Related Research Articles

Bioinformatics is an interdisciplinary field that develops methods and software tools for understanding biological data, in particular when the data sets are large and complex. As an interdisciplinary field of science, bioinformatics combines biology, computer science, information engineering, mathematics and statistics to analyze and interpret the biological data. Bioinformatics has been used for in silico analyses of biological queries using mathematical and statistical techniques.
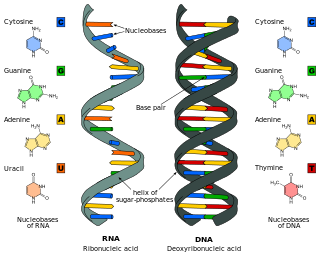
Nucleic acids are biopolymers, or large biomolecules, essential to all known forms of life. They are composed of nucleotides, which are the monomers made of three components: a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. The two main classes of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). If the sugar is ribose, the polymer is RNA; if the sugar is the ribose derivative deoxyribose, the polymer is DNA.
Zoology is the branch of biology that studies the animal kingdom, including the structure, embryology, evolution, classification, habits, and distribution of all animals, both living and extinct, and how they interact with their ecosystems. The term is derived from Ancient Greek ζῷον, zōion, i.e. "animal" and λόγος, logos, i.e. "knowledge, study".

Genomics is an interdisciplinary field of biology focusing on the structure, function, evolution, mapping, and editing of genomes. A genome is an organism's complete set of DNA, including all of its genes. In contrast to genetics, which refers to the study of individual genes and their roles in inheritance, genomics aims at the collective characterization and quantification of all of an organism's genes, their interrelations and influence on the organism. Genes may direct the production of proteins with the assistance of enzymes and messenger molecules. In turn, proteins make up body structures such as organs and tissues as well as control chemical reactions and carry signals between cells. Genomics also involves the sequencing and analysis of genomes through uses of high throughput DNA sequencing and bioinformatics to assemble and analyze the function and structure of entire genomes. Advances in genomics have triggered a revolution in discovery-based research and systems biology to facilitate understanding of even the most complex biological systems such as the brain.

A phylogenetic tree is a branching diagram or a tree showing the evolutionary relationships among various biological species or other entities based upon similarities and differences in their physical or genetic characteristics. All life on Earth is part of a single phylogenetic tree, indicating common ancestry.

Pseudogenes are nonfunctional segments of DNA that resemble functional genes. Most arise as superfluous copies of functional genes, either directly by DNA duplication or indirectly by reverse transcription of an mRNA transcript. Pseudogenes are usually identified when genome sequence analysis finds gene-like sequences that lack regulatory sequences needed for transcription or translation, or whose coding sequences are obviously defective due to frameshifts or premature stop codons.
DNA–DNA hybridization generally refers to a molecular biology technique that measures the degree of genetic similarity between pools of DNA sequences. It is usually used to determine the genetic distance between two organisms. This has been used extensively in phylogeny and taxonomy.
In biochemistry, the DNA methyltransferase family of enzymes catalyze the transfer of a methyl group to DNA. DNA methylation serves a wide variety of biological functions. All the known DNA methyltransferases use S-adenosyl methionine (SAM) as the methyl donor.

Filamentous bacteriophage is a family of viruses (Inoviridae) that infect bacteria. The phages are named for their filamentous shape, a worm-like chain, about 6 nm in diameter and about 1000-2000 nm long. The coat of the virion comprises five types of viral protein, which are located during phage assembly in the inner membrane of the host bacteria, and are added to the nascent virion as it extrudes through the membrane. The simplicity of this family makes it an attractive model system to study fundamental aspects of molecular biology, and it has also proven useful as a tool in immunology and nanotechnology.

In evolutionary biology, conserved sequences are identical or similar sequences in nucleic acids or proteins across species, or within a genome, or between donor and receptor taxa. Conservation indicates that a sequence has been maintained by natural selection.

Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus is a strain of virus that causes severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS). It is an enveloped, positive-sense, single-stranded RNA virus which infects the epithelial cells within the lungs. The virus enters the host cell by binding to angiotensin-converting enzyme 2. It infects humans, bats, and palm civets.

