
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is bordered by Pakistan to the east and south, Iran to the west, Turkmenistan to the northwest, Uzbekistan to the north, Tajikistan to the northeast, and China to the northeast and east. Occupying 652,864 square kilometres (252,072 sq mi) of land, the country is predominantly mountainous with plains in the north and the southwest, which are separated by the Hindu Kush mountain range. Kabul is the country's largest city and serves as its capital. As of 2021, Afghanistan's population is 40.2 million.

Mirza Nasir-ud-Din Muhammad, better known by his regnal name, Humāyūn;, was the second emperor of the Mughal Empire, who ruled over territory in what is now Eastern Afghanistan, Pakistan, Northern India, and Bangladesh from 1530 to 1540 and again from 1555 to 1556. At the time of his death in 1556, the Mughal Empire spanned almost one million square kilometres.

Kandahar is a city in Afghanistan, located in the south of the country on the Arghandab River, at an elevation of 1,010 m (3,310 ft). It is Afghanistan's second largest city after Kabul, with a population of about 614,118. It is the capital of Kandahar Province and the centre of the larger cultural region called Loy Kandahar. Kandahar is the founding city and spiritual center of the Taliban. Despite the capital of Afghanistan being Kabul, where the government administration is based, Kandahar is the seat of power in Afghanistan as the supreme leader and his spiritual advisers are based there. Kandahar has therefore been called the de facto capital of Afghanistan, though the Taliban maintain Kabul is the capital.

Transport in Afghanistan is done mostly by road, rail and air. Much of the nation's road network was built in the mid-20th century but left to ruin during the last two decades of that century due to war and political turmoil. Officials of the current Islamic Emirate have continued to improve the national highways, roads, and bridges. In 2008, there were about 700,000 vehicles registered in Kabul. At least 1,314 traffic collisions were reported in 2022.

MullahMuhammad Omar was an Afghan cleric, Islamist partisan fighter and political leader who founded the Taliban and was the supreme leader of Afghanistan from 1996 to 2001. Following the ouster of his government by the United States in 2001, he went into hiding and avoided capture until his reported 2013 death from tuberculosis.
Mullah Mohammad Rabbani Akhund was one of the main leaders of the Taliban movement who served as Prime Minister of Afghanistan from 1996 to 2001. He was second in power only to the supreme leader, Mullah Mohammed Omar, in the Taliban hierarchy.

Ghazni, historically known as Ghaznain (غزنين) or Ghazna (غزنه), also transliterated as Ghuznee, and anciently known as Alexandria in Opiana, is a city in southeastern Afghanistan with a population of around 190,000 people. The city is strategically located along Highway 1, which has served as the main road between Kabul and Kandahar for thousands of years. Situated on a plateau at 2,219 metres (7,280 ft) above sea level, the city is 150 kilometres (93 mi) south of Kabul and is the capital of Ghazni Province. The name Ghazni drives from the Persian word ganj ‘treasure’.

Bagram is a town and seat in Bagram District in Parwan Province of Afghanistan, about 60 kilometers north of the capital Kabul. It is the site of an ancient city located at the junction of the Ghorband and Panjshir Valley, near today's city of Charikar, Afghanistan. The location of this historical town made it a key passage from Ancient India along the Silk Road, leading westwards through the mountains towards Bamiyan, and north over the Kushan Pass to the Baghlan Valley and past the Kushan archeological site at Surkh Kotal, to the commercial centre of Balkh and the rest of northern Afghanistan. Bagram was the capital of the Kushan Empire in the first century CE.

Farah is one of the 34 provinces of Afghanistan, located in the southwestern part of the country next to Iran. It is a spacious and sparsely populated province, divided into eleven districts and contains hundreds of villages. It has a population of about 563,026, which is multi-ethnic and mostly a rural tribal society. Farah's population is dominated by Pashtun (80%) tribesmen although Tajiks and a small minority of Shi'a Hazaras can also be found in the countryside. The Farah Airport is located near the city of Farah, which serves as the capital of the province. Farah is linked with Iran via the Iranian border town of Mahirud. The province famous tourism sites include Pul Garden, New Garden, Kafee Garden, shrine of Sultan Amir and Kafer castle are from sightseeing places of Farah province

