
Emergency medical services (EMS), also known as ambulance services or paramedic services, are emergency services which treat illnesses and injuries that require an urgent medical response, providing out-of-hospital treatment and transport to definitive care. They may also be known as a first aid squad, FAST squad, emergency squad, rescue squad, ambulance squad, ambulance corps, life squad or by other initialisms such as EMAS or EMARS.

Cardiac arrest is a sudden loss of blood flow resulting from the failure of the heart to pump effectively. Signs include loss of consciousness and abnormal or absent breathing. Some individuals may experience chest pain, shortness of breath, or nausea before cardiac arrest. If not treated within minutes, it typically leads to death.

Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is an emergency procedure that combines chest compressions often with artificial ventilation in an effort to manually preserve intact brain function until further measures are taken to restore spontaneous blood circulation and breathing in a person who is in cardiac arrest. It is recommended in those who are unresponsive with no breathing or abnormal breathing, for example, agonal respirations.
Advanced cardiac life support, or advanced cardiovascular life support, often referred to by its abbreviation as "ACLS", refers to a set of clinical algorithms for the urgent treatment of cardiac arrest, stroke, myocardial infarction, and other life-threatening cardiovascular emergencies. Outside North America, Advanced Life Support (ALS) is used.

Defibrillation is a treatment for life-threatening cardiac dysrhythmias, specifically ventricular fibrillation (VF) and non-perfusing ventricular tachycardia (VT). A defibrillator delivers a dose of electric current to the heart. Although not fully understood, this process depolarizes a large amount of the heart muscle, ending the dysrhythmia. Subsequently, the body's natural pacemaker in the sinoatrial node of the heart is able to re-establish normal sinus rhythm. A heart which is in asystole (flatline) cannot be restarted by a defibrillator, but would be treated by cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR).

Ventricular fibrillation is an abnormal heart rhythm in which the ventricles of the heart quiver instead of pumping normally. It is due to disorganized electrical activity. Ventricular fibrillation results in cardiac arrest with loss of consciousness and no pulse. This is followed by death in the absence of treatment. Ventricular fibrillation is initially found in about 10% of people with cardiac arrest.

Asystole is the absence of ventricular contractions in the context of a lethal heart arrhythmia. Asystole is the most serious form of cardiac arrest and is usually irreversible. A cardiac flatline is the state of total cessation of electrical activity from the heart, which means no tissue contraction from the heart muscle and therefore no blood flow to the rest of the body.
Basic life support (BLS) is a level of medical care which is used for victims of life-threatening illnesses or injuries until they can be given full medical care at a hospital. It can be provided by trained medical personnel, including certified first responders, emergency medical technicians, and by qualified bystanders.
The Seattle & King County Emergency Medical Services System is a fire-based two-tier response system providing prehospital basic and advanced life support services.

Major trauma is any injury that has the potential to cause prolonged disability or death. There are many causes of major trauma, blunt and penetrating, including falls, motor vehicle collisions, stabbing wounds, and gunshot wounds. Depending on the severity of injury, quickness of management and transportation to an appropriate medical facility may be necessary to prevent loss of life or limb. The initial assessment is critical, and involves a physical evaluation and also may include the use of imaging tools to determine the types of injuries accurately and to formulate a course of treatment.

Advanced Life Support (ALS) is a set of life-saving protocols and skills that extend Basic Life Support to further support the circulation and provide an open airway and adequate ventilation (breathing).

Advanced trauma life support (ATLS) is a training program for medical providers in the management of acute trauma cases, developed by the American College of Surgeons. Similar programs exist for immediate care providers such as paramedics. The program has been adopted worldwide in over 60 countries, sometimes under the name of Early Management of Severe Trauma, especially outside North America. Its goal is to teach a simplified and standardized approach to trauma patients. Originally designed for emergency situations where only one doctor and one nurse are present, ATLS is now widely accepted as the standard of care for initial assessment and treatment in trauma centers. The premise of the ATLS program is to treat the greatest threat to life first. It also advocates that the lack of a definitive diagnosis and a detailed history should not slow the application of indicated treatment for life-threatening injury, with the most time-critical interventions performed early. However, there is no high-quality evidence to show that ATLS improves patient outcomes as it has not been studied.

In medicine, the Ottawa ankle rules are a set of guidelines for clinicians to help decide if a patient with foot or ankle pain should be offered X-rays to diagnose a possible bone fracture. Before the introduction of the rules most patients with ankle injuries would have been imaged. However the vast majority of patients with unclear ankle injuries do not have bone fractures. As a result, many unnecessary X-rays were taken, which was costly, time consuming and a slight health risk due to radiation exposure.
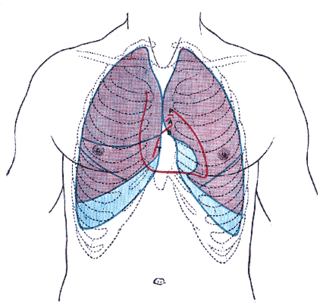
Commotio cordis is an often lethal disruption of heart rhythm that occurs as a result of a blow to the area directly over the heart at a critical time during the cycle of a heart beat, producing what is termed an R-on-T phenomenon that leads to the condition. It is a form of ventricular fibrillation (V-Fib), not mechanical damage to the heart muscle or surrounding organs, and not the result of heart disease. The fatality rate is about 65 percent even with prompt CPR and defibrillation, and more than 80 percent without.

The AutoPulse is an automated, portable, battery-powered cardiopulmonary resuscitation device created by Revivant and subsequently purchased and currently manufactured by ZOLL Medical Corporation. It is a chest compression device composed of a constricting band and half backboard that is intended to be used as an adjunct to CPR during advanced cardiac life support by professional health care providers. The AutoPulse uses a distributing band to deliver the chest compressions. In literature it is also known as LDB-CPR.
The chain of survival refers to a series of actions that, properly executed, reduce the mortality associated with sudden cardiac arrest. Like any chain, the chain of survival is only as strong as its weakest link. The four interdependent links in the chain of survival are early access, early CPR, early defibrillation, and early advanced cardiac life support.

Emergency medical services in Canada are the responsibility of each Canadian province or territory. The services, including both ambulance and paramedic services, may be provided directly by the province, contracted to a private provider, or delegated to local governments, which may in turn create service delivery arrangements with municipal departments, hospitals or private providers. The approach, and the standards, vary considerably between provinces and territories.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to emergency medicine:

Rearrest is a phenomenon that involves the resumption of a lethal cardiac dysrhythmia after successful return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC) has been achieved during the course of resuscitation. Survival to hospital discharge rates are as low as 7% for cardiac arrest in general and although treatable, rearrest may worsen these survival chances. Rearrest commonly occurs in the out-of-hospital setting under the treatment of health care providers.

Vasopressin infusions are in use for septic shock patients not responding to fluid resuscitation or infusions of catecholamines to increase the blood pressure while sparing the use of catecholamines. These argipressins have much shorter elimination half-life comparing to synthetic non-arginine vasopresines with much longer elimination half-life of many hours. Further, argipressins act on V1a, V1b, and V2 receptors which consequently lead to higher eGFR and lower vascular resistance in the lungs. A number of injectable arginine vasopressins are currently in clinical use in the United States and Europe. Pitressin among others, is a medication most commonly used in the treatment of frequent urination, increased thirst, and dehydration such as that resulting from diabetes insipidus, which causes increased and diluted urine. It is used to treat abdominal distension following some surgeries, and in stomach roentgenography. Vasopressin is a hormone that affects the kidneys and reduces urine flow.















