
Prader–Willi syndrome (PWS) is a genetic disorder caused by a loss of function of specific genes on chromosome 15. In newborns, symptoms include weak muscles, poor feeding, and slow development. Beginning in childhood, those affected become constantly hungry, which often leads to obesity and type 2 diabetes. Mild to moderate intellectual impairment and behavioral problems are also typical of the disorder. Often, affected individuals have a narrow forehead, small hands and feet, short height, and light skin and hair. Most are unable to have children.

Secretin is a hormone that regulates water homeostasis throughout the body and influences the environment of the duodenum by regulating secretions in the stomach, pancreas, and liver. It is a peptide hormone produced in the S cells of the duodenum, which are located in the intestinal glands. In humans, the secretin peptide is encoded by the SCT gene.
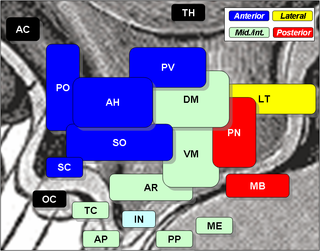
The arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus is an aggregation of neurons in the mediobasal hypothalamus, adjacent to the third ventricle and the median eminence. The arcuate nucleus includes several important and diverse populations of neurons that help mediate different neuroendocrine and physiological functions, including neuroendocrine neurons, centrally projecting neurons, and astrocytes. The populations of neurons found in the arcuate nucleus are based on the hormones they secrete or interact with and are responsible for hypothalamic function, such as regulating hormones released from the pituitary gland or secreting their own hormones. Neurons in this region are also responsible for integrating information and providing inputs to other nuclei in the hypothalamus or inputs to areas outside this region of the brain. These neurons, generated from the ventral part of the periventricular epithelium during embryonic development, locate dorsally in the hypothalamus, becoming part of the ventromedial hypothalamic region. The function of the arcuate nucleus relies on its diversity of neurons, but its central role is involved in homeostasis. The arcuate nucleus provides many physiological roles involved in feeding, metabolism, fertility, and cardiovascular regulation.

Ghrelin is a hormone produced by enteroendocrine cells of the gastrointestinal tract, especially the stomach, and is often called a "hunger hormone" because it increases the drive to eat. Blood levels of ghrelin are highest before meals when hungry, returning to lower levels after mealtimes. Ghrelin may help prepare for food intake by increasing gastric motility and stimulating the secretion of gastric acid.

Motilin is a 22-amino acid polypeptide hormone in the motilin family that, in humans, is encoded by the MLN gene.

Agouti-related protein (AgRP), also called agouti-related peptide, is a neuropeptide produced in the brain by the AgRP/NPY neuron. It is synthesized in neuropeptide Y (NPY)-containing cell bodies located in the ventromedial part of the arcuate nucleus in the hypothalamus. AgRP is co-expressed with NPY and acts to increase appetite and decrease metabolism and energy expenditure. It is one of the most potent and long-lasting of appetite stimulators. In humans, the agouti-related peptide is encoded by the AGRP gene.
Xenin is a peptide hormone secreted from the chromogranin A-positive enteroendocrine cells called the K-cells in the mucous membrane of the duodenum and stomach of the upper gut. The peptide has been found in humans, dogs, pigs, rats, and rabbits.
Pancreatic polypeptide (PP) is a polypeptide secreted by PP cells in the endocrine pancreas. It regulates pancreatic secretion activities, and also impacts liver glycogen storage and gastrointestinal secretion. Its secretion may be impacted by certain endocrine tumours.

Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) is a 30- or 31-amino-acid-long peptide hormone deriving from the tissue-specific posttranslational processing of the proglucagon peptide. It is produced and secreted by intestinal enteroendocrine L-cells and certain neurons within the nucleus of the solitary tract in the brainstem upon food consumption. The initial product GLP-1 (1–37) is susceptible to amidation and proteolytic cleavage, which gives rise to the two truncated and equipotent biologically active forms, GLP-1 (7–36) amide and GLP-1 (7–37). Active GLP-1 protein secondary structure includes two α-helices from amino acid position 13–20 and 24–35 separated by a linker region.

