Related Research Articles
Payload is the object or the entity which is being carried by an aircraft or launch vehicle. Sometimes payload also refers to the carrying capacity of an aircraft or launch vehicle, usually measured in terms of weight. Depending on the nature of the flight or mission, the payload of a vehicle may include cargo, passengers, flight crew, munitions, scientific instruments or experiments, or other equipment. Extra fuel, when optionally carried, is also considered part of the payload.

A forklift is a powered industrial truck used to lift and move materials over short distances. The forklift was developed in the early 20th century by various companies, including Clark, which made transmissions, and Yale & Towne Manufacturing, which made hoists. Since World War II, the use and development of the forklift truck have greatly expanded worldwide. Forklifts have become an indispensable piece of equipment in manufacturing and warehousing. In 2013, the top 20 manufacturers worldwide posted sales of $30.4 billion, with 944,405 machines sold.

A crane is a type of machine, generally equipped with a hoist rope, wire ropes or chains, and sheaves, that can be used both to lift and lower materials and to move them horizontally. It is mainly used for lifting heavy objects and transporting them to other places. The device uses one or more simple machines to create mechanical advantage and thus move loads beyond the normal capability of a human. Cranes are commonly employed in transportation for the loading and unloading of freight, in construction for the movement of materials, and in manufacturing for the assembling of heavy equipment.

A lifting bag is an item of diving equipment consisting of a robust and air-tight bag with straps, which is used to lift heavy objects underwater by means of the bag's buoyancy. The heavy object can either be moved horizontally underwater by the diver or sent unaccompanied to the surface.

The British Aerospace 125 is a twinjet mid-size business jet. Originally developed by de Havilland and initially designated as the DH.125 Jet Dragon, it entered production as the Hawker Siddeley HS.125, which was the designation used until 1977. Later on, more recent variants of the type were marketed as the Hawker 800.

The Hawker 800 is a mid-size twinjet corporate aircraft. It is a development of the British Aerospace 125, and was assembled by Hawker Beechcraft.

A Schnabel car or Schnabel wagon is a specialized type of railroad freight car. It is designed to carry heavy and oversized loads in such a way that the load makes up part of the car. The load is suspended between the two ends of the cars by lifting arms; the lifting arms are connected to an assembly of span bolsters that distribute the weight of the load and the lifting arm over many wheels.

A telescopic handler, also called a lull, telehandler, teleporter, reach forklift, or zoom boom, is a machine widely used in agriculture and industry. It is somewhat like a forklift but has a boom, making it more a crane than a forklift, with the increased versatility of a single telescopic boom that can extend forwards and upwards from the vehicle. The boom can be fitted with different attachments, such as a bucket, pallet forks, muck grab, or winch.

A diesel generator (DG) (also known as a diesel genset) is the combination of a diesel engine with an electric generator (often an alternator) to generate electrical energy. This is a specific case of engine generator. A diesel compression-ignition engine is usually designed to run on diesel fuel, but some types are adapted for other liquid fuels or natural gas (CNG).

BEML Limited, formerly Bharat Earth Movers Limited, is an Indian public sector undertaking which manufactures a variety of heavy equipment, such as that used for earth moving, railways, transport and mining. It is headquartered in Bangalore. BEML is Asia's second-largest manufacturer of earth moving equipment. Its stock trades on the National Stock Exchange of India under the symbol "BEML", and on the Bombay Stock Exchange under the code "500048".

An ice road or ice bridge is a human-made structure that runs on a frozen water surface. Ice roads are typically part of a winter road, but they can also be simple stand-alone structures, connecting two shorelines. Ice roads may be planned, built and maintained so as to remain safe and effective, and a number of guidelines have been published with information in these regards. An ice road may be constructed year after year, for instance to service community needs during the winter. It could also be for a single year or two, so as to supply particular operations, such as a hydroelectric project or offshore drill sites.
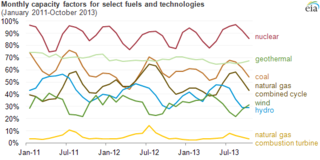
The net capacity factor is the unitless ratio of actual electrical energy output over a given period of time to the theoretical maximum electrical energy output over that period. The theoretical maximum energy output of a given installation is defined as that due to its continuous operation at full nameplate capacity over the relevant period. The capacity factor can be calculated for any electricity producing installation, such as a fuel consuming power plant or one using renewable energy, such as wind or the sun. The average capacity factor can also be defined for any class of such installations, and can be used to compare different types of electricity production.

A fly crew is a group of people who are in charge of maintaining and operating the fly system during theatre production. A member of a fly crew is also called a flyman. Despite the name, there is no gender restriction in order to work within a fly crew.
The stability conditions of watercraft are the various standard loading configurations to which a ship, boat, or offshore platform may be subjected. They are recognized by classification societies such as Det Norske Veritas, Lloyd's Register and American Bureau of Shipping (ABS). Classification societies follow rules and guidelines laid down by International Convention for the Safety of Life at Sea (SOLAS) conventions, the International Maritime Organization and laws of the country under which the vessel is flagged, such as the Code of Federal Regulations.

Material handling equipment (MHE) is mechanical equipment used for the movement, storage, control, and protection of materials, goods and products throughout the process of manufacturing, distribution, consumption, and disposal. The different types of equipment can be classified into four major categories: transport equipment, positioning equipment, unit load formation equipment, and storage equipment.

A laboratory centrifuge is a piece of laboratory equipment, driven by a motor, which spins liquid samples at high speed. There are various types of centrifuges, depending on the size and the sample capacity.

A conveyor system is a common piece of mechanical handling equipment that moves materials from one location to another. Conveyors are especially useful in applications involving the transport of heavy or bulky materials. Conveyor systems allow quick and efficient transport for a wide variety of materials, which make them very popular in the material handling and packaging industries. They also have popular consumer applications, as they are often found in supermarkets and airports, constituting the final leg of item/ bag delivery to customers. Many kinds of conveying systems are available and are used according to the various needs of different industries. There are chain conveyors as well. Chain conveyors consist of enclosed tracks, I-Beam, towline, power & free, and hand pushed trolleys.

Haul trucks are off-highway, rigid dump trucks specifically engineered for use in high-production mining and heavy-duty construction environments. Haul trucks are also used for transporting construction equipment from job site to job site. Some are multi-axle in order to support the equipment that is being hauled.

The Changhe Z-18, also known as Z-8G, is a medium-lift transport helicopter developed by Changhe Aircraft Industries Corporation (CAIC) to replace the Changhe/Harbin Z-8.
Vehicle weight is a measurement of wheeled motor vehicles; either an actual measured weight of the vehicle under defined conditions or a gross weight rating for its weight carrying capacity.
References
- ↑ Brothers, Ritchie. "Operating Weight". RitchieWiki Everything about Equipment. RitchieWiki. Retrieved 13 March 2014.
- ↑ "The Relevant Range of Operating Capacity | Chron.com". smallbusiness.chron.com. Retrieved 2014-03-13.