Ghazni is one of the 34 provinces of Afghanistan, located in southeastern Afghanistan. The province contains 19 districts, encompassing over a thousand villages and roughly 1.3 million people, making it the 5th most populous province. The city of Ghazni serves as the capital. It lies on the important Kabul–Kandahar Highway, and has historically functioned as an important trade center. The Ghazni Airport is located next to the city of Ghazni and provides limited domestic flights to Afghanistan's capital, Kabul.
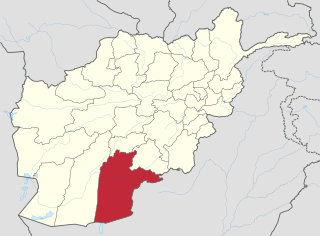
Kandahār is one of the thirty-four provinces of Afghanistan, located in the southern part of the country, sharing a border with Pakistan, to the south. It is surrounded by Helmand in the west, Uruzgan in the north and Zabul Province in the east. Its capital is the city of Kandahar, Afghanistan's second largest city, which is located on the Arghandab River. The greater region surrounding the province is called Loy Kandahar. The Emir of Afghanistan sends orders to Kabul from Kandahar making it the de facto capital of Afghanistan, although the main government body operates in Kabul. All meetings with the Emir take place in Kandahar, meetings excluding the Emir are in Kabul.

Mullah Abdul Salam Zaeef is an Afghan diplomat who was the Afghan ambassador to Pakistan before the US invasion of Afghanistan.

Kandahar is a 2001 Iranian film directed by Mohsen Makhmalbaf, set in Afghanistan during the rule of the Taliban. Its original Afghan title is Safar-e Ghandehar, which means "Journey to Kandahar", and it is alternatively known as The Sun Behind the Moon. The film is based on a partly true, partly fictionalized story of Nafas, a successful Afghan-Canadian woman played by Nelofer Pazira.
Farah is the capital and largest city of Farah Province in western Afghanistan. It is located on the Farah River, close to the border with Iran. It is one of the largest cities of western Afghanistan in terms of population, with about 1.5 million people living in its urban area.
Jason Burke is a British journalist and the author of several non-fiction books. A correspondent covering Africa for The Guardian, he is currently based in Johannesburg, having previously been based in New Delhi as the same paper's South Asia correspondent. In his years of journalism, Burke has addressed a wide range of topics including politics, social affairs and culture in Europe and the Middle East. He has written extensively on Islamic extremism and, among numerous other conflicts, covered the wars of 2001 in Afghanistan and 2003 in Iraq, the latter of which he described as "entirely justifiable from a humanitarian perspective".

Buddhism, an Indian religion founded by Gautama Buddha, first arrived in modern-day Afghanistan through the conquests of Ashoka, the third emperor of the Maurya Empire. Among the earliest notable sites of Buddhist influence in the country is a bilingual mountainside inscription in Greek and Aramaic that dates back to 260 BCE and was found on the rocky outcrop of Chil Zena near Kandahar.
The Arghun dynasty was a Turco-Mongol dynasty, who ruled over the area between Southern Afghanistan and Sindh from the late 15th century to the early 16th century. The Arghuns claimed their descent and name from Ilkhanid-Mongol Arghun Khan. Arghun rule can be divided into two branches: the Arghun branch of Dhu'l-Nun Beg Arghun that ruled until 1554, and the Tarkhan branch of Muhammad 'Isa Tarkhan that ruled until 1591.
Canada's role in the Afghanistan War began in late 2001. Canada sent its first element of soldiers secretly in October 2001 from Joint Task Force 2, and the first contingents of regular Canadian Armed Forces (CAF) troops arrived in Afghanistan in January–February 2002. The operations were aimed at identifying and neutralizing Al-Qaeda members in that country and toppling the Taliban regime which was supporting international terrorism. Canada's role in the Afghan conflict grew in 2006 when Canadian troops relieved US forces in Kandahar province, taking command of the multinational brigade in the region during a major Taliban offensive.

Alexandria in Arachosia also known as Alexandropolis (Ἀλεξανδρόπολις) was a city in ancient times that is now called Kandahar in Afghanistan. It was one of more than twenty cities founded or renamed by Alexander the Great. It was founded around 330 BC, on the foundations of an earlier Achaemenid fortress. Arachosia is the Greek name of an ancient province of the Achaemenid, Seleucid and Parthian empires. The province of Arachosia was centered around the Argandab valley in Kandahar. It did not reach the Hindu Kush, but it apparently extended east as far as the Indus River, although its exact extents are not yet clear.

The Great War for Civilisation: The Conquest of the Middle East is a book published in 2005 by the English journalist Robert Fisk. The book is based on many of the articles Fisk wrote when he was serving as a correspondent in the Middle East for The Times and The Independent. The book revolves around several key themes regarding the history of the modern Middle East: the Arab–Israeli conflict, the Soviet invasion of Afghanistan, the Gulf Wars, the Algerian Civil War, as well as other regional topics such as the Armenian genocide. The Great War for Civilisation is the second book Fisk has written about the Middle East. The first one, Pity the Nation, was about the Lebanese Civil War.















