Obesity in Austria has been increasingly cited as a major health issue in recent years. [1] Forty per cent of Austrians between 18 and 65 are considered overweight while eleven per cent of those overweight meet the definition of obesity. [2] Forbes.com ranks Austria as the 52nd fattest country in the World with a rate of 57.1%. [3] Approximately 900,000 people are considered obese. [4]
A lack of exercise is a cause of obesity. [5] A study showed that children only got 30 minutes of exercise instead of the hour that is required. [5] Proper skeletal development, muscle building, heart and circulation are among the benefits of exercising during childhood. [5]
Several studies have shown that obese men tend to have a lower sperm count, fewer rapidly mobile sperm and fewer progressively motile sperm compared to normal-weight men. [6]
Source:Forbes.com [3] [7] The following list reflects the percentage of overweight adults aged 15 and over. These are individuals who have individual body mass indexes, which measures weight relative to height, greater than or equal to 25
| Ranking | Country | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| 47 | Vanuatu | 59.6 |
| 48 | Finland | 58.7 |
| 49 | Jamaica | 57.4 |
| 50 | Israel | 57.3 |
| 51 | Saint Lucia | 57.3 |
| 52 | Austria | 57.1 |
| 53 | Azerbaijan | 57.1 |
| 54 | Turkey | 56.8 |
| 55 | Tuvalu | 56.6 |
| 56 | Dominican Republic | 56.5 |
| 57 | Slovakia | 56.3 |

Body mass index (BMI) is a value derived from the mass (weight) and height of a person. The BMI is defined as the body mass divided by the square of the body height, and is expressed in units of kg/m2, resulting from mass in kilograms (kg) and height in metres (m).

Obesity is a medical condition, sometimes considered a disease, in which excess body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it can potentially have negative effects on health. People are classified as obese when their body mass index (BMI)—a person's weight divided by the square of the person's height—is over 30 kg/m2; the range 25–30 kg/m2 is defined as overweight. Some East Asian countries use lower values to calculate obesity. Obesity is a major cause of disability and is correlated with various diseases and conditions, particularly cardiovascular diseases, type 2 diabetes, obstructive sleep apnea, certain types of cancer, and osteoarthritis.
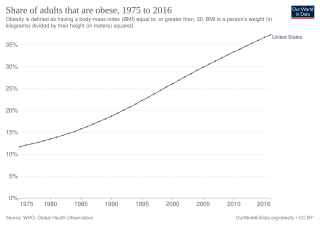
Obesity is common in the United States and is a major health issue associated with numerous diseases, specifically an increased risk of certain types of cancer, coronary artery disease, type 2 diabetes, stroke, and cardiovascular disease, as well as significant increases in early mortality and economic costs.

Being overweight or fat is having more body fat than is optimally healthy. Being overweight is especially common where food supplies are plentiful and lifestyles are sedentary.

Obesity has been observed throughout human history. Many early depictions of the human form in art and sculpture appear obese. However, it was not until the 20th century that obesity became common — so much so that, in 1997, the World Health Organization (WHO) formally recognized obesity as a global epidemic and estimated that the worldwide prevalence of obesity has nearly tripled since 1975. Obesity is defined as having a body mass index (BMI) greater than or equal to 30 kg/m2, and in June 2013 the American Medical Association classified it as a disease.

Obesity in the United Kingdom is a significant contemporary health concern, with authorities stating that it is one of the leading preventable causes of death. In February 2016, former Health Secretary Jeremy Hunt described rising rates of childhood obesity as a "national emergency". The National Childhood Measurement Programme, which measures obesity prevalence among school-age pupils in reception class and year 6, found obesity levels rocketed in both years groups by more than 4 percentage points between 2019–20 and 2020–21, the highest rise since the programme began. Among reception-aged children, those aged four and five, the rates of obesity rose from 9.9% in 2019–20 to 14.4% in 2020–21. By the time they are aged 10 or 11, more than a quarter are obese. In just 12 months, the rate is up from 21% in 2019–20 to 25.5% in 2020–21.

Cardiovascular disease is the principal cause of death in the UAE, constituting 28 percent of total deaths; other major causes are accidents and injuries, malignancies, and congenital anomalies.

