Related Research Articles

The Finger Lakes are a group of eleven long, narrow, roughly north–south lakes located directly south of Lake Ontario in an area called the Finger Lakes region in New York, in the United States. This region straddles the northern and transitional edge of the Northern Allegheny Plateau, known as the Finger Lakes Uplands and Gorges ecoregion, and the Ontario Lowlands ecoregion of the Great Lakes Lowlands.
The Mohicans are an Eastern Algonquian Native American tribe that historically spoke an Algonquian language. As part of the Eastern Algonquian family of tribes, they are related to the neighboring Lenape, whose indigenous territory was to the south as far as the Atlantic coast. The Mohican lived in the upper tidal Hudson River Valley, including the confluence of the Mohawk River and into western New England centered on the upper Housatonic River watershed. After 1680, due to conflicts with the powerful Mohawk to the west during the Beaver Wars, many were driven southeastward across the present-day Massachusetts western border and the Taconic Mountains to Berkshire County around Stockbridge, Massachusetts.

Thayendanegea or Joseph Brant was a Mohawk military and political leader, based in present-day New York and, later, Brantford, in what is today Ontario, who was closely associated with Great Britain during and after the American Revolution. Perhaps the best known Native American of his generation, he met many of the most significant American and British people of the age, including both United States President George Washington and King George III of Great Britain.
Onondaga may refer to:

The Kanien'kehá:ka are in the easternmost section of the Haudenosaunee, or Iroquois Confederacy. They are an Iroquoian-speaking Indigenous people of North America, with communities in southeastern Canada and northern New York State, primarily around Lake Ontario and the St. Lawrence River. As one of the five original members of the Iroquois League, the Mohawk are known as the Keepers of the Eastern Door – the traditional guardians of the Iroquois Confederation against invasions from the east. The Mohawk are federally recognized in the United States as the Saint Regis Mohawk Tribe.

The 1779 Sullivan Expedition was a United States military campaign during the American Revolutionary War, lasting from June to October 1779, against the four British-allied nations of the Iroquois. The campaign was ordered by George Washington in response to Iroquois and Loyalist attacks on the Wyoming Valley, German Flatts, and Cherry Valley. The campaign had the aim of "taking the war home to the enemy to break their morale." The Continental Army carried out a scorched-earth campaign in the territory of the Iroquois Confederacy in what is now western and central New York.
The Seneca are a group of Indigenous Iroquoian-speaking people who historically lived south of Lake Ontario, one of the five Great Lakes in North America. Their nation was the farthest to the west within the Six Nations or Iroquois League (Haudenosaunee) in New York before the American Revolution. For this reason, they are called “The Keepers of the Western Door.”

The Phelps and Gorham Purchase was the sale, in 1788, of a portion of a large tract of land in western New York State owned by the Seneca nation of the Iroquois Confederacy to a syndicate of land developers led by Oliver Phelps and Nathaniel Gorham. The larger tract of land is generally known as the "Genesee tract" and roughly encompasses all that portion of New York State west of Seneca Lake, consisting of about 6,000,000 acres (24,000 km2).

The Onondaga people are one of the five original nations of the Haudenosaunee (Iroquois) Confederacy in the Northeastern Woodlands. Their historical homelands are in and around present-day Onondaga County, New York, south of Lake Ontario.

The Oneida people are a Native American tribe and First Nations band. They are one of the five founding nations of the Iroquois Confederacy in the area of upstate New York, particularly near the Great Lakes.

Onondaga Lake is located in Central New York, immediately northwest of and adjacent to Syracuse, New York. The southeastern end of the lake and the southwestern shore abut industrial areas and expressways; the northeastern shore and northwestern end border a series of parks and museums.

