This article needs to be updated.(July 2015) |
| Oppian Hill | |
|---|---|
| Hill of Rome | |
| Latin name | Oppius Mons |
| Italian name | Colle Oppio |
| Rione | Rione Monti |
| People | Oppius |

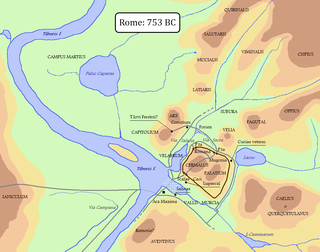
The Oppian Hill (Latin, Oppius Mons; Italian : Colle Oppio) is the southern spur of the Esquiline Hill, [1] one of the Seven hills of Rome, Italy. It is separated from the Cispius on the north by the valley of the Suburra, and from the Caelian Hill on the south by the valley of the Colosseum. The Oppius and the Cispius together form the Esquiline plateau just inside the line of the Servian Wall.
Contents
In the divisions of the Septimontium (seven hills) [2] Fagutal appears as an independent locality, which implies that originally "Oppius" was strictly applied to this spur except the western end. [3] The northern tip of this western end was also called Carinae, which extended between the Velian Hill and the Clivus Pullius, looked out to the southwest (across the swamps of the Palus Ceroliae towards the Aventine), incorporated the Fagutal and was one of ancient Rome's most exclusive neighborhoods.
At least for religious purposes the name Oppius continued in use to the end of the Roman Republic; [4] no later instance has been found. According to Varro, [5] its name derives from Oppius, a citizen of Tusculum who came to the Romans' assistance during Tullus Hostilius's siege of Veii. However, the word's true etymology is obscure. It may possibly be that of a clan that lived in this area, [6] a gens name of plebeian status. Detlefsen's conjecture [7] that Oppius is derived from Oppidus was revived by Pinza, [8] who regards the name as comparatively late.
The Oppian Hill Park (Italian : Parco del Colle Oppio) covers about eleven hectares. [9] It was developed in 1871, as part of the urban reorganization that followed the establishment of Rome as the capital of Italy. From that time, the area was used as a public garden; it was during the Italian fascist era that work was carried out to give the park its present appearance. This was planned in 1928 under the guidance of the architect Raffaele De Vico, and completed in 1936. Work included the fountains, statues and marble sculptures that decorate the park today. [10] A central avenue leads down the hill to the Colosseum, providing an attractive view.
The Oppian Hill Park is considered to be an archaeological park. Much of the Domus Aurea (Golden House of Nero) lies under it, and it also contains the ruins of the Baths of Trajan and the earlier Baths of Titus. [11]