Related Research Articles

Labaya was the ruler of Shechem and warlord in the central hill country of southern Canaan during the Amarna Period. He lived contemporaneously with Pharaoh Akhenaten. Labaya is mentioned in several of the Amarna Letters. He is the author of letters EA 252–54.

Abdi-Ḫeba was a local chieftain of Jerusalem during the Amarna period. Egyptian documents have him deny he was a mayor (ḫazānu) and assert he is a soldier (we'w), the implication being he was the son of a local chief sent to Egypt to receive military training there.
Zimredda, also Zimr-Edda or Zimr-Eddi was the mayor of Sidon, in the mid 14th century BC. He is mentioned in several of the Amarna letters, in the late Rib-Hadda series, and later. He authored letters EA 144–45.
NIN-UR.MAH.MEŠ, or the "Lady" of the Lions, was the author of two letters to the pharaoh, the King of Ancient Egypt, in the 1350–1335 BC Amarna letters correspondence. Her name is a representation of the original written script characters of Babylonian 'Sumerograms' , "NIN- + UR.MAH + (plural:MEŠ)", and means, "woman–lion–plural", namely: "Lady Lions".. The Amarna letters are mostly written in Akkadian cuneiform, with local words/phrases/etc due to various city-states or countries.

Ayyab was a ruler of Aštartu south of Damascus. According to the Amarna letters, cities/city-states and their kings in the region — just like countries to the north, such as Hatti of the Hittites, fell prey to a wave of attacks by ʿApiru raiders. The Amarna correspondence corpus covers a period from 1350–1335 BC.
Abimilki around 1347 BC held the rank of Prince of Tyre, during the period of the Amarna letters correspondence. He is the author of ten letters to the Egyptian pharaoh, EA 146–155. In letter EA 147, Pharaoh Akhenaten confirmed him as ruler of Tyre upon the death of his father, and in EA 149, referred to him with the rank of rabisu (general).
Abdi-Riša was a ruler-'mayor' of Enišasi, during the period of the Amarna letters correspondence. Another mayor of Enišasi, Šatiya, is found in the Amarna letters corpus. The name "Abdi-Riša" means "servant-Riša".

In the 1350 BC correspondence of 382 letters, called the Amarna letters, the prostration formula is usually the opening subservient remarks to the addressee, the Egyptian pharaoh. The formula is based on prostration, namely reverence and submissiveness. Often the letters are from vassal rulers or vassal city-states, especially in Canaan but also in other localities.
Hannathon, and of the 1350-1335 BC Amarna letters, Hinnatuna, or Hinnatuni/Hinnatunu, is the Biblical city/city-state of Hannathon, ; in the Amarna letters correspondence as Hinnatuna, it is a site in southern Canaan, site uncertain. Ancient settlement of Tel Hanaton in Lower Galilee has been suggested as a candidate.
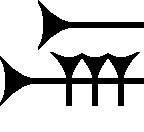
The cuneiform ir, or er sign is a sign used in the Epic of Gilgamesh, and the Amarna letters. It is in a small group that have smaller, 3-verticals, as well as 2- and 1-vertical strokes, sitting on a lower horizontal cuneiform stroke.

Amarna letter EA 161, titled An Absence Explained, is a tall clay tablet letter of 8 paragraphs, with single paragraphing lines. The surface is somewhat degraded, but most cuneiform signs that remain, allow for a relative complete translation context for the letter, and the eight paragraphs. The clay tablet is no. BM 29818 at the British Museum; the number is visible at the top of the tablet, above Para I-(in black ink, the top half of the number visible).

The cuneiform U sign is found in both the 14th century BC Amarna letters and the Epic of Gilgamesh. It can be used for the alphabetic u, instead of the more common 2nd u, (ú). It has two other uses, commonly. It can be used for the number 10, but its probable greater use is for the conjunction, u, with any of the conjunction meanings: and, but, else, etc.

Amarna letter EA 252, titled: Sparing One's Enemies, is a square, mostly flat clay tablet letter written on both sides, and the bottom edge. Each text line was written with a horizontal line scribed below the text line, as well as a vertical left margin-line, scribe line on the obverse of the tablet. The letter contains 14 (15) lines on the obverse, continuing on the bottom tablet edge to conclude at line 31 on the reverse, leaving a small space before the final tablet edge. At least 4 lines from the obverse intrude into the text of the reverse, actually dividing the reverse into a top half and bottom half, and even creating a natural spacing segue to the reverse's text, and the story.

Amarna letter EA 365, titled Furnishing Corvée Workers, is a squarish, mostly flat clay tablet, but thick enough (pillow-shaped), to contain text that continues toward the right margin, the right side of the obverse side, and also to the right side of the reverse side of the tablet.

Amarna letter EA 364, titled Justified War, is a clay tablet letter from Ayyab, ruler of Aštartu, to Pharaoh Akhenaten.

Amarna letter EA 153, titled Ships on Hold, is a short-length clay tablet letter from Abimilku of the island of city-state Tyre.

Amarna letter EA 271, titled: "The Power of the 'Apiru," is a moderately short, tallish, rectangular clay tablet letter, approximately 3 in wide x 4 in tall, from Milkilu the mayor/ruler of Gazru (Gezer), of the mid 14th century BC Amarna letters.

Amarna letter EA 323, titled: A Royal Order for Glass, is a smaller, square, mostly flat clay tablet letter written on both sides, but only half of the reverse; it is also written on the bottom, and is a letter from 'governor' Yidya, and is a short letter like many of his other Amarna letters, numbered EA 320 to EA 326.
Amarna letter EA 147, titled A Hymn to the Pharaoh, is a moderate length clay tablet Amarna letter from Abimilku of Tyre-(called Ṣurru in the Abimilku letters, and an island, until the time of Alexander the Great, 330 BC). The letter is a twin letter to EA 149, which is identical in length, and complexity, and EA 147 appears to precede EA 149.
In Ancient Egypt, the Amarna Period saw diplomatic correspondence sent to the city of Akhetaten (Amarna), providing valuable insights into the political situations at the time.
References
- Moran, William L. The Amarna Letters. Johns Hopkins University Press, 1987, 1992. (softcover, ISBN 0-8018-6715-0)