
Transport in Belgium is facilitated with well-developed road, air, rail and water networks. The rail network has 2,950 km (1,830 mi) of electrified tracks. There are 118,414 km (73,579 mi) of roads, among which there are 1,747 km (1,086 mi) of motorways, 13,892 km (8,632 mi) of main roads and 102,775 km (63,861 mi) of other paved roads. There is also a well-developed urban rail network in Brussels, Antwerp, Ghent and Charleroi. The ports of Antwerp and Bruges-Zeebrugge are two of the biggest seaports in Europe. Brussels Airport is Belgium's biggest airport.

Flanders is the Dutch-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to culture, language, politics, and history, and sometimes involving neighbouring countries. The demonym associated with Flanders is Fleming, while the corresponding adjective is Flemish, which can also refer to the collective of Dutch dialects spoken in that area, or more generally the Belgian variant of Standard Dutch. The official capital of Flanders is the City of Brussels, although the Brussels-Capital Region that includes it has an independent regional government. The powers of the government of Flanders consist, among others, of economic affairs in the Flemish Region and the community aspects of Flanders life in Brussels, such as Flemish culture and education.

Gerard David was an Early Netherlandish painter and manuscript illuminator known for his brilliant use of color. Only a bare outline of his life survives, although some facts are known. He may have been the Meester gheraet van brugghe who became a master of the Antwerp guild in 1515. He was very successful in his lifetime and probably ran two workshops, in Antwerp and Bruges. Like many painters of his period, his reputation diminished in the 17th century until he was rediscovered in the 19th century.

The Hanseatic League was a medieval commercial and defensive network of merchant guilds and market towns in Central and Northern Europe. Growing from a few North German towns in the late 12th century, the League expanded between the 13th and 15th centuries and ultimately encompassed nearly 200 settlements across eight modern-day countries, ranging from Estonia in the north and east, to the Netherlands in the west, and extended inland as far as Cologne, the Prussian regions and Kraków, Poland.

Adriaen Isenbrandt or Adriaen Ysenbrandt was a painter in Bruges, in the final years of Early Netherlandish painting, and the first of the Dutch and Flemish Renaissance painting of the Northern Renaissance. Documentary evidence suggests he was a significant and successful artist of his period, even though no specific works by his hand are clearly documented. Art historians have conjectured that he operated a large workshop specializing in religious subjects and devotional paintings, which were executed in a conservative style in the tradition of the Early Netherlandish painting of the previous century. By his time, the new booming economy of Antwerp had made this the centre of painting in the Low Countries, but the previous centre of Bruges retained considerable prestige.
The Steelyard, from the Middle Low German Stâlhof, was the kontor of the Hanseatic League in London, and their main trading base in England, between the 13th and 16th centuries. The main goods that the League exported from London were wool and from the 14th century woollen cloths. An important import good was beeswax. The kontor tended to be dominated by Rhenish and Westphalian traders, especially from Cologne.

Marcus Gheeraerts the Elder, Marc Gerard and Marcus Garret was a Flemish painter, draughtsman, print designer and etcher who was active in his native Flanders and in England. He practised in many genres, including portraits, religious paintings, landscapes and architectural themes. He designed heraldic designs and decorations for tombs. He is known for his creation of a print depicting a map of his native town Bruges and the illustrations for a Dutch-language publication recounting stories from Aesop's Fables. His attention to naturalistic detail and his practice of drawing animals from life for his prints had an important influence on European book illustration. His son Marcus the Younger became a prominent court painter at the English court.
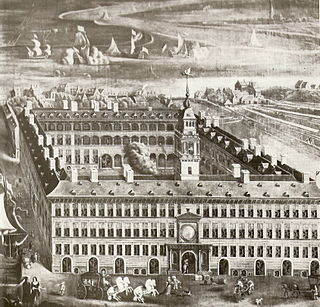
A kontor was a major foreign trading post of the Hanseatic League. Kontors were legal entities established in a foreign city, with a degree of legal autonomy. Most kontors were also enclaves. They were located, in London, Bruges, Bergen (Bryggen), and Novgorod (Peterhof). Smaller Hanseatic trading posts were called factorien, i.e., factories.

The Church of Our Lady is a Roman Catholic church in Bruges, Belgium, dating mainly from the 13th, 14th and 15th centuries. Its 115.6-metre-high (379 ft) tower remains the tallest structure in the city and the third tallest brickwork tower in the world.

Factory was the common name during the medieval and early modern eras for an entrepôt – which was essentially an early form of free-trade zone or transshipment point. At a factory, local inhabitants could interact with foreign merchants, often known as factors. First established in Europe, factories eventually spread to many other parts of the world. The origin of the word factory is from Latin factorium 'place of doers, makers'.

The Guild of Saint Luke was the most common name for a city guild for painters and other artists in early modern Europe, especially in the Low Countries. They were named in honor of the Evangelist Luke, the patron saint of artists, who was identified by John of Damascus as having painted the Virgin's portrait.

The Master of the Female Half-Lengths is the notname given to a painter, or more likely a group of painters of a workshop, active in the Low Countries in the early sixteenth century. The name was given in the 19th century to identify the maker or makers of a body of work consisting of 67 paintings to which since 40 more have been added. The Master created female figures in genre scenes, small religious and mythological works, landscapes and portraits.

The Master of 1499, sometimes called the Bruges Master of 1499, was a Flemish painter active at the end of the fifteenth century, known from four paintings, all closely related to earlier works by others, and one dated "1499".
The development of urban centres in the Low Countries shows the process by which the Low Countries, a region in Western Europe, evolved from a highly rural outpost of the Roman Empire into the largest urbanised area north of the Alps by the 15th century CE. As such, this article covers the development of Dutch and Flemish cities beginning at the end of the migration period till the end of the Dutch Golden Age.
A cloth hall or linen hall is a historic building located in the centre of the main marketplace of a European town. Cloth halls were built from medieval times into the 18th century.

Bruges is the capital and largest city of the province of West Flanders in the Flemish Region of Belgium, in the northwest of the country. It is the sixth most populous city in the country.
The Kontor of Bruges was the Hanseatic kontor, one of the Hanseatic League's four major trading posts, in Bruges, County of Flanders. A kontor was a corporation (universitas) with a level of legal autonomy in a foreign non-Hanseatic city, the one of Bruges was formally organised in the 14th century. Bruges was a major Flemish port in the high and late Middle Ages. Flanders was a fiefdom of France until the Treaty of Senlis was signed in 1493, after that it belonged to the Holy Roman Empire.













