
The Andaman Islands are an archipelago, made up of 200 islands, in the northeastern Indian Ocean about 130 km (81 mi) southwest off the coasts of Myanmar's Ayeyarwady Region. Together with the Nicobar Islands to their south, the Andamans serve as a maritime boundary between the Bay of Bengal to the west and the Andaman Sea to the east. Most of the islands are part of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, a Union Territory of India, while the Coco Islands and Preparis Island are part of the Yangon Region of Myanmar.

The Andaman Sea is a marginal sea of the northeastern Indian Ocean bounded by the coastlines of Myanmar and Thailand along the Gulf of Martaban and the west side of the Malay Peninsula, and separated from the Bay of Bengal to its west by the Andaman Islands and the Nicobar Islands. Its southern end is at Breueh Island just north of Sumatra, with the Strait of Malacca further southeast.

On 26 December 2004, at 07:58:53 local time (UTC+7), a major earthquake with a magnitude of 9.2–9.3 struck with an epicentre off the west coast of northern Sumatra, Indonesia. The undersea megathrust earthquake, known by the scientific community as the Sumatra–Andaman earthquake, was caused by a rupture along the fault between the Burma Plate and the Indian Plate, and reached a Mercalli intensity up to IX in some areas.

According to official estimates in India, 10,749 people were killed, 5,640 people were missing and thousands of people became homeless when a tsunami triggered by the 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake near the Indonesian island of Sumatra struck the southern coast on 26 December 2004. The earthquake registered 9.1–9.3 Mw and was the largest in five decades. It was followed by strong aftershocks on the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. The death toll of the earthquake was 1,500 people.
Car Nicobar is the northernmost of the Nicobar Islands. It is also one of three local administrative divisions of the Indian district of Nicobar, part of the Indian union territory of Andaman and Nicobar Islands. Annual rainfall is 2800 millimetres.
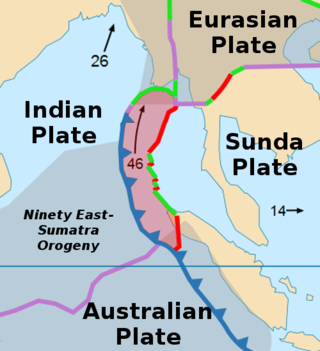
The Burma Plate is a minor tectonic plate or microplate located in Southeast Asia, sometimes considered a part of the larger Eurasian Plate. The Andaman Islands, Nicobar Islands, and northwestern Sumatra are located on the plate. This island arc separates the Andaman Sea from the main Indian Ocean to the west.

The 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake and tsunami occurred on Sunday, December 26, 2004. The earthquake itself, with a moment magnitude of around 9.1-9.3, devastated Aceh Province, Indonesia, while the tsunami affected countries all around the Indian Ocean. Nations which were affected are listed below in alphabetical order. For detailed information about each country affected by the earthquake and tsunami, see their individual articles. Countries with a smaller number of casualties, as well as those that lost citizens who were travelling abroad, are listed further on in the article.

Port Blair is the capital city of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, a union territory of India in the Bay of Bengal. It is also the local administrative sub-division (tehsil) of the islands, the headquarters for the district of South Andaman, and the territory's only notified town.
Great Nicobar is the southernmost and largest of the Nicobar Islands of India, north of Sumatra. It is part of India, in the Nicobar district within the union territory of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
Trinket Island is one of the 24 islands that make up the Nicobar Islands chain, located in the northeast Indian Ocean between the Bay of Bengal and the Andaman Sea. It is located east of Kamorta Island.

Sri Lanka was one of the countries struck by the tsunami resulting from the Indian Ocean earthquake on December 26, 2004. On January 3, 2005, Sri Lankan authorities reported 30,000+ confirmed deaths.

Car Nicobar Air Force Station is located in IAF Camp village, on Car Nicobar Island in the union territory of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, India.

Library damage resulting from the 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake has been reported in six Asian countries. On December 26, the massive 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake struck off the northwest coast of the Indonesian island of Sumatra. The resulting tsunamis killed more than 180,000 people. In addition to the loss of human lives, cultural institutions were destroyed in several Asian nations. Libraries on the Eastern coast of Sri Lanka and the northern province of Aceh on Sumatra were most severely affected by the disaster.
The Andaman and Nicobar Command (ANC) is a integrated tri-services command of the Indian Armed Forces, based at Port Blair in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, a Union Territory of India. It was created in 2001 to safeguard India's strategic interests in Southeast Asia and the Strait of Malacca by increasing rapid deployment of military assets in the region. It provides logistical and administrative support to naval ships which are sent on deployment to East Asia and the Pacific Ocean.
Operation Madad is the name of rescue operations conducted by Indian Navy in various occasions within India. The word "madad" in Hindi means "help".
The 2012 Indian Ocean earthquakes were magnitude 8.6 and 8.2 Mw undersea earthquakes that struck near the Indonesian province of Aceh on 11 April at 15:38 local time. Initially, authorities feared that the initial earthquake would cause a tsunami and warnings were issued across the Indian Ocean; however, these warnings were subsequently cancelled. These were unusually strong intraplate earthquakes and the largest strike-slip earthquake ever recorded.
Pulomilo is an island in the Nicobar district of Andaman and Nicobar Islands, India, and is home to a village of the same name. It is located just north of Little Nicobar Island.
Anul is a village in the Nicobar district of Andaman and Nicobar Islands, India. It is located in the Great Nicobar tehsil.

INS Sutlej (J17) is a hydrographic survey ship of the Sandhayak class in the Indian Navy, under the Southern Naval Command. Like other ships of the same class, this ship is also equipped with an Operating Theater and associated equipment needed to attend to medical emergencies at sea.
The Andaman and Nicobar Islands is an archipelago of 572 islands of which 37 are inhabited. It is a union territory of India.










