pending resolution of the dispute over sovereignty.

Aker BP ASA is a Norwegian oil exploration and development company focusing petroleum resources on the Norwegian Continental Shelf. It is present all over Norway. The headquarters are in Fornebu with additional offices in Trondheim, Stavanger and Harstad. The company employs a staff of more than 2,400.
The petroleum fiscal regime of a country is a set of laws, regulations and agreements which governs the economical benefits derived from petroleum exploration and production. The regime regulates transactions between the political entity and the legal entities involved. A commercial or legal entity in this context is commonly an oil company, and two or more companies may establish partnerships to share economic risks and investment capital.
















