Related Research Articles

Greenland is located between the Arctic Ocean and the North Atlantic Ocean, northeast of Canada and northwest of Iceland. The territory comprises the island of Greenland—the largest island in the world—and more than a hundred other smaller islands. As an island, Greenland has no land boundaries and 44,087 km of coastline. A sparse population is confined to small settlements along certain sectors of the coast. Greenland possesses the world's second largest ice sheet.

Jan Mayen is a Norwegian volcanic island in the Arctic Ocean, with no permanent population. It is 55 km (34 mi) long (southwest-northeast) and 373 km2 (144 sq mi) in area, partly covered by glaciers. It has two parts: larger northeast Nord-Jan and smaller Sør-Jan, linked by a 2.5 km (1.6 mi) wide isthmus. It lies 600 km (370 mi) northeast of Iceland, 500 km (310 mi) east of central Greenland and 1,000 km (620 mi) west of the North Cape, Norway. The island is mountainous, the highest summit being the Beerenberg volcano in the north. The isthmus is the location of the two largest lakes of the island, Sørlaguna, and Nordlaguna. A third lake is called Ullerenglaguna. Jan Mayen was formed by the Jan Mayen hotspot.

The Norwegian Sea is a marginal sea in the Atlantic Ocean, northwest of Norway between the North Sea and the Greenland Sea, adjoining the Barents Sea to the northeast. In the southwest, it is separated from the Atlantic Ocean by a submarine ridge running between Iceland and the Faroe Islands. To the north, the Jan Mayen Ridge separates it from the Greenland Sea.

Svalbard, previously known as Spitsbergen, or Spitzbergen, is a Norwegian archipelago in the Arctic Ocean. North of mainland Europe, it is about midway between the northern coast of Norway and the North Pole. The islands of the group range from 74° to 81° north latitude, and from 10° to 35° east longitude. The largest island is Spitsbergen, followed by Nordaustlandet and Edgeøya. The largest settlement is Longyearbyen.

The Barents Sea is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean, located off the northern coasts of Norway and Russia and divided between Norwegian and Russian territorial waters. Known among Russians in the Middle Ages as the Murman Sea, the current name of the sea is after the historical Dutch navigator Willem Barentsz.

Norway is a country located in Northern Europe on the northern and western parts of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The majority of the country borders water, including the Skagerrak inlet to the south, the North Sea to the southwest, the North Atlantic Ocean to the west, and the Barents Sea to the north. It has a land border with Sweden to the east and a shorter border with Finland and an even shorter border with Russia to the northeast.
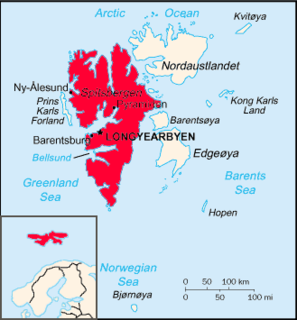
Spitsbergen is the largest and only permanently populated island of the Svalbard archipelago in northern Norway.

Bear Island is the southernmost island of the Norwegian Svalbard archipelago. The island is located in the western part of the Barents Sea, approximately halfway between Spitsbergen and the North Cape.

Longyearbyen is the world's northernmost settlement and largest inhabited area of Svalbard, Norway. It stretches along the foot of the left bank of the Longyear Valley and on the shore of Adventfjorden, the short estuary leading into Isfjorden on the west coast of Spitsbergen, the island's broadest inlet. As of 2002 Longyearbyen Community Council became an official Norwegian municipality. It is the seat of the Governor of Svalbard, whose current mayor is Arild Olsen.

Barentsburg is the second-largest settlement on Svalbard, with about 455 inhabitants (2020), almost entirely made up of ethnic Russians and Ukrainians.

Edgeøya, occasionally anglicised as Edge Island, is a Norwegian island located in southeast of the Svalbard archipelago; with an area of 5,073 square kilometres (1,960 sq mi), it is the third-largest island in this archipelago. An Arctic island, it forms part of the Søraust-Svalbard Nature Reserve, home to polar bears and reindeer. An ice field covers its eastern side. The island takes its name from Thomas Edge, an English merchant and whaler. It is seldom visited today.

The Greenland Sea is a body of water that borders Greenland to the west, the Svalbard archipelago to the east, Fram Strait and the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Norwegian Sea and Iceland to the south. The Greenland Sea is often defined as part of the Arctic Ocean, sometimes as part of the Atlantic Ocean. However, definitions of the Arctic Ocean and its seas tend to be imprecise or arbitrary. In general usage the term "Arctic Ocean" would exclude the Greenland Sea. In oceanographic studies the Greenland Sea is considered part of the Nordic Seas, along with the Norwegian Sea. The Nordic Seas are the main connection between the Arctic and Atlantic oceans and, as such, could be of great significance in a possible shutdown of thermohaline circulation. In oceanography the Arctic Ocean and Nordic Seas are often referred to collectively as the "Arctic Mediterranean Sea", a marginal sea of the Atlantic.
Alex Hartley is a British artist whose work addresses complicated and sometimes contradictory attitudes toward built environments and landscapes.
Cape Farewell is an artist led organisation that works to create an urgent cultural response to climate change. Launched by David Buckland in 2001 with a series of ground-breaking artist and scientist manned expeditions to the Arctic, Cape Farewell has become an international not-for-profit programme based at the University of the Arts London: Chelsea.

Benjamin Leigh Smith was an English Arctic explorer and yachtsman. He is the grandson of the Radical abolitionist William Smith.

Svalbard is a Norwegian archipelago in the Arctic Ocean. The climate of Svalbard is principally a result of its latitude, which is between 74° and 81° north. Climate is defined by the World Meteorological Organization as the average weather over a 30-year period. The North Atlantic Current moderates Svalbard's temperatures, particularly during winter, giving it up to 20 °C (36 °F) higher winter temperature than similar latitudes in continental Russia and Canada. This keeps the surrounding waters open and navigable most of the year. The interior fjord areas and valleys, sheltered by the mountains, have fewer temperature differences than the coast, with about 2 °C lower summer temperatures and 3 °C higher winter temperatures. On the south of the largest island, Spitsbergen, the temperature is slightly higher than further north and west. During winter, the temperature difference between south and north is typically 5 °C, and about 3 °C in summer. Bear Island (Bjørnøya) has average temperatures even higher than the rest of the archipelago.
Svalbard is an Arctic, wilderness series of islands comprising the northernmost part of the Norwegian territories. It is mostly uninhabited, with only about 3,000 people, yet covers an area of 61,020 square kilometres (23,560 sq mi).

Nowhereisland was an artwork by artist Alex Hartley, produced by the Bristol-based arts organisation, Situations. Nowhereisland was an ‘Artists Taking the Lead’ project, funded by Arts Council England as part of the London 2012 Cultural Olympiad.

The wildlife of Norway includes the diverse flora and fauna of Norway. The habitats include high mountains, tundras, rivers, lakes, wetlands, sea coast and some lower cultivated land in the south. Mainland Norway has a long coastline, protected by skerries and much dissected by fjords, and the mostly-icebound archipelago of Svalbard lies further north. The flora is very varied and a large range of mammals, birds, fish and invertebrate species live here, as well as a few species of reptiles and amphibians.
References
- ↑ "Mapping in the Arctic". www.arcticsystem.no. Retrieved 2021-01-24.
- ↑ "Cultural Olympiad | London 2012". 2011-05-09. Archived from the original on 2011-05-09. Retrieved 2021-01-24.
- ↑ "Home - Cape Farewell - The cultural response to climate change". capefarewell.com. Retrieved 2021-01-24.