Related Research Articles

Pyrrolysine is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins in some methanogenic archaea and bacteria; it is not present in humans. It contains an α-amino group, a carboxylic acid group. Its pyrroline side-chain is similar to that of lysine in being basic and positively charged at neutral pH.
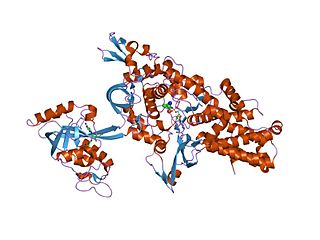
An aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase, also called tRNA-ligase, is an enzyme that attaches the appropriate amino acid onto its corresponding tRNA. It does so by catalyzing the transesterification of a specific cognate amino acid or its precursor to one of all its compatible cognate tRNAs to form an aminoacyl-tRNA. In humans, the 20 different types of aa-tRNA are made by the 20 different aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases, one for each amino acid of the genetic code.

Ribonuclease L or RNase L, known sometimes as ribonuclease 4 or 2'-5' oligoadenylate synthetase-dependent ribonuclease, is an interferon (IFN)-induced ribonuclease which, upon activation, destroys all RNA within the cell. RNase L is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the RNASEL gene.
The stringent response, also called stringent control, is a stress response of bacteria and plant chloroplasts in reaction to amino-acid starvation, fatty acid limitation, iron limitation, heat shock and other stress conditions. The stringent response is signaled by the alarmone (p)ppGpp, and modulates transcription of up to 1/3 of all genes in the cell. This in turn causes the cell to divert resources away from growth and division and toward amino acid synthesis in order to promote survival until nutrient conditions improve.

2'-5'-oligoadenylate synthetase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the OAS1 gene.

Glycine—tRNA ligase also known as glycyl–tRNA synthetase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the GARS1 gene.
Tyrosine—tRNA ligase, also known as tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase is an enzyme that is encoded by the gene YARS. Tyrosine—tRNA ligase catalyzes the chemical reaction

Elongation factor 1-alpha 1 (eEF1a1) is a translation elongation protein, expressed across eukaryotes. In humans, it is encoded by the EEF1A1 gene.

Lysyl-tRNA synthetase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the KARS gene.

Interferon-induced protein with tetratricopeptide repeats 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IFIT1 gene.

Glutaminyl-tRNA synthetase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the QARS gene.

Valyl-tRNA synthetase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the VARS gene.

2'-5'-oligoadenylate synthetase 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the OAS2 gene.

SARS and cytoplasmic seryl-tRNA synthetase are a human gene and its encoded enzyme product, respectively. SARS belongs to the class II amino-acyl tRNA family and is found in all humans; its encoded enzyme, seryl-tRNA synthetase, is involved in protein translation and is related to several bacterial and yeast counterparts.
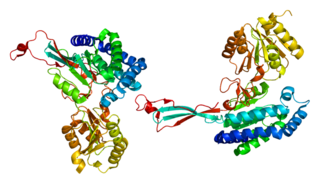
Delta-1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthetase (P5CS) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ALDH18A1 gene. This gene is a member of the aldehyde dehydrogenase family and encodes a bifunctional ATP- and NADPH-dependent mitochondrial enzyme with both gamma-glutamyl kinase and gamma-glutamyl phosphate reductase activities. The encoded protein catalyzes the reduction of glutamate to delta1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate, a critical step in the de novo biosynthesis of proline, ornithine and arginine. Mutations in this gene lead to hyperammonemia, hypoornithinemia, hypocitrullinemia, hypoargininemia and hypoprolinemia and may be associated with neurodegeneration, cataracts and connective tissue diseases. Alternatively spliced transcript variants, encoding different isoforms, have been described for this gene. As reported by Bruno Reversade and colleagues, ALDH18A1 deficiency or dominant-negative mutations in P5CS in humans causes a progeroid disease known as De Barsy Syndrome.

59 kDa 2'-5'-oligoadenylate synthetase-like protein is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the OASL gene.

2'-5'-oligoadenylate synthetase 3 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the OAS3 gene.

LanC-like protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LANCL2 gene. It is a protein broadly expressed in the plasma a nuclear membranes of immune, epithelial and muscle cells and a potential therapeutic target for chronic inflammatory, metabolic and immune-mediated diseases such as Crohn's disease and diabetes.

In molecular biology, 2'-5'-oligoadenylate synthetase is an enzyme that reacts to interferon signal. It is an antiviral enzyme that counteracts viral attack by degrading RNAs, both viral and host. The enzyme uses ATP in 2'-specific nucleotidyl transfer reactions to synthesize 2'-5'-oligoadenylates, which activate latent ribonuclease (RNASEL), resulting in degradation of viral RNA and inhibition of virus replication.
In molecular biology mir-153 microRNA is a short RNA molecule. MicroRNAs function to regulate the expression levels of other genes by several mechanisms.
References
- 1 2 "2'-5' oligoadenylate synthetase-like 2" . Retrieved 2011-12-11.