Six Nations is demographically the largest First Nations reserve in Canada. As of the end of 2017, it has a total of 27,276 members, 12,848 of whom live on the reserve. These nations are the Mohawk, Cayuga, Onondaga, Oneida, Seneca and Tuscarora. Some Lenape live in the territory as well.
The Haudenosaunee was formed around the Great Law of Peace Kaianere'kó:wa, a constitution detailing a shared value system which informs the policy and economics of their society.
The Great Peacemaker, sometimes referred to as Deganawida or Tekanawí:ta was by tradition, along with Jigonhsasee and Hiawatha, the founder of the Haudenosaunee, commonly called the Iroquois Confederacy. This is a political and cultural union of six Iroquoian-speaking Native American tribes governing parts of the present-day state of New York, northern Pennsylvania, and the eastern portion of the provinces of Ontario, and Quebec Canada, recognized as sovereign by both the USA and Canada.
Father Simon Le Moyne, S.J., sometimes spelled Simon Le Moine, was a French Jesuit priest who became involved with the mission to the Hurons and Iroquois in the Americas. Le Moyne had acquired sixteen years of education and experience through priesthood in France before his arrival in New France in 1638. During that same year, he headed out to his mission in Huron country. The destruction of the Huron nation by the Iroquois brought him back east to what is modern day Quebec in 1650.

The Conrad Weiser Homestead was the home of Johann Conrad Weiser, who enlisted the Iroquois on the British side in the French and Indian War. The home is located near Womelsdorf, Berks County, Pennsylvania in the United States. A designated National Historic Landmark, it is currently administered as a historic house museum by the Pennsylvania Historical and Museum Commission. The historic site was established in 1923 to preserve an example of a colonial homestead and to honor Weiser, an important figure in the settlement of the colonial frontier.

Conrad Weiser, born Johann Conrad Weiser, Jr., was a Pennsylvania Dutch (German) pioneer who served as an interpreter and diplomat between the Pennsylvania Colony and Native American nations. Primarily a farmer, he also worked as a tanner, and later served as a soldier and judge. He lived part of the time for six years at Ephrata Cloister, a Protestant monastic community in Lancaster County.
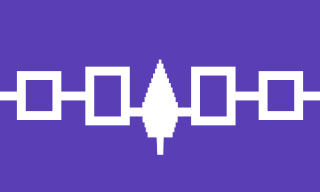
The Iroquois, also known as the Five Nations, and later as the Six Nations from 1722 onwards; alternatively referred to by the endonym Haudenosaunee are an Iroquoian-speaking confederacy of Native Americans and First Nations peoples in northeast North America. They were known by the French during the colonial years as the Iroquois League, and later as the Iroquois Confederacy, while the English simply called them the "Five Nations". The peoples of the Iroquois included the Mohawk, Oneida, Onondaga, Cayuga, and Seneca. After 1722, the Iroquoian-speaking Tuscarora people from the southeast were accepted into the confederacy, from which point it was known as the "Six Nations".

Tadodaho was a Native American Hoyenah (sachem) of the Onondaga nation before the Deganawidah and Hiawatha formed the Iroquois League. According to oral tradition, he had extraordinary characteristics and was widely feared, but he was persuaded to support the confederacy of the Five Nations.

John Arthur Gibson (1850–1912) was a chief of the Seneca nation of the North American Iroquois confederation. Part Onondaga and part Seneca, he resided within the reserve of the Six Nations of the Grand River in Ontario, Canada. Knowledgeable about Iroquois (Haudosaunee) culture, he is best known for the versions he provided of the Iroquois oral constitution, the Great Law of Peace. He acted as an advisor to the Canadian Department of Indian Affairs in matters relating both to Iroquois and non-Iroquois indigenous people. He was a well-respected player of the traditional Iroquois sport of lacrosse until he was blinded during a game when he was 31.
References
- ↑ Nash, Gary B. Red, White and Black: The Peoples of Early North America Los Angeles 2015. Chapter 1, p. 11
- 1 2 3 Francis Jennings, ed., The History and culture of Iroquois diplomacy: an interdisciplinary guide to the treaties of the Six Nations and their league (Syracuse, N.Y.: Syracuse University Press, 1985; ISBN 0-8156-2650-9), 221.
- ↑ Robert Steven Grumet, Historic Contact: Indian People and Colonists in today's northeastern United States in the Sixteenth through Eighteenth Centuries (Norman: University of Oklahoma Press, 1995; ISBN 0-8061-2700-7), 393.