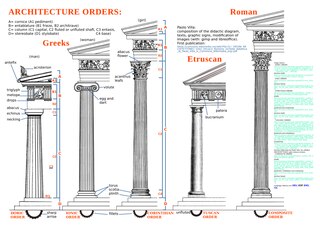
An order in architecture is a certain assemblage of parts subject to uniform established proportions, regulated by the office that each part has to perform. Coming down to the present from Ancient Greek and Ancient Roman civilization, the architectural orders are the styles of classical architecture, each distinguished by its proportions and characteristic profiles and details, and most readily recognizable by the type of column employed. The three orders of architecture—the Doric, Ionic, and Corinthian—originated in Greece. To these the Romans added, in practice if not in name, the Tuscan, which they made simpler than Doric, and the Composite, which was more ornamental than the Corinthian. The architectural order of a classical building is akin to the mode or key of classical music; the grammar or rhetoric of a written composition. It is established by certain modules like the intervals of music, and it raises certain expectations in an audience attuned to its language.

Vitruvius was a Roman architect and engineer during the 1st century BC, known for his multi-volume work titled De architectura. As the only treatise on architecture to survive from antiquity, it has been regarded since the Renaissance as the first book on architectural theory, as well as a major source on the canon of classical architecture. It is not clear to what extent his contemporaries regarded his book as original or important.

Ancient Roman architecture adopted the external language of classical ancient Greek architecture for the purposes of the ancient Romans, but was different from Greek buildings, becoming a new architectural style. The two styles are often considered one body of classical architecture. Roman architecture flourished in the Roman Republic and to an even greater extent under the Empire, when the great majority of surviving buildings were constructed. It used new materials, particularly Roman concrete, and newer technologies such as the arch and the dome to make buildings that were typically strong and well engineered. Large numbers remain in some form across the former empire, sometimes complete and still in use today.

Plaster is a building material used for the protective or decorative coating of walls and ceilings and for moulding and casting decorative elements. In English, "plaster" usually means a material used for the interiors of buildings, while "render" commonly refers to external applications. The term stucco refers to plasterwork that is worked in some way to produce relief decoration, rather than flat surfaces.

Stucco or render is a construction material made of aggregates, a binder, and water. Stucco is applied wet and hardens to a very dense solid. It is used as a decorative coating for walls and ceilings, exterior walls, and as a sculptural and artistic material in architecture. Stucco can be applied on construction materials such as metal, expanded metal lath, concrete, cinder block, or clay brick and adobe for decorative and structural purposes.
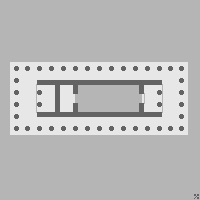
In Classical architecture, a cella or naos is the inner chamber of an ancient Greek or Roman temple. Its enclosure within walls has given rise to extended meanings, of a hermit's or monk's cell, and since the 17th century, of a biological cell in plants or animals.
The architecture of the California missions was influenced by several factors, those being the limitations in the construction materials that were on hand, an overall lack of skilled labor, and a desire on the part of the founding priests to emulate notable structures in their Spanish homeland. While no two mission complexes are identical, they all employed the same basic building style.

De architectura is a treatise on architecture written by the Roman architect and military engineer Marcus Vitruvius Pollio and dedicated to his patron, the emperor Caesar Augustus, as a guide for building projects. As the only treatise on architecture to survive from antiquity, it has been regarded since the Renaissance as the first known book on architectural theory, as well as a major source on the canon of classical architecture.

Lime plaster is a type of plaster composed of sand, water, and lime, usually non-hydraulic hydrated lime. Ancient lime plaster often contained horse hair for reinforcement and pozzolan additives to reduce the working time.

Cavaedium or atrium are Latin names for the principal room of an ancient Roman house, which usually had a central opening in the roof (compluvium) and a rainwater pool (impluvium) beneath it. The cavaedium passively collected, filtered, stored, and cooled rainwater. It also daylit, passively cooled and passively ventilated the house.

Opus reticulatum is a facing used for concrete walls in Roman architecture from about the first century BCE to the early first century CE. They were built using small pyramid shaped tuff, a volcanic stone embedded into a concrete core. Reticulate work was also combined with a multitude of other building materials to provide polychrome colouring and other facings to form new techniques. Opus reticulatum was generally used in central and southern Italy with the exception being its rare appearance in Africa and Jericho. This was because of tuff's wider availability and ease of local transport in central Italy and Campania compared to other regions.

Opus signinum is a building material used in ancient Rome. It is a form of Roman concrete, the main difference being the addition of small pieces of broken pot, including amphorae, tiles or brick, instead of other aggregates. Its main advantage over opus caementicium was that it is waterproof, the reason for its widespread use in Roman baths, aqueducts, cisterns and any buildings involving water. In floors it provided damp-proofing.
Core-and-veneer, brick and rubble, wall and rubble, ashlar and rubble, and emplekton all refer to a building technique where two parallel walls are constructed and the core between them is filled with rubble or other infill, creating one thick wall. Originally, and in later poorly constructed walls, the rubble was not consolidated. Later, mortar and cement were used to consolidate the core rubble and produce sturdier construction.

Opus latericium is an ancient Roman construction technique in which course-laid brickwork is used to face a core of opus caementicium.

Marmorino Veneziano is a type of plaster or stucco. It is based on calcium oxide and used for interior and exterior wall decorations. Marmorino plaster can be finished via multiple techniques for a variety of matte, satin, and glossy final effects. It was used as far back as Roman times, but was made popular once more during the Renaissance 500 years ago in Venice.
Polished plaster is a term for the finish of some plasters and for the description of new and updated forms of traditional Italian plaster finishes. The term covers a whole range of decorative plaster finishes, from the very highly polished Venetian plaster and Marmorino to the rugged look of textured polished plasters. Polished plaster itself tends to consist of slaked lime, marble dust, and/or marble chips, which give each plaster its distinctive look. A lime-based polished plaster may contain over 40% of marble powder.

Opus craticum or craticii is an ancient Roman construction technique described by Vitruvius in his books De architectura as wattlework which is plastered over. It is often employed to construct partition walls and floors. Vitruvius disparaged this building technique as a grave fire risk, likely to have cracked plaster, and not durable. Surviving examples were found in the archaeological excavations at Pompeii and more so at Herculaneum, buried by the eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD and excavated beginning in 1929.

Roman concrete, also called opus caementicium, was used in construction in ancient Rome. Like its modern equivalent, Roman concrete was based on a hydraulic-setting cement added to an aggregate.

Opus isodomum is an ancient technique of wall construction with ashlars. It uses perfectly cut, completely regular squared stone blocks of equal height, and sometimes of the same length.
This glossary of the culture of ancient Rome includes terms used by academics studying Roman history and archaeologists excavating Roman sites.
