Peptide YY (PYY) also known as peptide tyrosine tyrosine is a peptide that in humans is encoded by the PYY gene. Peptide YY is a short peptide released from cells in the ileum and colon in response to feeding. In the blood, gut, and other elements of periphery, PYY acts to reduce appetite; similarly, when injected directly into the central nervous system, PYY is also anorexigenic, i.e., it reduces appetite.
Nesfatin-1 is a neuropeptide produced in the hypothalamus of mammals. It participates in the regulation of hunger and fat storage. Increased nesfatin-1 in the hypothalamus contributes to diminished hunger, a 'sense of fullness', and a potential loss of body fat and weight.
Delta-sleep-inducing peptide (DSIP) is a neuropeptide that when infused into the mesodiencephalic ventricle of recipient rabbits induces spindle and delta EEG activity and reduced motor activities.
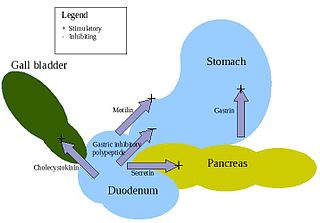
Enteroendocrine cells are specialized cells of the gastrointestinal tract and pancreas with endocrine function. They produce gastrointestinal hormones or peptides in response to various stimuli and release them into the bloodstream for systemic effect, diffuse them as local messengers, or transmit them to the enteric nervous system to activate nervous responses. Enteroendocrine cells of the intestine are the most numerous endocrine cells of the body. They constitute an enteric endocrine system as a subset of the endocrine system just as the enteric nervous system is a subset of the nervous system. In a sense they are known to act as chemoreceptors, initiating digestive actions and detecting harmful substances and initiating protective responses. Enteroendocrine cells are located in the stomach, in the intestine and in the pancreas. Microbiota plays key roles in the intestinal immune and metabolic responses in these enteroendocrine cells via their fermentation product, acetate.

Motilin receptor is a G protein-coupled receptor that binds motilin. Motilin in turn is an intestinal peptide that stimulates contraction of gut smooth muscle.

Prolyl endopeptidase (PE) also known as prolyl oligopeptidase or post-proline cleaving enzyme is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PREP gene.

Growth hormone secretagogue receptor(GHS-R), also known as ghrelin receptor, is a G protein-coupled receptor that binds growth hormone secretagogues (GHSs), such as ghrelin, the "hunger hormone". The role of GHS-R is thought to be in regulating energy homeostasis and body weight. In the brain, they are most highly expressed in the hypothalamus, specifically the ventromedial nucleus and arcuate nucleus. GSH-Rs are also expressed in other areas of the brain, including the ventral tegmental area, hippocampus, and substantia nigra. Outside the central nervous system, too, GSH-Rs are also found in the liver, in skeletal muscle, and even in the heart.

Growth hormone-releasing peptide 6 (GHRP-6), also known as growth hormone-releasing hexapeptide, is one of several synthetic met-enkephalin analogues that include unnatural D-amino acids, were developed for their growth hormone-releasing activity and are called growth hormone secretagogues. They lack opioid activity but are potent stimulators of growth hormone (GH) release. These secretagogues are distinct from growth hormone releasing hormone (GHRH) in that they share no sequence relation and derive their function through activation of a completely different receptor. This receptor was originally called the growth hormone secretagogue receptor (GHSR), but due to subsequent discoveries, the hormone ghrelin is now considered the receptor's natural endogenous ligand, and it has been renamed as the ghrelin receptor. Therefore, these GHSR agonists act as synthetic ghrelin mimetics.

G protein-coupled receptor 119 also known as GPR119 is a G protein-coupled receptor that in humans is encoded by the GPR119 gene.

Ghrelin O-acyltransferase also known as membrane bound O-acyltransferase domain containing 4 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MBOAT4 gene. It is homologous to other membrane-bound O-acyltransferases. It is a polytopic membrane protein what takes part in lipid signaling reactions. It is the only known enzyme that catalyzes the acylation of ghrelin through the transfer of n-octanoic acid to ghrelin Ser3. Ghrelin O-acyltransferase function is essential in regulation of appetite and the release of growth hormone. Ghrelin O-acyltransferase is a target for scientific research due to promising applications in the treatment of diabetes, eating disorders, and metabolic diseases.
Asprosin is a protein hormone produced by mammals in tissues that stimulates the liver to release glucose into the blood stream. Asprosin is encoded by the gene FBN1 as part of the protein profibrillin and is released from the C-terminus of the latter by specific proteolysis. In the liver, asprosin activates rapid glucose release via a cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP)-dependent pathway.















