Evolution of the offside rule in diagrams
 |  |  |  |
There is currently no offside rule in field hockey. There were prior offside rules, rules that restricted the positioning of players from the attacking team in a way similar to the offside rule in association football. The evolution of the field hockey offside rule culminated with its abolition in the mid-1990s.
A set of rules of field hockey was drawn up by several clubs in London in January 1876 following the establishment of the first, briefly existing, Hockey Association (of England) the year before. (The second, and final, Hockey Association was formed in 1886.) An offside rule was included in the 1876 rules. Under this rule, a player who was nearer to the opponent team's goal-line than both the ball and the third to last opponent was said to be at an offside position (simply put: an attacking player was offside if the ball was behind them and there were fewer than three defenders between them and the goal they were attacking). The rule was applied on the whole pitch, except when the ball was hit from the goal-line.
In 1886, the second England Hockey Association drew up a code of Rules based on those used by clubs in the London area. Offside was then applied to attacking players from the half-way line only.
The 1886 offside rule remained unchanged until 1972, when offside was changed from 3 to 2 defenders.
In 1987, the offside was amended to apply only in the 25 yards area.
After various amendments, the offside rule was finally repealed. "No offside" was introduced as a mandatory experiment in 1996 and it was confirmed as a rule in 1998 by the Hockey Rules Board. [1] The aims of this change were:
New tactics were developed by many teams to exploit this new rule.[ citation needed ]
 |  |  |  |

Bandy is a winter sport and ball sport played by two teams wearing ice skates on a large ice surface while using sticks to direct a ball into the opposing team's goal.

Field hockey is a team sport structured in standard hockey format, in which each team plays with ten outfield players and a goalkeeper. Teams must drive a round hockey ball by hitting it with a hockey stick towards the rival team's shooting circle and then into the goal. The match is won by the team that scores the most goals. Matches are played on grass, watered turf, artificial turf, synthetic field, or indoor boarded surface.

Ice hockey is a team sport played on ice skates, usually on an ice skating rink with lines and markings specific to the sport. It belongs to a family of sports called hockey. In ice hockey, two opposing teams use ice hockey sticks to control, advance and shoot a closed, vulcanized, rubber disc called a "puck" into the other team's goal. Each goal is worth one point. The team which scores the most goals is declared the winner. In a formal game, each team has six skaters on the ice at a time, barring any penalties, one of whom is the goaltender. Ice hockey is a full contact sport.

Offside is one of the laws in association football, codified in Law 11 of the Laws of the Game. The law states that a player is in an offside position if any of their body parts, except the hands and arms, are in the opponents' half of the pitch, and closer to the opponents' goal line than both the ball and the second-last opponent.
Team tactics as well as individual skills are necessities for playing association football. Football is in theory a very simple game, illustrated by Kevin Keegan's namely assertion that his tactics for winning a match were to "score more goals than the opposition". Tactical prowess within the sport is nevertheless a craftsmanship of its own, and one of the reasons why managers are paid well on the elite level. Well-organised and ready teams are often seen beating teams with more skillful players on paper. Manuals and books generally cover not only individual skills but tactics as well.

In the sport of association football, each of the 11 players on a team is assigned to a particular position on the field of play. A team is made up of one goalkeeper and ten outfield players who fill various defensive, midfield, and attacking positions depending on the formation deployed. These positions describe both the player's main role and their area of operation on the pitch.
The Laws of the Game are the codified rules of association football. The laws mention the number of players a team should have, the game length, the size of the field and ball, the type and nature of fouls that referees may penalize, the offside law, and many other laws that define the sport. During a match, it is the task of the referee to interpret and enforce the Laws of the Game.

