
Ambracia was a city of ancient Greece on the site of modern Arta. It was captured by the Corinthians in 625 BC and was situated about 11 km (7 mi) from the Ambracian Gulf, on a bend of the navigable river Arachthos, in the midst of a fertile wooded plain.

Polybius was a Greek historian of the Hellenistic period. He is noted for his work The Histories, which covered the period of 264–146 BC and the Punic Wars in detail.
This article concerns the period 319 BC – 310 BC.
Year 295 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. It was known in the Roman Republic as the Year of the Consulship of Rullianus and Mus. The denomination 295 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Ptolemy V Epiphanes Eucharistos was the King of Ptolemaic Egypt from July or August 204 BC until his death in 180 BC.

Philip V was king (Basileus) of Macedonia from 221 to 179 BC. Philip's reign was principally marked by an unsuccessful struggle with the emerging power of the Roman Republic. He would lead Macedon against Rome in the First and Second Macedonian Wars, losing the latter but allying with Rome in the Roman-Seleucid War towards the end of his reign.
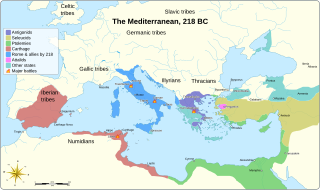
The First Macedonian War was fought by Rome, allied with the Aetolian League and Attalus I of Pergamon, against Philip V of Macedon, contemporaneously with the Second Punic War against Carthage. There were no decisive engagements, and the war ended in a stalemate.

Nabis was the last king of independent Sparta. He was probably a member of the Heracleidae, and he ruled from 207 BC to 192 BC, during the years of the First and Second Macedonian Wars and the eponymous "War against Nabis", i.e. against him. After taking the throne by executing two claimants, he began rebuilding Sparta's power. During the Second Macedonian War, Nabis sided with King Philip V of Macedon and in return he received the city of Argos. However, when the war began to turn against the Macedonians, he defected to Rome. After the war, the Romans, urged by the Achaean League, attacked Nabis and defeated him. He then was assassinated in 192 BC by the Aetolian League. He represented the last phase of Sparta's reformist period.

Hellenistic Greece is the historical period of the country following Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the annexation of the classical Greek Achaean League heartlands by the Roman Republic. This culminated at the Battle of Corinth in 146 BC, a crushing Roman victory in the Peloponnese that led to the destruction of Corinth and ushered in the period of Roman Greece. Hellenistic Greece's definitive end was with the Battle of Actium in 31 BC, when the future emperor Augustus defeated Greek Ptolemaic queen Cleopatra VII and Mark Antony, the next year taking over Alexandria, the last great center of Hellenistic Greece.

Philopoemen was a skilled Greek general and statesman, who was Achaean strategos on eight occasions.
Demetrius of Pharos was a ruler of Pharos involved in the First Illyrian War, after which he ruled a portion of the Illyrian Adriatic coast on behalf of the Romans, as a client king.
Scerdilaidas or Skerdilaid was an Illyrian ruler of the Illyrian kingdom under the Labeatan dynasty. Before taking the throne, Scerdilaidas was commander of the Illyrian armies and played a major role in the Illyrian Wars against the Romans.
The First Battle of Lamia was fought in 209 BC between the forces of Philip V of Macedon and the Aetolians led by Pyrrhias. The Aetolians were aided by a small Roman force and a force from the kingdom of Pergamon. The Macedonians were victorious. Another battle was fought at Lamia within the year.
The Second Battle of Lamia was fought in 209 BC between the forces of Philip V of Macedon and Pyrrhias, a general of the Aetolian League. Pyrrhias was once again aided by Pergamene forces and Roman advisors but again he was defeated. His side suffered heavy casualties.

Attalus I, surnamed Soter ruled Pergamon, an Ionian Greek polis, first as a dynast, later as king, from 241 BC to 197 BC. He was the first cousin once removed and the adopted son of Eumenes I, whom he succeeded, and was the first of the Attalid dynasty to assume the title of king in 238 BC. He was the son of Attalus and his wife Antiochis.

The Cretan War was fought by King Philip V of Macedon, the Aetolian League, many Cretan cities and Spartan pirates against the forces of Rhodes and later Attalus I of Pergamum, Byzantium, Cyzicus, Athens, and Knossos.

Maroneia is a village and a former municipality in Rhodope regional unit, East Macedonia and Thrace, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Maroneia-Sapes, of which it is a municipal unit. The municipal unit has an area of 287.155 km2. Population 6,350 (2011). The seat of the municipality was in Xylagani.

The Antigonid Macedonian army was the army that evolved from the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia in the period when it was ruled by the Antigonid dynasty from 276 BC to 168 BC. It was seen as one of the principal Hellenistic fighting forces until its ultimate defeat at Roman hands at the Battle of Pydna in 168 BC. However, there was a brief resurgence in 150-148 during the revolt of Andriscus, a supposed heir to Perseus.
Pleuratus III was a ruler of the Illyrian kingdom under the Labeatan dynasty. He was the son of Scerdilaidas. Pleuratus continued his father's pro-Roman policy even more decidedly, so much that his loyalty to Rome was well known, even to other dynasts. He managed to extend the boundaries of the Illyrian State in the south when he was rewarded land annexed by Philip V of Macedon. He became one of the most prominent Illyrian kings of the time all because of his loyalty to the Romans. Pleuratus was succeeded by his son Gentius, who was the last Illyrian king.

The kingdom of Macedonia was an ancient state in what is now the Macedonian region of northern Greece, founded in the mid-7th century BC during the period of Archaic Greece and lasting until the mid-2nd century BC. Led first by the Argead dynasty of kings, Macedonia became a vassal state of the Achaemenid Empire of ancient Persia during the reigns of Amyntas I of Macedon and his son Alexander I of Macedon. The period of Achaemenid Macedonia came to an end in roughly 479 BC with the ultimate Greek victory against the second Persian invasion of Greece led by Xerxes I and the withdrawal of Persian forces from the European mainland.