According to 2007 statistics from the World Health Organization (WHO), Australia has the third-highest prevalence of overweight adults in the English-speaking world. Obesity in Australia is an "epidemic" with "increasing frequency." The Medical Journal of Australia found that obesity in Australia more than doubled in the two decades preceding 2003, and the unprecedented rise in obesity has been compared to the same health crisis in America. The rise in obesity has been attributed to poor eating habits in the country closely related to the availability of fast food since the 1970s, sedentary lifestyles and a decrease in the labour workforce.
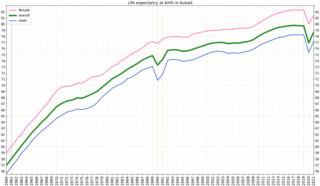
In Kuwait, life expectancy at birth in 2013 was 78 for men and 79 for women.
Obesity in Saudi Arabia is a growing health concern, with health officials stating that it is one of the country's leading causes of preventable deaths. According to Forbes, Saudi Arabia ranks 29 on a 2007 list of the fattest countries with a percentage of 68.3% of its citizens being overweight (BMI≥25). Compounding the problem, according to a presentation at the 3rd International Obesity Conference in February 2014, is that obesity-related surgeries are not covered under Saudi healthcare.

Pacific island nations and associated states make up the top seven on a 2007 list of heaviest countries, and eight of the top ten. In all these cases, more than 70% of citizens aged 15 and over are obese. A mitigating argument is that the BMI measures used to appraise obesity in Caucasian bodies may need to be adjusted for appraising obesity in Polynesian bodies, which typically have larger bone and muscle mass than Caucasian bodies; however, this would not account for the drastically higher rates of cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes among these same islanders.

Obesity is a major issue for the Republic of Nauru. The World Health Organization (WHO) has estimated that 94.5% of Nauruans are overweight or obese, with an obesity rate of 71.7%.

Obesity in Germany has been increasingly cited as a major health issue in recent years. The federal government has declared this to be a major issue.

Obesity in Sweden has been increasingly cited as a major health issue in recent years. Sweden is the 90th fattest country in the world. In 2009, the number of people who are considered overweight or obese had not increased for the first time in 70 years. Claude Marcus, a leading Swedish nutrition expert from the Karolinska Institutet, stated that one solution is to introduce a fat tax. Folksam refused to insure a 5-year-old girl from Orust. The insurance company refused her insurance based on "serious overweight/obesity". A report showed that children whose parents were better educated had a lower chance of becoming overweight.
Obesity in France is a growing health issue. Obesity in children is growing at a faster rate than obesity in adults.
Obesity in Italy has been increasingly cited as a major health issue in recent years.

Obesity in the Middle East and North Africa is a notable health issue. Out of the fifteen fattest nations in the world as of 2014, 5 were located in the Middle East and North Africa region.
Obesity in Pakistan is a health issue that has effected concern only in the past few years. Urbanisation, fast food, changing lifestyles and the fact that Traditional Pakistani Cuisine tends to be high in fat and sugar are among the root causes contributing to obesity in the country. Pakistan is ranked 165 in terms of its overweight population, with 22.2% of individuals over the age of 15 crossing the threshold of obesity. This ratio roughly corresponds with other studies, which state one-in-four Pakistani adults as being overweight. In Pakistan, the problem of excess weight is quite high among adults.
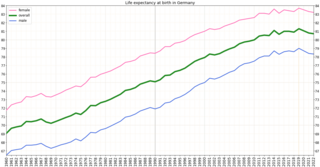
Germany ranked 20th in the world in life expectancy in 2014 with 76.5 years for men and 82.1 years for women. It had a very low infant mortality rate, and it was eighth place in the number of practicing physicians, at 3.3 per 1,000 people.
Obesity is defined as an abnormal accumulation of body fat, usually 20% or more over an individual's ideal body weight. This is often described as a body mass index (BMI) over 30. However, BMI does not account for whether the excess weight is fat or muscle, and is not a measure of body composition. For most people, however, BMI is an indication used worldwide to estimate nutritional status. Obesity is usually the result of consuming more calories than the body needs and not expending that energy by doing exercise. There are genetic causes and hormonal disorders that cause people to gain significant amounts of weight but this is rare. People in the obese category are much more likely to suffer from fertility problems than people of normal healthy weight.