A corner kick is the method of restarting play in a game of association football when the ball goes out of play over the goal line, without a goal being scored and having last been touched by a member of the defending team. The kick is taken from the corner of the field of play nearest to the place where the ball crossed the goal line.
In ice hockey, a play is offside if a player on the attacking team does not control the puck and is in the offensive zone when a different attacking player causes the puck to enter the offensive zone, until either the puck or all attacking players leave the offensive zone. Simply put, the puck must not enter the attacking zone after attacking players. If a player on the attacking team is in the offensive zone before the puck, either an immediate offside occurs, or they must retreat to the neutral zone.

Roller inline hockey, or inline hockey is a variant of hockey played on a hard, smooth surface, with players using inline skates to move and ice hockey sticks to shoot a hard, plastic puck into their opponent's goal to score points. The sport is a very fast-paced and free-flowing game and is considered a contact sport, but body checking is prohibited. There are five players including the goalkeeper from each team on the rink at a time, while teams normally consist of 16 players. There are professional leagues, one of which is the National Roller Hockey League (NRHL). While it is not a contact sport, there are exceptions, i.e. the NRHL involves fighting.

The Sheffield Rules was a code of football devised and played in the English city of Sheffield between 1858 and 1877. The rules were initially created and revised by Sheffield Football Club, with responsibility for the laws passing to the Sheffield Football Association upon that body's creation in 1867. The rules spread beyond the city boundaries to other clubs and associations in the north and midlands of England, making them one of the most popular forms of football during the 1860s and 1870s.

Passing the ball is a key part of association football. The purpose of passing is to keep possession of the ball by maneuvering it on the ground between different players with the objective of advancing it up the playing field.
This list of rugby league terms is a general glossary of the terminology used in the sport of rugby league football. The sport has accrued a considerable amount of jargon to describe aspects of the game. Many terms originate from the Laws of the Game. A number of aspects of the game have more than one term that refers to them. Different terms have become popularly used to describe an aspect of the game in different places with notable differences between the northern and southern hemispheres.

Offside is a rule used by several different team sports regulating aspects of player positioning. It is particularly used in field sports with rules deriving from the various codes of football, such as association football, rugby union and rugby league, and in similar 'stick and ball' sports e.g. ice hockey, broomball, field hockey and bandy.
In rugby league football, the Laws of the Game are the rules governing how the sport is played. The Laws are the responsibility of the Rugby League International Federation, and cover the play, officiating, equipment and procedures of the game.
Cherry picking, in basketball and certain other sports, refers to play where one player does not play defense with the rest of the team, but rather remains near half court or closer to their own team's goal.
Offside is a rule in bandy which states that if a player is in an offside position when the ball is touched or played by a teammate, the player may not become actively involved in the play. A player is in an offside position when closer to the opponent's goal-line than both the ball and the second-to-last defender, and also in the opponent's half of the bandy field. "Offside position" is a matter of fact, whereas committing an "offside offence" occurs when a player is "actively participating" and is subject to the interpretation of the referee. Goals scored after committing an offside offence are nullified if caught by the referee.
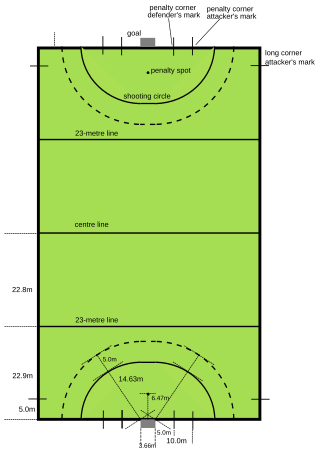
A hockey pitch is the playing surface for the game of field hockey. Historically, the game was played on natural turf (grass) and nowadays it is predominantly played on an artificial turf. The transition onto artificial pitches came during the 1970s and was made mandatory for major competitions in 1976. All the lines, markings and goal specifications are outlined by the International Hockey Federation in "The Rules of Hockey".

Futsal began in the 1930s in South America as a version of association football, taking elements of its parent game into an indoor format so players could still play during inclement weather. Over the years, both sports have developed, creating a situation where the two sports share common traits while also hosting various differences.

A free kick is a method of restarting play in association football. It is awarded after an infringement of the laws by the opposing team.