
Radiocarbon dating is a method for determining the age of an object containing organic material by using the properties of radiocarbon, a radioactive isotope of carbon.

Dendrochronology is the scientific method of dating tree rings to the exact year they were formed in a tree. As well as dating them, this can give data for dendroclimatology, the study of climate and atmospheric conditions during different periods in history from the wood of old trees. Dendrochronology derives from the Ancient Greek dendron, meaning "tree", khronos, meaning "time", and -logia, "the study of".
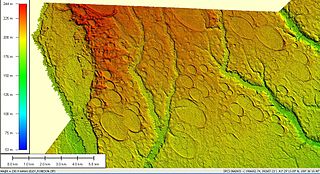
Carolina bays are elliptical to circular depressions concentrated along the East Coast of the United States within coastal New York, New Jersey, Delaware, Maryland, Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, Georgia, and north Florida. In Maryland, they are called Maryland basins. Within the Delmarva Peninsula, they and other coastal ponds are also called Delmarva bays.
Before Present (BP) years, also known as "time before present" or "years before present (YBP)", is a time scale used mainly in archaeology, geology and other scientific disciplines to specify when events occurred relative to the origin of practical radiocarbon dating in the 1950s. Because the "present" time changes, standard practice is to use 1 January 1950 as the commencement date (epoch) of the age scale. The abbreviation "BP" has been interpreted retrospectively as "Before Physics", which refers to the time before nuclear weapons testing artificially altered the proportion of the carbon isotopes in the atmosphere, which scientists must now account for.

Dendroarchaeology is a term used for the study of vegetation remains, old buildings, artifacts, furniture, art and musical instruments using the techniques of dendrochronology. It refers to dendrochronological research of wood from the past regardless of its current physical context. This form of dating is the most accurate and precise absolute dating method available to archaeologists, as the last ring that grew is the first year the tree could have been incorporated into an archaeological structure.
Bryant G. Wood is an American biblical archaeologist and young earth creationist. Wood is known for arguing that the destruction of Jericho could be accorded with the biblical literalist chronology of c. 1400 BC. This date is some 150 years later than the accepted date of c. 1550 BC, first determined by Kathleen Kenyon and subsequently confirmed with a variety of methods including radiocarbon dating.
Absolute dating is the process of determining an age on a specified chronology in archaeology and geology. Some scientists prefer the terms chronometric or calendar dating, as use of the word "absolute" implies an unwarranted certainty of accuracy. Absolute dating provides a numerical age or range, in contrast with relative dating, which places events in order without any measure of the age between events.

The Tsodilo Hills are a UNESCO World Heritage Site (WHS), consisting of rock art, rock shelters, depressions, and caves in southern Africa. It gained its WHS listing in 2001 because of its unique religious and spiritual significance to local peoples, as well as its unique record of human settlement over many millennia. UNESCO estimates there are over 4500 rock paintings at the site. The site consists of a few main hills known as the Child Hill, Female Hill, and Male Hill.
Luminescence dating refers to a group of methods of determining how long ago mineral grains were last exposed to sunlight or sufficient heating. It is useful to geologists and archaeologists who want to know when such an event occurred. It uses various methods to stimulate and measure luminescence.

The Avellino eruption of Mount Vesuvius refers to a Vesuvian eruption in c. 1995 BC. It is estimated to have had a VEI of 6, making it larger and more catastrophic than Vesuvius's more famous and well-documented 79 AD eruption. It is the source of the Avellino pumice deposits extensively found in the comune of Avellino in Campania.

Bouldnor Cliff is a submerged prehistoric settlement site in the Solent. The site dates from the Mesolithic era and is in approximately 11 metres of water just offshore of the village of Bouldnor on the Isle of Wight in the United Kingdom. The preservation of organic materials from this era that do not normally survive on dry land has made Bouldnor important to the understanding of Mesolithic Britain, and the BBC Radio 4's Making History programme described it "probably Europe's most important Mesolithic site" albeit concealed under water.

In archaeology, a biofact is any organic material including flora or fauna material found at an archaeological site that has not been technologically altered by humans yet still has cultural relevance. Biofacts can include but are not limited to plants, seeds, pollen, animal bones, insects, fish bones and mollusks. The study of biofacts, alongside other archaeological remains such as artifacts are a key element to understanding how past societies interacted with their surrounding environment and with each other. Biofacts also play a role in helping archaeologists understand questions of subsistence and reveals information about the domestication of certain plant species and animals which demonstrates, for example, the transition from a hunter-gatherer society to a farming society.
Yuchanyan is an early Neolithic cave site in Dao County (Daoxian), Hunan, China. The site yielded sherds of ceramic vessels and other artifacts which were dated by analysis of charcoal and bone collagen, giving a date range of 17,500 to 18,300 years old for the pottery. The pottery specimens may be the oldest known examples of pottery.
The calculation of radiocarbon dates determines the age of an object containing organic material by using the properties of radiocarbon, a radioactive isotope of carbon.
Samples used for radiocarbon dating must be handled carefully to avoid contamination. Not all material can be dated by this method; only samples containing organic matter can be tested: the date found will be the date of death of the plants or animals from which the sample originally came.
Radiocarbon dating measurements produce ages in "radiocarbon years", which must be converted to calendar ages by a process called calibration. Calibration is needed because the atmospheric 14
C:12
C ratio, which is a key element in calculating radiocarbon ages, has not been constant historically.
Gogo Falls is an archaeological site near a former and since 1956 dammed waterfall, located in the Lake Victoria Basin in Migori County, western Kenya. This site is important to archaeology as it includes some of the earliest appearances of artifacts and domestic animals in the area. The findings at the site help to reconstruct the later prehistory around Lake Victoria, including a Pastoral Neolithic occupation by Elmenteitan peoples and a later Iron Age occupation. Artifacts found at the site included pottery and iron artifacts. Through these artifacts some of the cultural traditions of the people who lived near Gogo Falls were discovered.
Elands Bay Cave is located near the mouth of the Verlorenvlei estuary on the Atlantic coast of South Africa's Western Cape Province. The climate has continuously become drier since the habitation of hunter-gatherers in the Later Pleistocene. The archaeological remains recovered from previous excavations at Elands Bay Cave have been studied to help answer questions regarding the relationship of people and their landscape, the role of climate change that could have determined or influenced subsistence changes, and the impact of pastoralism and agriculture on hunter-gatherer communities.
There have been changing views about initial Polynesian discovery and settlement of Hawaii, beginning with Abraham Fornander in the late 19th century and continuing through early archaeological investigations of the mid-20th century. There is no definitive date for the Polynesian discovery of Hawaii. Through the use of more advanced radiocarbon methods, taxonomic identification of samples, and stratigraphic archaeology, during the 2000s the consensus was established that the first arrived in Kauai sometime around 1000 AD, and in Oahu sometime between 1100 AD and 1200 AD. However, with more testing and refined samples, including chronologically tracing settlements in Society Islands and the Marquesas, two archipelagoes which have long been considered to be the immediate source regions for the first Polynesian voyagers to Hawaii, it has been concluded that the settlement of the Hawaiian Islands took place around 1219 to 1266 AD, with the paleo-environmental evidence of agriculture indicating the Ancient Hawaiian population to have peaked around 1450 AD around 140,000 to 200,000.
This page is a glossary of archaeology, the study of the human past from material remains.