Bacteria are a type of biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a number of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals. Bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit soil, water, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of the earth's crust. Bacteria also live in symbiotic and parasitic relationships with plants and animals. Most bacteria have not been characterised, and only about 27 percent of the bacterial phyla have species that can be grown in the laboratory. The study of bacteria is known as bacteriology, a branch of microbiology.
Biology is the natural science that studies life and living organisms, including their physical structure, chemical processes, molecular interactions, physiological mechanisms, development and evolution. Despite the complexity of the science, certain unifying concepts consolidate it into a single, coherent field. Biology recognizes the cell as the basic unit of life, genes as the basic unit of heredity, and evolution as the engine that propels the creation and extinction of species. Living organisms are open systems that survive by transforming energy and decreasing their local entropy to maintain a stable and vital condition defined as homeostasis.
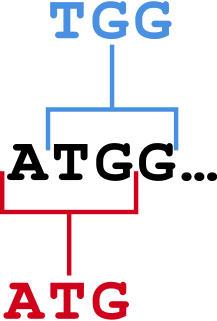
In bioinformatics, k-mers are substrings of length contained within a biological sequence. Primarily used within the context of computational genomics and sequence analysis, in which k-mers are composed of nucleotides, k-mers are capitalized upon to assemble DNA sequences, improve heterologous gene expression, identify species in metagenomic samples, and create attenuated vaccines. Usually, the term k-mer refers to all of a sequence's subsequences of length , such that the sequence AGAT would have four monomers, three 2-mers, two 3-mers and one 4-mer (AGAT). More generally, a sequence of length will have k-mers and total possible k-mers, where is number of possible monomers.

Mitochondrial carriers are proteins from solute carrier family 25 which transfer molecules across the membranes of the mitochondria. Mitochondrial carriers are also classified in the Transporter Classification Database. The Mitochondrial Carrier (MC) Superfamily has been expanded to include both the original Mitochondrial Carrier (MC) family and the Mitochondrial Inner/Outer Membrane Fusion (MMF) family.
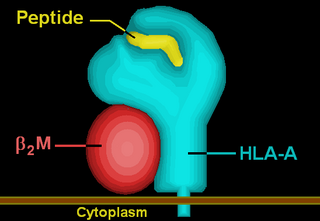
HLA-A69 (A69) is a human leukocyte antigen serotype within HLA-A serotype group. The serotype is determined by the antibody recognition of α69 subset of HLA-A α-chains. For A69, the alpha "A" chain are encoded by the HLA-A*69 allele group and the β-chain are encoded by B2M locus. This group currently is dominated by A*6901. A69 and A*69 are almost synonymous in meaning. A69 is a split antigen of the broad antigen serotype A28. A69 is a sister serotype of A68.

Bacterial phyla constitute the major lineages of the domain Bacteria. While the exact definition of a bacterial phylum is debated, a popular definition is that a bacterial phylum is a monophyletic lineage of bacteria whose 16S rRNA genes share a pairwise sequence identity of ~75% or less with those of the members of other bacterial phyla.
In bacteriology, a taxon in disguise is a species, genus or higher unit of biological classification whose evolutionary history reveals has evolved from another unit of a similar or lower rank, making the parent unit paraphyletic. That happens when rapid evolution makes a new species appear so radically different from the ancestral group that it is not (initially) recognised as belonging to the parent phylogenetic group, which is left as an evolutionary grade.
Bacterial taxonomy is the taxonomy, i.e. the rank-based classification, of bacteria.

BacDive is a bacterial metadatabase that provides strain-linked information about bacterial and archaeal biodiversity.
References
- ↑ Roring, S; Brittain, D; Bunschoten, A. E; Hughes, M. S; Skuce, R. A; van Embden, J. D. A; Neill, S. D (15 March 1998). "Spacer oligotyping of Mycobacterium bovis isolates compared to typing by restriction fragment length polymorphism using PGRS, DR and IS6110 probes". Veterinary Microbiology. 61 (1–2): 111–120. doi:10.1016/S0378-1135(98)00178-3. PMID 9646470.
- ↑ Mabilat, C.; Courvalin, P. (1 November 1990). "Development of "oligotyping" for characterization and molecular epidemiology of TEM beta-lactamases in members of the family Enterobacteriaceae". Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. 34 (11): 2210–2216. doi:10.1128/AAC.34.11.2210. ISSN 0066-4804. PMC 172024 . PMID 2073111.
- ↑ Rani, Rajni; Fernandez-Vina, M. A.; Zaheer, S. A.; Beena, K. R.; Stastny, Peter (1 July 1993). "Study of HLA class II alleles by PCR oligotyping in leprosy patients from North India". Tissue Antigens. 42 (1): 133–137. doi:10.1111/j.1399-0039.1993.tb02179.x. ISSN 1399-0039. PMID 8284786.